The aerospace industry has undergone a dramatic transformation in the past decade. Governments no longer play a leading role in space exploration ; instead, private companies and billionaire entrepreneurs are making breakthroughs that were considered impossible just a decade ago. As a result, the sector is experiencing explosive growth, creating a space race.
Today, space missions have become commonplace. By 2022, SpaceX will be launching an average of one object into space every week. From building the next generation of reusable rockets to scaling low-Earth communication satellites and reaching the outer planets of the solar system with the ultimate goal of sending humans to Mars, there is no limit to innovation! However, to achieve these goals, validating the technology as expected has become a crucial factor.
However, the biggest challenge for technology is the harsh environment of space. From surviving the shock of a launch, to large temperature fluctuations, to the effects of radiation in orbit, to the challenges of communications and avoiding space debris, these hurdles cannot be underestimated. Therefore, hardware and software must be robust enough to withstand these pressures and continue to function as expected.
Space and software
Space equipment and technology have become increasingly complex and software-dependent. For example, satellites of the 1970s had little or no software, while recently deployed mega-satellites rely heavily on software services for connectivity.
These technologies need to be rigorously tested in every possible scenario to ensure they operate reliably. However, manually testing such a large volume of software is not feasible due to reasons such as complexity, cost and time.
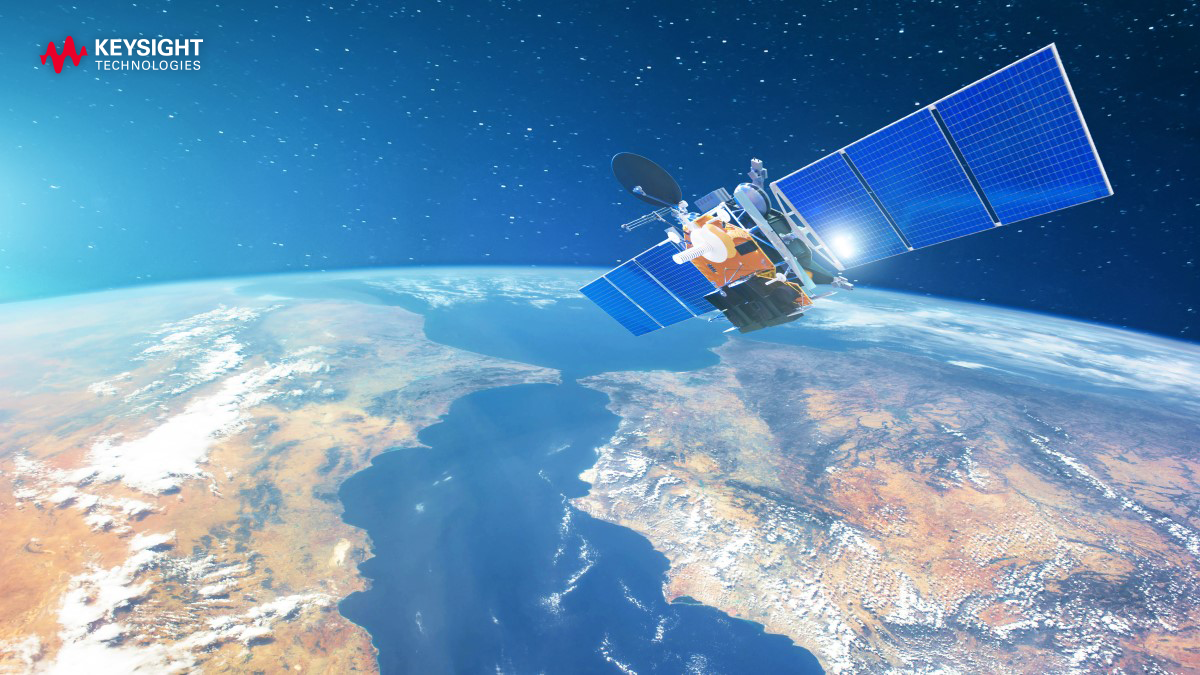

Applying AI technology to software deployment automation is the only way to ensure technology is ready for space operations. Intelligent test automation can provide insights into launch and on-orbit readiness. Rapid and thorough testing of every potential scenario is essential, with the information gathered being able to identify potential issues that are most likely to occur and fix them before launch. This approach ensures that software and technology deliver the desired results.
User experience testing
In any environment, especially the harsh aerospace environment, simply testing software for compliance is not enough. Use automated testing to test from the user's perspective - including the entire experience, functionality, performance, and usability - to accurately reflect user activities.
Another benefit of AI in testing is that it can accelerate the development of key technologies in the space race, where being first to market can bring significant financial benefits. Additionally, testing can be scaled more easily as technology develops and increases in complexity. This ability is important in the context of the rapidly growing and constantly innovating aerospace sector. As a result, businesses and agencies are increasingly using automated testing to ensure that software performs as expected.
For example, NASA has integrated Keysight Technologies’ Eggplant intelligent automation platform to test the Orion spacecraft’s software to ensure it performs as expected and meets requirements under challenging scenarios. To monitor the mission’s status and provide guidance to the crew, the spacecraft’s cockpit is equipped with software-driven digital displays, instead of the paper manuals used in the past.

Orion test engineers are deploying automation to dynamically evaluate the software’s user experience, ensuring it operates reliably and as expected. Testing will continue while Orion is in orbit to monitor the spacecraft’s health and ability to control it in emergency situations when it loses contact with mission control on Earth.
The space race and aerospace innovation show no signs of slowing down, and as a result, the need for rigorous testing to ensure the operation and safety of critical systems will continue to grow.
Gareth Smith (Keysight Technologies)
Source


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's online conference with localities](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/264793cfb4404c63a701d235ff43e1bd)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh launched a peak emulation campaign to achieve achievements in celebration of the 14th National Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/8869ec5cdbc740f58fbf2ae73f065076)





















































![[VIDEO] Summary of Petrovietnam's 50th Anniversary Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/abe133bdb8114793a16d4fe3e5bd0f12)

![[VIDEO] GENERAL SECRETARY TO LAM AWARDS PETROVIETNAM 8 GOLDEN WORDS: "PIONEER - EXCELLENT - SUSTAINABLE - GLOBAL"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/23/c2fdb48863e846cfa9fb8e6ea9cf44e7)



































Comment (0)