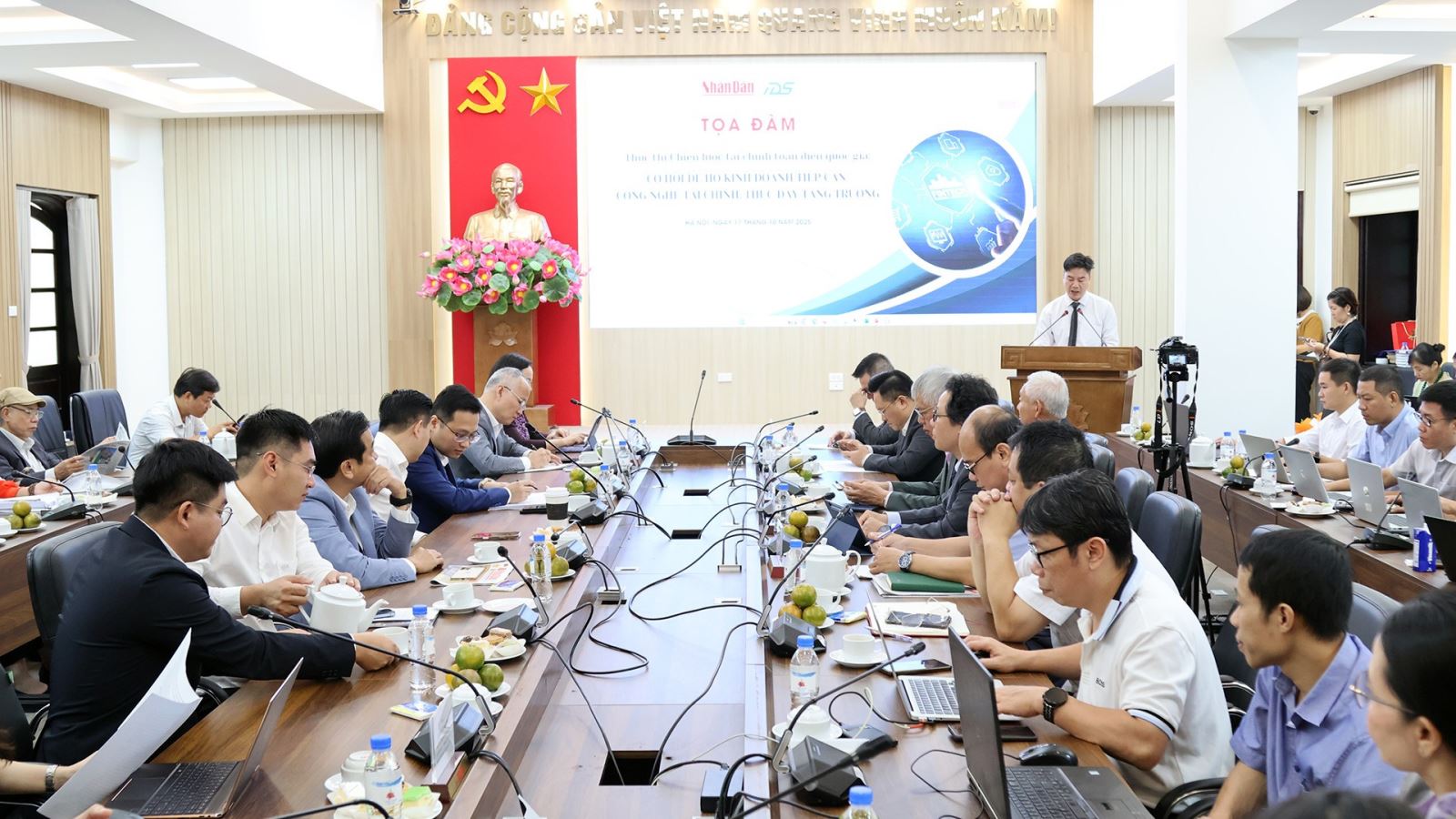

Mr. Le Quoc Minh, Editor-in-Chief of Nhan Dan Newspaper, Deputy Head of the Central Propaganda and Mass Mobilization Commission, said that Vietnam currently has more than 5 million business households, contributing approximately 30% of GDP, creating more than 10 million jobs. Resolution No. 68-NQ/TW, dated May 4, 2025, of the Politburo on private economic development clearly states: "Review and perfect the legal framework on individual businesses; minimize the gap, create all favorable conditions in terms of management organization and financial and accounting regimes to encourage business households to transform into enterprises".
Supporting business households to access financial technology and convert to enterprise models is one of the necessary solutions that has been strongly implemented in the market in recent times. Thereby, contributing to promoting the private economy , improving competitiveness and creating larger budget revenue.
According to Dr. Tran Van, Director of the Institute for Digital Economic Development Strategy (IDS), after nearly 40 years of innovation, Vietnam is once again facing the opportunity to make a strong breakthrough thanks to the scientific and technological revolution and national digital transformation. If in the past only large enterprises with financial resources had the conditions to digitize the production and business management process, now even 5 million small individual business households can access new opportunities through financial technology platforms.
The integration of the latest scientific and technological achievements that smart digital financial platforms have supported millions of individual business households across the country, including in remote, isolated and particularly difficult areas, in production, business and consumption of goods. Grocery store owners who were once hesitant about technology have now proactively embraced financial technology services, thereby saving costs, time and significantly increasing business efficiency.
Thanks to that, many business households have had the conditions to expand their scale, diversify their products, serve consumers better, create accumulation, improve legal conditions, and be ready to transform into legitimate small and medium enterprises in line with the goals set by the Party and the State.
However, the process of digitizing production and business households still faces many difficulties. Specifically, the legal framework has not kept up with the business model; the awareness of technology among a number of business owners and small producers is still limited; while technology enterprises also face challenges in terms of high-quality human resources and financial investment in technology research and development.
The Institute for Digital Economic Development Strategy believes that although small, micro and household businesses in Vietnam have improved their access to financial services, it is still uneven. Accordingly, the lowest income group of individuals has only increased its account ownership rate by about 6% after 5 years. Small, micro and household businesses, although accounting for a large proportion of the economy, still face many barriers in accessing formal credit. The gap in access to financial services between income groups and business sizes is widening, to the disadvantage of low-income individuals and small and micro businesses.
Many other important indicators to measure the level of financial services coverage are still poor, especially when compared with countries with similar social conditions and economic development levels to Vietnam, the account ownership rate of small and medium enterprises in Vietnam is only 50%, far lower than countries compared to Vietnam, which are usually at 80% - 90%. Vietnamese enterprises use more informal capital than other countries. Vietnam is among the group of countries that are slow to improve access to capital for small and medium enterprises; with the main and inherent reasons being that loans require collateral; high interest rates; and complicated procedures.
In that context, the application of technology, especially Fintech (financial technology), has contributed to strongly promoting financial inclusion through simple, low-cost, and accessible service models - especially suitable for low-income individuals and those without credit history: through e-wallet applications, non-traditional credit scoring, micro-savings; small and micro enterprises, business households: thanks to digital financial platforms, cash flow management applications, digital POS and financial tools to replace traditional banks.
According to Mr. Nguyen Quang Khai, Deputy Director of Retail Solutions, Misa Joint Stock Company, from January 1, 2026, the policy of eliminating lump-sum tax will be officially implemented. For this transition to take place smoothly, business households need to be carefully prepared - not only in terms of legal knowledge, but also in terms of tools and technological solutions so that the issuance of invoices, declarations and tax payments can be done quickly, accurately and easily. Currently, MISA has provided tax-related support applications and tax accounting for 50,000 business households of all sizes.
Fintech is also the key factor in promoting and popularizing cashless payments in Vietnam in recent times. IDS's report clearly shows that cashless payments are one of the areas with the strongest growth and development after the implementation of the Strategy. At the same time, cashless payments are also the only area in which Vietnam is superior to other countries in the same social context and economic development level that are included in the comparison.
Sharing about the future of Fintech in Vietnam, the IDS research team noted that the trend of building policies towards Fintech has shown signs of being less open in the recent period. Accordingly, Fintech being licensed to test payment intermediary services in 2008 has helped create a breakthrough growth for non-cash payment activities. However, by July 2025, the next testing mechanism for piloting new Fintech solutions was issued, with the birth of Decree No. 94/2025/ND-CP. Thus, it took up to 17 years for specialized management agencies to expand the legal basis for Fintech to provide new types of services.
Dr. Nguyen Duc Kien, Chairman of the IDS Scientific Council, Former Head of the Prime Minister's Economic Advisory Group, emphasized that building a policy environment that continuously supports innovation and promotes the development of new factors such as Fintech is very important for financial market participants to continuously learn, improve, and enhance their competitiveness. If there is no continued open-mindedness in policy making to promote digital transformation, the initial achievements will be pushed back.
During the discussion session at the seminar, representatives of the National Assembly Committees, ministries, branches, and economic experts shared more about the challenges and solutions to improve the policy environment for healthy and sustainable development of the digital financial services market, serving the effective implementation of the National Financial Inclusion Strategy in the next phase.
Source: https://baotintuc.vn/kinh-te/co-hoi-so-cho-ho-kinh-doanh-phat-trien-20251017133452955.htm


![[Photo] Collecting waste, sowing green seeds](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/18/1760786475497_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)



![[Photo] Closing ceremony of the 18th Congress of Hanoi Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/17/1760704850107_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 95th Anniversary of the Party Central Office's Traditional Day](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/18/1760784671836_a1-bnd-4476-1940-jpg.webp)





































































































Comment (0)