
Collagen is like the “glue” that keeps skin firm and joints flexible. As we age, natural collagen levels decrease, causing sagging skin and less flexible joints.
Many people turn to collagen-rich foods to compensate, but does eating collagen-rich foods really benefit you as you age? Let's take a look at natural sources of collagen that you can add to your diet.
Collagen and its role in the body
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body, accounting for about 30% of total protein. It helps maintain the structure of skin, muscles, bones, tendons, and ligaments. According to the Cleveland Clinic, the human body has at least 16 types of collagen, of which types I, II, and III account for more than 80%.
However, the ability to produce collagen gradually decreases with age, from the age of 25 onwards. Combined with factors such as sunlight, stress, smoking and a poor diet, collagen is destroyed faster than new production. That is why many people turn to foods or collagen supplements to "save" their skin and joints.
Are collagen-rich foods really effective?
In theory, animal foods like meat, skin, cartilage, and fish all contain collagen. However, according to Harvard Health Publishing, when eaten, collagen is broken down into amino acids—small pieces that the body uses to make different proteins, not necessarily collagen.
This means that eating collagen-rich foods won't directly increase collagen in your skin or joints, but may provide the building blocks your body needs to synthesize collagen more effectively — especially when combined with vitamin C, zinc, and copper.
Here are 7 collagen-rich foods and their potential benefits.
1. Bone broth - a popular natural source
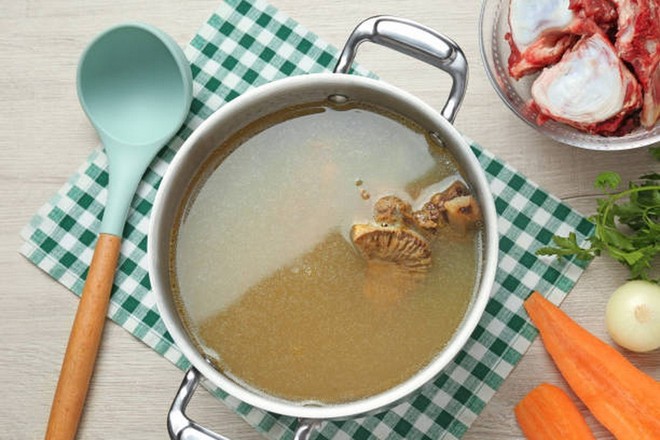

Bone broth is cooked from animal bones and connective tissues for hours, which helps extract collagen and minerals.
A study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry (2022) found that bone broth contains collagen peptides that have antioxidant properties and support skin structure. However, the actual collagen content depends largely on the simmering time and the type of bone used.
Additionally, Johns Hopkins Medicine notes that the amount of heavy metals in bone broth is very low, not a concern if prepared properly.
2. Jellyfish - an unexpected source of marine collagen
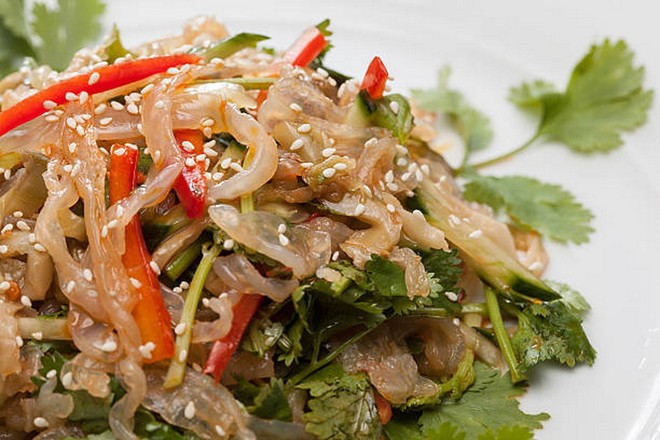

Jellyfish contain high amounts of protein, and about 50% of it is collagen. According to research by Food Chemistry (2021), collagen extracted from jellyfish has anti-inflammatory properties and aids in tissue repair.
In addition, jellyfish is almost fat-free and rich in minerals such as iron and magnesium, which help improve circulation. You can try refreshing jellyfish salads - both nutritious and supporting healthy skin.
3. Beef - rich in collagen types I and III
Collagen in beef, especially in tendons and connective tissue, is mainly types I and III – two types associated with skin elasticity and bone and joint health.
However, WHO recommends limiting red meat consumption to no more than 500g per week, as eating too much can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and colon cancer. Therefore, if you want to supplement collagen from beef, choose the meat with tendons and cook slowly to extract maximum collagen, but only eat it in moderation.
4. Chicken skin and cartilage - a popular source of collagen in meals

Collagen peptides from chicken skin have been shown to reduce inflammation in a study published in the Journal of Medicinal Food (2020).
Chicken cartilage is also an ingredient in many collagen supplements, which help improve joint flexibility and reduce pain caused by osteoarthritis. However, chicken skin contains a lot of saturated fat, so people with high cholesterol should limit it.
5. Pig skin - a familiar source of collagen
Pork skin (or pig skin) is a collagen-rich ingredient used in Asian and European cuisine .
A study in the National Library of Medicine (2021) found that collagen extracted from pig skin helps improve skin elasticity and reduce knee pain. However, similar to chicken skin, the skin contains a lot of saturated fat - so eat it in small amounts and avoid deep-frying it.
6. Salmon - collagen and omega-3 in one dish
Salmon contains collagen mainly in its skin and scales. When you cook or grill the fish with the skin on, you can absorb some of the natural collagen.
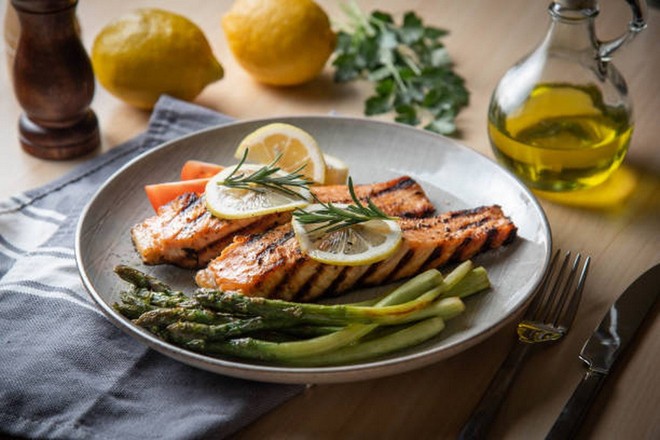

Research from the Cleveland Clinic (2023) shows that fish collagen combined with omega-3 helps improve skin moisture and elasticity, while reducing inflammation in the body. Adding vitamin C from accompanying vegetables can increase the effectiveness of collagen absorption.
7. Sardines - rich in type I collagen and calcium
Sardines are one of the rare fish that are eaten with their skin, bones, and organs – the parts that contain the most collagen. According to the Journal of Nutritional Science (2022), the type I collagen in sardines helps support tissue regeneration and maintain bone density.
Canned sardines are convenient, can be eaten with bread or salad, and are a good choice for those who want to supplement collagen while still controlling saturated fat intake.
Are there any risks to eating collagen-rich foods?
Foods like chicken skin, pork skin, and red meat, while rich in collagen, are also high in saturated fat. Harvard TH Chan School of Public Health warns that a diet high in saturated fat can raise “bad” cholesterol (LDL), promote inflammation, and increase the risk of heart disease.
If you want to supplement collagen in a healthy way, prioritize marine collagen sources (fish, jellyfish) combined with unsaturated fats like omega-3 - which both support natural collagen production and are beneficial for the heart.
How to increase collagen naturally without eating skin or meat
In addition to foods that already contain collagen, you can support collagen production with foods rich in amino acids like glycine, proline, and lysine.
These substances are abundant in foods such as eggs, fermented soybeans (natto, tempeh); beans, peas; whole grains such as barley, amaranth; seaweed and dairy products.
Combining these foods with vitamin C (oranges, kiwis, bell peppers) will help increase the body's natural collagen synthesis ability.
Source: https://baolaocai.vn/7-thuc-pham-giau-collagen-va-su-that-ve-cong-dung-cua-chung-voi-co-the-ban-post885095.html


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting on railway projects](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/23/1761206277171_dsc-9703-jpg.webp)











































































































Comment (0)