However, despite all that power, have users ever noticed that their smartphones lack a cooling fan?
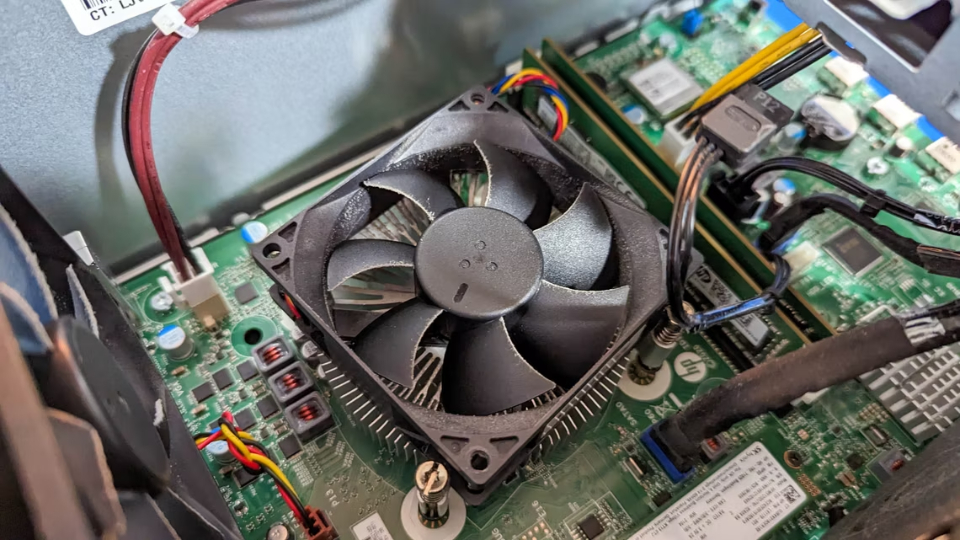

Computer cooling fans cannot be found on smartphones for some reasons.
Fragile
Smartphone manufacturers have been trying for years to make their devices as thin as possible and these handsets wouldn't just be a few millimeters thick if you factor in the fan, but the fan is also bulky and requires space to move around.
The fan also breaks down pretty quickly due to actions like moving around with the phone, dropping it on the floor, etc. Everything in the phone still works, but the fan will start to rattle or work poorly, causing everything to gradually overheat and break down.
Need open space
Devices that rely on fans for cooling are often not suitable for cramped spaces and when operating at high intensity will be very uncomfortable. Smartphones are always on and the cooling fan will have to be running all the time. When placed in a pocket or bag, cooling with a fan will become difficult because of the limited space. Imagine with a laptop, even using it under a blanket in bed is already uncomfortable.
Mobile chips use less power, generate less heat
A key term that determines how power-efficient a CPU is is the thermal design power (TDP), which is usually listed in watts and represents the maximum power the CPU can generate under full load. The Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 is the current flagship chip for high-end smartphones with a 12.5W TDP, which is higher than the 5W of the original Snapdragon chips but comparable to lower-power Intel CPUs.

Snapdragon 8 Gen 3 is powerful but only has 12.5W TDP
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090 has a 450w TDP, and that's just for a PC component. That kind of power consumption is unfeasible for a battery-powered mobile device, and it also generates more heat. That's part of the reason why PCs and laptops need fans, while phones don't. It also explains why smartphones, no matter how advanced, can't match the graphics of a dedicated gaming PC.
Mobile apps generate less heat, reducing cooling needs
Apps don’t take up physical space, but they do drain system power. If a bad app keeps making network requests, processes run in the background while it’s asleep, and the device uses more power. Not all mobile apps are perfect, but they generally have a low impact on battery life, reducing the need for active cooling.
Smartphones use passive cooling systems
Fans use active cooling, unlike smartphones that rely on passive cooling. This is a process of heat exchange based on the difference in temperature between materials without any mechanical help. In simpler terms, things can cool down without moving anything. Phones often use metal plates between the electrical components and their external design to dissipate heat.
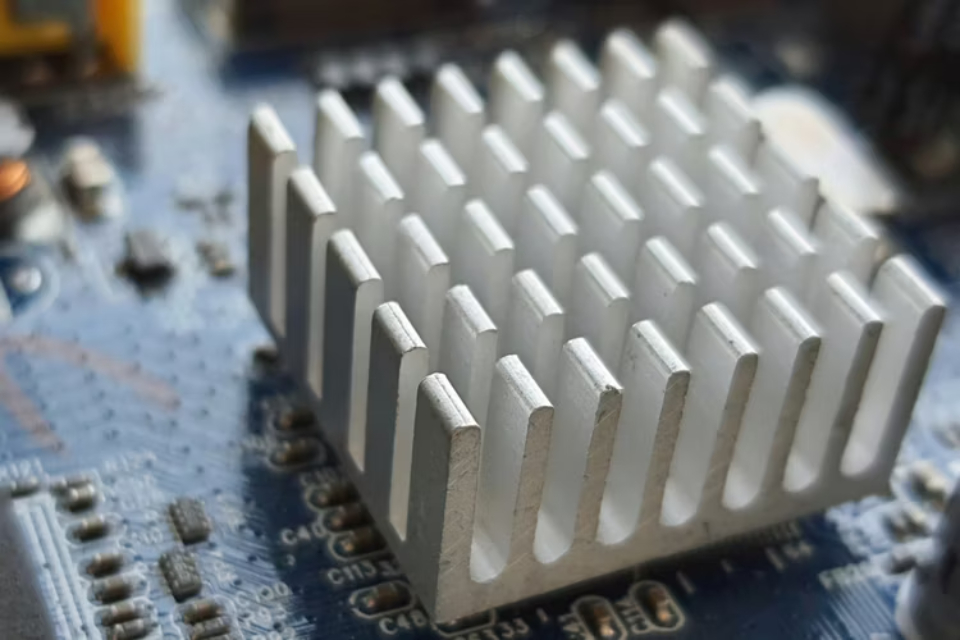
Passive cooling mechanism has limitations in heat dissipation under heavy load
Passive cooling works great for everyday use, but unlike active cooling, it can’t reduce the temperature to cool down quickly. That’s why some smartphones get particularly cranky during heavy tasks like gaming, where the CPU is generating more heat and the smartphone can’t compensate. This is when thermal throttling kicks in, reducing performance to give the components time to cool down.
Several alternatives are being developed.
Some smartphones today have special cooling modes to solve the problem of heavy loads, especially gaming products, such as vapor chamber cooling on the Galaxy S23 series, or carbon water cooling on the Galaxy Note 9, Xiaomi's Loop LiquidCool technology, or the AeroActive Cooler 6 accessory for Asus's ROG Phone 6.
Source link




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs a meeting of the Government Standing Committee to remove obstacles for projects.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/06/1759768638313_dsc-9023-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chaired a meeting of the Steering Committee on the arrangement of public service units under ministries, branches and localities.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/06/1759767137532_dsc-8743-jpg.webp)




























































































Comment (0)