Compared to the 2013 Employment Law, the 2025 Employment Law (effective from January 1, 2026) expands the scope of unemployment insurance (UI) participants, increases unemployment benefits, shortens the time to process unemployment benefits, and is more flexible in regulations on support for employers...
These new regulations not only contribute to increasing the benefits of unemployment insurance policies for employees and businesses, but also ensure the flexibility of the policy, especially in cases of economic recession, natural disasters, epidemics, etc.
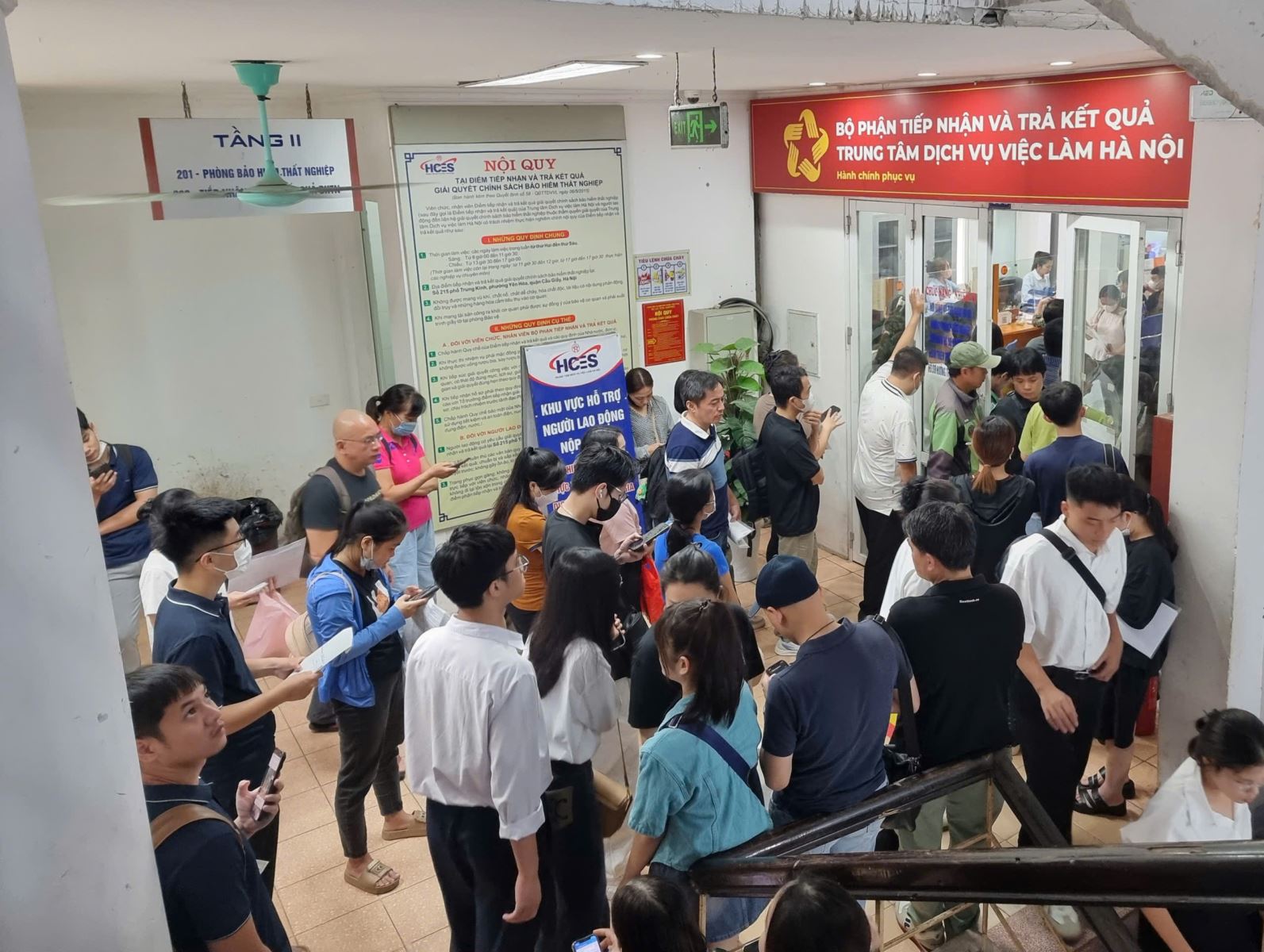

Some new regulations on participants and beneficiaries of social insurance policies take effect from January 1, 2026, specifically as follows:
Subjects responsible for participating in social insurance
In Clause 1, Article 31 of the 2025 Law on Employment, in addition to the subjects working under indefinite-term contracts, the Law stipulates the following cases are subject to participation in unemployment insurance from January 1, 2026, specifically as follows:
Contracts with a term of 1 month or more.
Part-time workers whose monthly salary is equal to or higher than the lowest salary used as the basis for compulsory social insurance contributions as prescribed by the Law on Social Insurance;
Salarian management positions: Enterprise managers, controllers, representatives of enterprise capital as prescribed by law; members of the Board of Directors, General Directors, Directors, members of the Supervisory Board or controllers and other elected management positions of cooperatives and cooperative unions as prescribed by the Law on Cooperatives receiving salaries.
Compared to the 2013 Employment Law, the 2025 Employment Law expands the number of subjects required to participate in unemployment insurance. Expanding the number of subjects participating in unemployment insurance not only helps expand the safety net, bringing direct benefits to employees, but also contributes to stabilizing the labor market in the long term, especially the group of short-term, part-time workers, freelance workers... who often face the risk of losing their jobs and reducing their income.
Social insurance policy regimes
For support regime for employees participating in training and improving vocational skills: Additional support for meal expenses during the time employees participate in training courses and improve vocational skills.
This new regulation helps unemployed people reduce difficulties when participating in vocational training, thereby contributing to increasing the rate of workers participating in vocational training and increasing opportunities to find new, more suitable and better jobs.
For unemployment benefits: Reduce the waiting time to qualify for unemployment benefits from 15 working days to 10 working days. Accordingly, the time to receive unemployment benefits for employees is 05 working days earlier than current regulations (from the 11th working day from the date of submitting complete documents instead of from the 16th working day as currently).
Increase the maximum unemployment benefit to 5 times the monthly regional minimum wage (according to the provisions of the 2013 Employment Law, for employees subject to the State-regulated wage regime, the maximum monthly unemployment benefit shall not exceed 5 times the basic salary).
Unemployed workers have reduced income. In this case, the regulation of reducing the waiting time to qualify for benefits will help workers receive unemployment benefits soon to cover their living expenses and return to the labor market; at the same time, raising awareness of compliance with the law on social insurance and unemployment insurance.
Regarding the regime of supporting employers in training, fostering and improving vocational skills to maintain employment for employees
The 2025 Law on Employment amends the conditions for supporting employers in training, fostering, and improving vocational skills. Compared to the 2013 Law on Employment, the 2023 Law on Employment has removed the provisions on conditions for employers to be supported such as: "Insufficient funds to organize training, fostering, and improving vocational skills for employees;" and the condition "Facing difficulties due to economic downturn or other force majeure reasons, forcing them to change the structure or technology of production and business". Instead, the conditions for support are regulated in more detail and specifically such as: Changing the structure, technology or for economic reasons as prescribed in the Labor Code; Natural disasters, fires, enemy attacks or dangerous epidemics; Implementing the decision of a competent state agency on relocating or reducing the location of production and business; Other cases as prescribed by the Government .
Different from the provisions of the 2013 Employment Law, the amendment of support conditions in the 2025 Employment Law makes it easier for employers to access this regime, aiming to increase the number of supported employers, contributing to maintaining and developing jobs for employees, limiting unemployment. At the same time, with increased job counseling, referrals and support for employees to train and improve their vocational skills, it will help unemployed people return to the labor market sooner, shortening the time to receive unemployment benefits compared to the present.
The Government shall base on the actual situation and the balance of the Unemployment Insurance Fund to prescribe the reduction of unemployment insurance contributions, and provide cash or other support in case of crisis, economic recession, natural disaster, fire, war or dangerous epidemic.
Previously, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the decision to use the remaining funds of the unemployment insurance fund to provide cash support to employees and support the reduction of unemployment insurance contributions for employers had to be made by the National Assembly and the National Assembly Standing Committee. Now, the 2025 Employment Law assigns the Government to decide. This regulation will facilitate the issuance of support policies faster, promptly resolving the regime for employees and employers to quickly stabilize production and business.
This new regulation is meaningful not only for employees and employers but also for State management agencies. Specifically, for employees and employers, there is timely support and sharing to overcome difficulties when crises, economic recessions, natural disasters, fires, war or dangerous epidemics occur. For competent State management agencies: Issue support policies more quickly and promptly; thereby actively promoting the role, humane meaning and superiority of unemployment insurance policies in reducing the burden on employees and employers, especially in urgent and difficult situations and contexts.
Source: https://baotintuc.vn/xa-hoi/luat-viec-lam-2025-mo-rong-doi-tuong-tang-quyen-loi-thu-huong-bao-hiem-that-nghiep-tu-nam-2026-20251016165540762.htm






![[Photo] Nhan Dan Newspaper launches “Fatherland in the Heart: The Concert Film”](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760622132545_thiet-ke-chua-co-ten-36-png.webp)




























![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 18th Hanoi Party Congress, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/16/1760581023342_cover-0367-jpg.webp)









































































Comment (0)