Nutrition from carrots
Dr. Nguyen Thu Ha, Head of the Nutrition and Dietetics Department, Saigon South International General Hospital, shared that carrots contain many micronutrients, especially beta-carotene. This is a powerful antioxidant and a precursor of vitamin A. 100g of carrots contains 6597 mcg of beta-carotene. Meanwhile, the recommended vitamin A requirement for adults is 850 - 900 mcg/day for men and 650 - 700 mcg/day for women. Pregnant women need about 1200 - 1300 mcg/day.
In addition, carrots are a rich source of important vitamins and minerals such as vitamins C, D, E and B vitamins. Carotene in carrots when entering the body will be converted into vitamin A to help brighten eyes, increase resistance and keep skin smooth. The potassium content in carrots helps prevent the risk of high blood pressure and other cardiovascular problems.
Vitamin C contained in carrots contributes to the production of collagen - the main component of connective tissue, which is essential for wound healing and keeping the body healthy, creating antibodies that protect the immune system. In addition, the fiber content in carrots helps maintain a healthy weight, reduces the risk of constipation, is good for the intestines, digestive system and reduces the risk of heart disease.
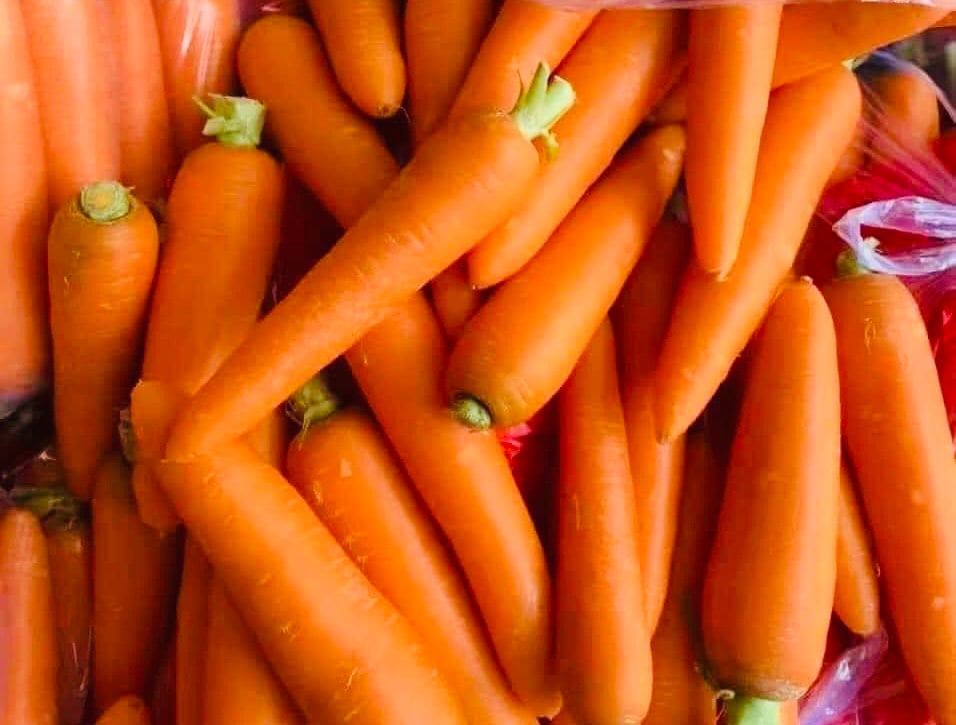

Carrots contain a lot of beta-carotene, a precursor of vitamin A.
Carrots also contain vitamin K, calcium and phosphorus, which contribute to bone health and help prevent osteoporosis. The antioxidants in carrots help fight harmful free radicals in the body, thereby helping to reduce the risk of cancer. In particular, consuming foods rich in carotene can reduce the risk of colon cancer and is good for overall digestive health.
Does eating a lot of carrots cause jaundice?
"However, if you eat a lot of carrots, your body will not be able to convert all the beta-carotene into vitamin A. When the amount of carotene increases about 3-4 times normal, it will cause jaundice in the palms of the hands and feet, the face will turn orange-yellow but the eyes and mucous membranes under the tongue will not turn yellow and are often accompanied by symptoms of indigestion, loss of appetite, and fatigue," Dr. Ha analyzed.
This condition is common in infants, young children and people who regularly eat yellow, orange, red foods such as carrots, pumpkin, gac fruit, papaya, bell peppers... or use functional foods such as gac oil capsules, acne treatment drugs containing high concentrations of vitamin A derivatives.
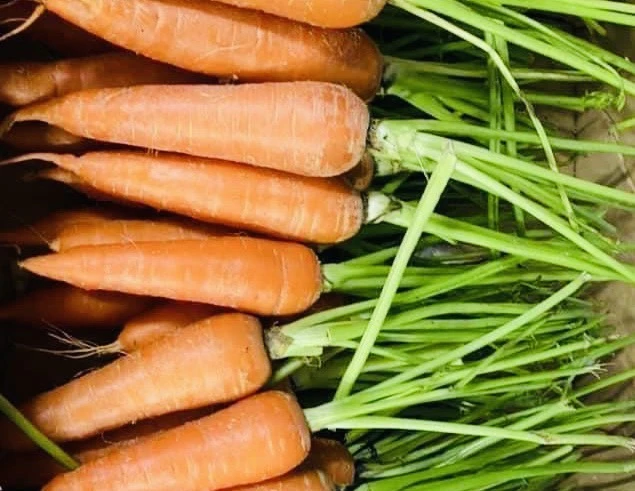

When eating too many carrots, the amount of carotene increases about 3-4 times normal, causing jaundice.
To avoid jaundice caused by eating too many carrots or foods containing a lot of vitamin A, Dr. Ha recommends that we should only eat or drink carrot juice 2-3 times a week, every other day. In case the child has jaundice but no yellow eyes, no yellow retinal membranes, poor appetite... the child should stop eating foods containing a lot of vitamin A.
"Jaundice caused by increased beta-carotene in the blood will gradually disappear after a few days. However, if jaundice is accompanied by yellow eyes and does not improve after stopping the use of the above foods, you need to see a doctor soon to be diagnosed to differentiate between true jaundice and jaundice caused by eating too much carotene," Dr. Ha recommends.
Source link


![[Photo] Bustling Mid-Autumn Festival at the Museum of Ethnology](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/da8d5927734d4ca58e3eced14bc435a3)


![[Photo] Solemn opening of the 8th Congress of the Central Public Security Party Committee, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/f3b00fb779f44979809441a4dac5c7df)


























![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 8th Congress of the Central Public Security Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/79fadf490f674dc483794f2d955f6045)





















![[VIDEO] Summary of Petrovietnam's 50th Anniversary Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/abe133bdb8114793a16d4fe3e5bd0f12)

![[VIDEO] GENERAL SECRETARY TO LAM AWARDS PETROVIETNAM 8 GOLDEN WORDS: "PIONEER - EXCELLENT - SUSTAINABLE - GLOBAL"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/23/c2fdb48863e846cfa9fb8e6ea9cf44e7)


































Comment (0)