Ferrari is starting to “unveil” its first EV in three phases: the chassis, powertrain and battery will be revealed first; the exterior/interior design and final specifications will follow in Q1 and Q2 2026. While the bodywork remains a mystery, the technical foundation is enough to show that this is a serious project: 4 electric motors developed in-house, 800 V architecture, 122 kWh (gross) battery and 3rd generation active suspension co-developed with Multimatic.
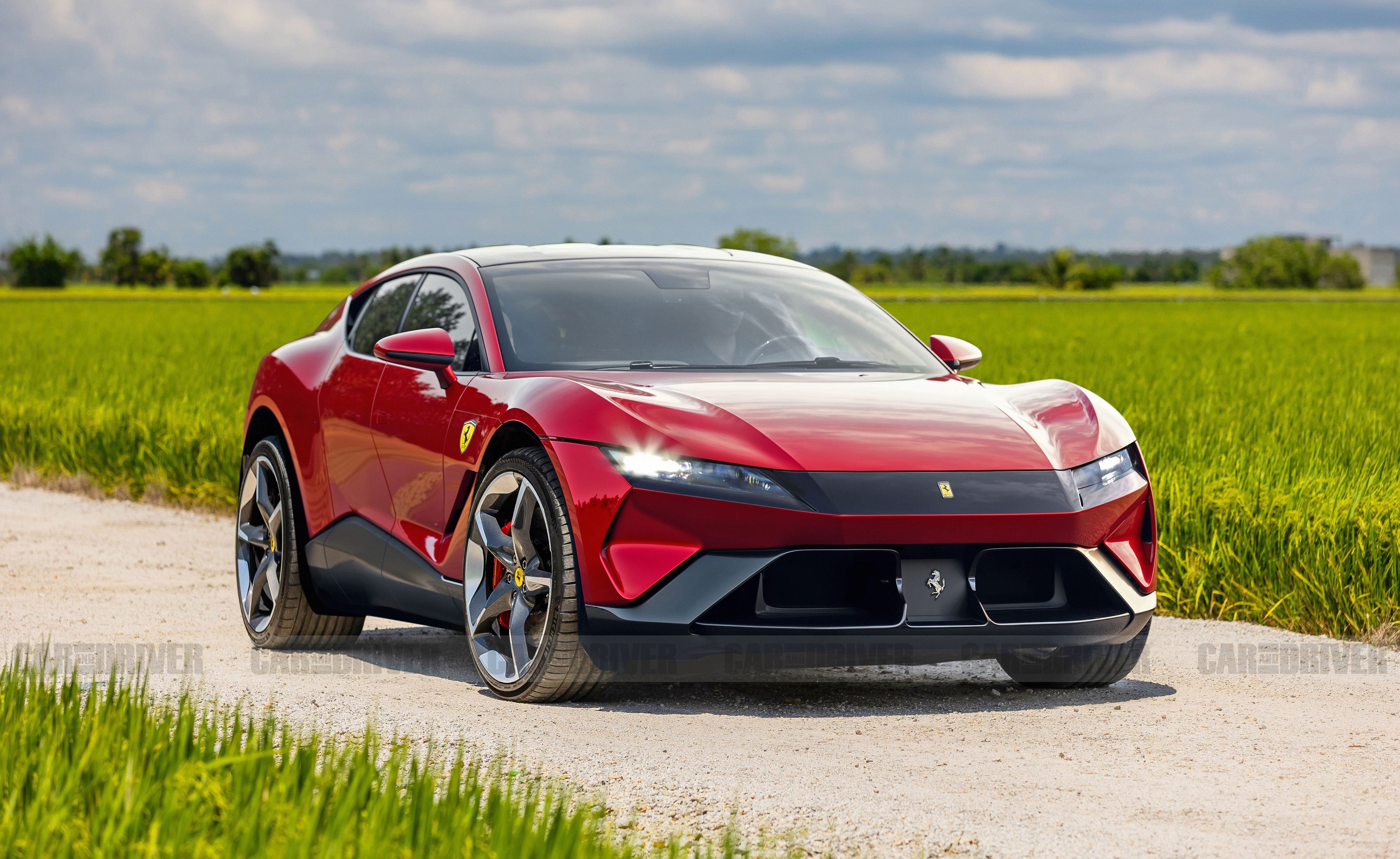

Proceed cautiously, the foundation is ready
Ferrari says the design is locked, with four doors, a 116.5-inch wheelbase (base; approximately 2,959 mm), and a curb weight of just under 5,100 lb (base; approximately 2,313 kg). While no body style has been announced, the platform and powertrain are production-ready.
Secret shape, base proportions revealed
Exterior dimensions, ground clearance, luggage compartment capacity, or aerodynamics have not been shared. At base level, the four-door and 116.5-inch wheelbase information suggests that passenger space could be more spacious than traditional two-door Ferraris; however, a detailed assessment of the design will only come when Ferrari reveals the upper body.
Interior: temporarily put aside, prioritize basic technology
Ferrari has not revealed the materials, dashboard layout, seat configuration, or infotainment system. This is part of a phased announcement plan; the cabin, amenities, and finish will likely be revealed in 2026.
4-motor electric brain: Halbach, 30,000 rpm
At the heart of the Elettrica are four permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), two of which are independently controlled per bridge for precise torque vectoring. The Halbach magnet structure concentrates the magnetic flux on the stator, and the rotors are reinforced with carbon fiber to withstand very high speeds: the front motor reaches a maximum of 30,000 rpm, the rear motor up to 25,500 rpm.
The default drivetrain is four-wheel drive, but the driver can switch to rear-wheel drive via the e-Manettino on the steering wheel. As for power, Ferrari only confirms “over 1,000 CV” in Performance Launch mode. Additionally, the company says the front axle can reach 282 hp and the rear axle 831 hp (base value in hp), implying a potential peak power of around 1,113 hp under optimal conditions.
Ferrari claims a 0–100 km/h time of 2.5 seconds (base: 0–62 mph, 2.5 seconds). For the 0–60 mph mark, the company suggests it could be under 2.5 seconds depending on conditions. The top speed is stated as 193 mph (base; equivalent to approximately 310.6 km/h). Ferrari emphasizes the durability of power over multiple accelerations/laps as a design criterion.
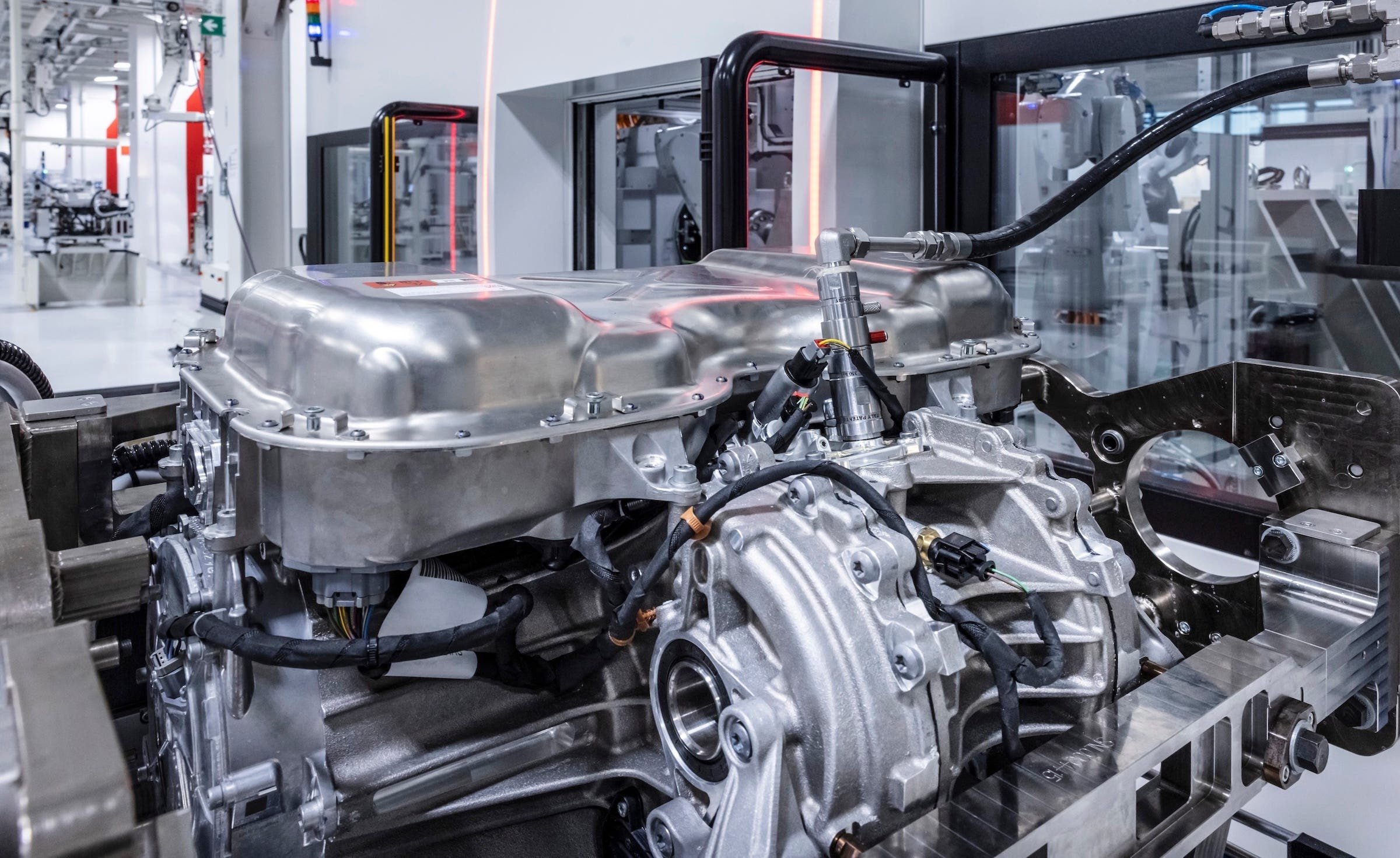
122 kWh battery, 800 V and 350 kW charging capability
The battery pack consists of 15 internally assembled modules; each module uses 14 pouch cells from SK and integrates a monitoring system. 13 modules are floor-mounted, 2 modules are stacked behind under the rear seats. The design allows for module replacement for maintenance.
The battery operates at 800 V, with a total capacity of 122 kWh (gross; Ferrari will announce the net capacity later). Supports DC fast charging up to 350 kW, and can be recharged with about 70 kWh in 15 minutes, according to the company. In terms of range, Ferrari says over 330 miles according to WLTP (base value; approximately > 531 km). Converted to the more realistic EPA standard, this number could be around 280 miles (~ 451 km), depending on tire configuration.
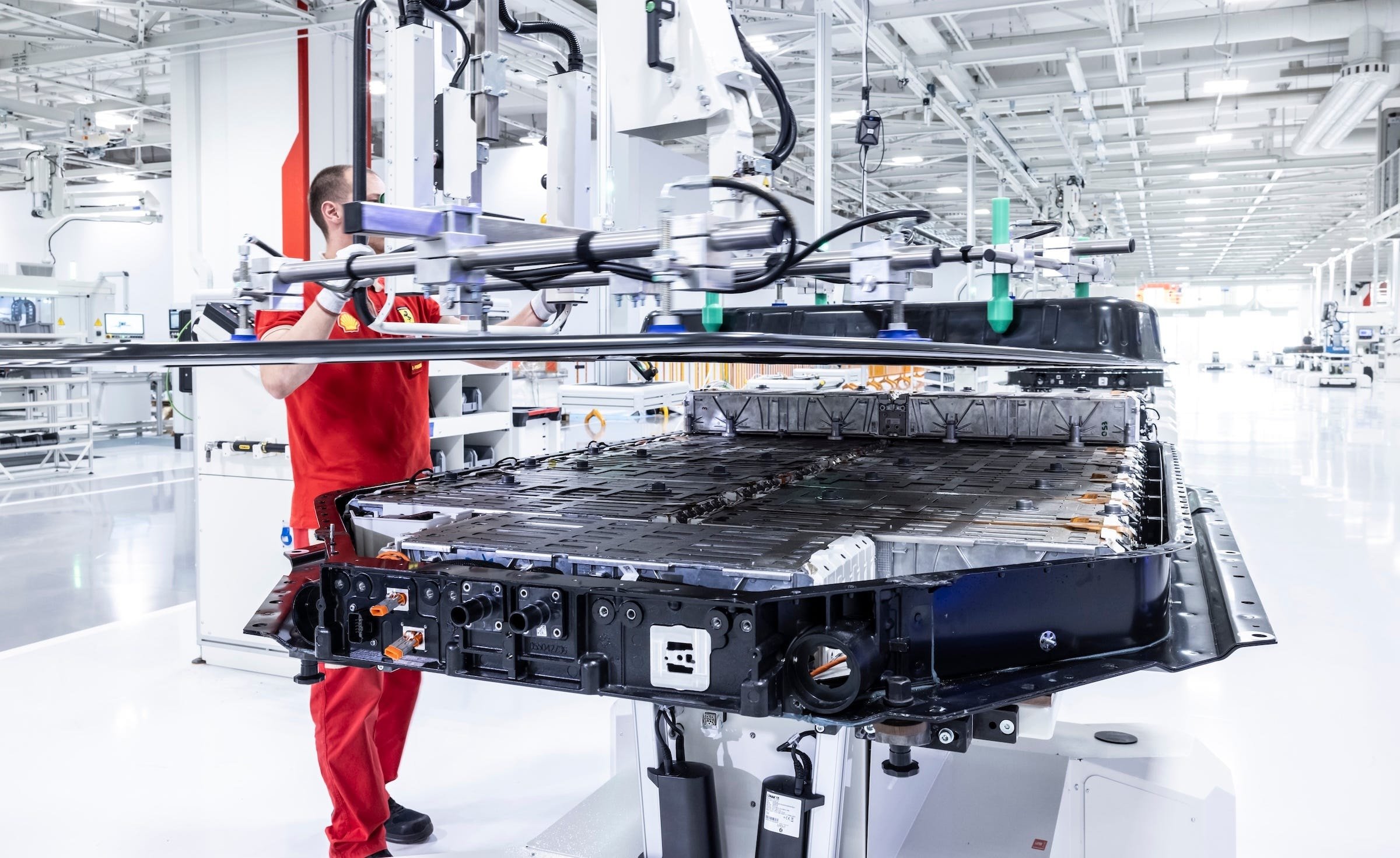

3rd generation active suspension and 2.15° rear steering
The third-generation suspension, co-developed with Multimatic, continues the solution seen on the Purosangue. The 'damper' features a central ball screw driven by a 48 V electric motor in place of the main spring. The spring is still present, primarily to hold the body when the car is off; when running, the electric motor adjusts the micro-displacements in real time at a frequency of 100 Hz to create the necessary damping force. The new generation changes the pitch angle of the screw by 20°, and adds a temperature sensor to compensate for the influence of oil viscosity.
All-aluminum suspension, hollow front/rear hubs. Front is multi-link with dual lower and upper A-arms; rear is multi-link with integral link below and single camber link above. The rear axle uses independent actuators instead of toe-in braces, allowing for ±2.15° of rear wheel steering. Notably, this is the first time Ferrari has used a rear subframe to isolate vibration/noise, as EVs have no engine noise to mask it.
Carbon-ceramic brakes: 6-piston calipers with 15.4-inch front discs (stock value; ≈ 391 mm), 4-piston and 14.6-inch rear discs (stock value; ≈ 371 mm). The energy regeneration system reaches a maximum of 0.68 g, so under normal conditions, the friction brake rarely has a high thermal load.
Sound: exploiting vibrations, not “simulating”
Ferrari isn’t using synthetic sounds. It’s using a “hard point” on the rear motor assembly that picks up vibrations proportional to load, speed, and rotation direction using accelerometers, then amplifies the resulting signal, much like an electric guitar pickup. A demo of the sound hasn’t been released yet; it’s still early days.
Safety and technology
Ferrari hasn’t shared any ADAS details or safety ratings. Dynamic control platforms like four-wheel independent torque vectoring, rear steering, and active suspension are the current engineering focus; any advanced driver assistance systems will be updated closer to production.
Price and positioning: 2026 will be clearer
Ferrari says the Elettrica is aimed at expanding its customer base, with interest already high. Details on pricing, model configurations and availability will be announced in subsequent waves in 2026.
Temporary technical data sheet
| Category | Information |
|---|---|
| Transmission system | 4 PMSM motors, 2 motors per bridge, independent torque vector |
| Capacity | > 1,000 CV (according to Ferrari); front axle maximum 282 hp, rear axle maximum 831 hp (original value) |
| Drive | AWD by default; front motor can be detached to run RWD via e-Manettino |
| Accelerate | 0–100 km/h 2.5 seconds (base: 0–62 mph, 2.5 seconds) |
| Maximum speed | 193 mph (base value; ≈ 310.6 km/h) |
| Battery | 122 kWh gross, 15 modules (14 cells/module), 800 V |
| Charging | DC max 350 kW; add about 70 kWh in 15 minutes (according to Ferrari) |
| Range of movement | > 330 miles WLTP (base value; ≈ > 531 km); EPA estimated ~ 280 miles (≈ 451 km) |
| Wheelbase | 116.5 inches (original value; ≈ 2.959 mm) |
| Mass | Under 5,100 lb (original value; ≈ 2,313 kg) |
| Suspension system | Active generation 3 (Multimatic), 48 V electrical control, 100 Hz update |
| Rear steering | ±2.15° via rear axle independent actuator |
| Brake | Carbon-ceramic: front 15.4 inches (≈ 391 mm), rear 14.6 inches (≈ 371 mm); maximum regeneration 0.68 g |
| Announcement roadmap | Next phase in Q1 and Q2/2026 |
Conclusion: Select for sustainable performance
The Elettrica shows Ferrari’s approach to EVs in pure tech terms: four motors with Halbach and carbon-fiber rotors, an 800V 122kWh battery, 350kW DC charging, third-generation active suspension, rear steering, and carbon-ceramic brakes. The accompanying 0–100km/h 2.5-second and 193mph targets emphasize performance repeatability.
Pros: In-house powertrain platform, advanced dynamic controls, purposeful suspension and NVH handling. Cons: Design/body and interior not yet revealed, EPA range expected to be average for a high-volume, performance EV. All will be clearer when Ferrari finalizes the reveal in 2026.
Source: https://baonghean.vn/ferrari-elettrica-tien-san-xuat-ev-hon-1-000-cv-4-mo-to-10307930.html


![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City is brilliant with flags and flowers on the eve of the 1st Party Congress, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/10/1760102923219_ndo_br_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-43-png.webp)

![[Photo] General Secretary attends the parade to celebrate the 80th anniversary of the founding of the Korean Workers' Party](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/11/1760150039564_vna-potal-tong-bi-thu-du-le-duyet-binh-ky-niem-80-nam-thanh-lap-dang-lao-dong-trieu-tien-8331994-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] Opening of the World Cultural Festival in Hanoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/10/1760113426728_ndo_br_lehoi-khaimac-jpg.webp)

































































































Comment (0)