ANTD.VN - Most organizations' forecasts have reduced expectations for another interest rate cut this year due to increasing exchange rate pressure.
In a recently published report titled “Vietnam At A Glance: Light at the End of the Tunnel”, HSBC Global Research has removed its previous prediction of a final cut in the policy rate by 0.5%, citing pressure from exchange rates and inflation.
While inflation in September was contained at 3.7%, below the ceiling of 4.5%, the continued incline in inflation has raised concerns, according to HSBC. On the one hand, food prices have increased by about 3% month-on-month for two consecutive months, pushing year-on-year inflation above 10%.
Although HSBC does not expect recent developments to push average inflation above the State Bank of Vietnam's (SBV) ceiling of 4.5%, this "misfortune never comes singly" situation poses a significant risk of increased risks.
"We have revised our quarterly inflation forecasts and slightly raised our average inflation forecast to 3.4% (previously: 3.2%) for 2023. Therefore, we no longer expect the State Bank to cut interest rates this year.
In our view, the conditions that previously warranted a further 50 basis point rate cut are no longer in place: the recovery is underway while inflation and foreign exchange pressures are rising,” HSBC analysts stressed.
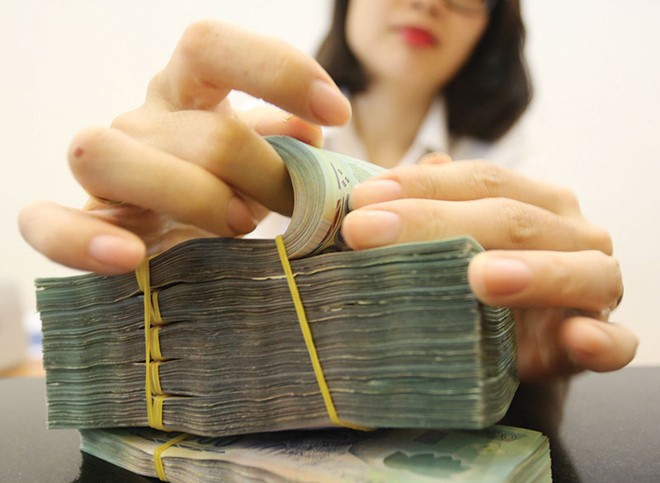 |
Room to reduce operating interest rates is increasingly narrowing |
With the above assessment, HSBC expects the SBV to keep the policy interest rate stable at 4.5% until the end of 2024, unless there are external shocks.
On the other hand, HSBC does not expect the same thing to happen again in October last year, when the continuous increase in the USD/VND exchange rate forced the SBV to drastically increase interest rates. The reason is that the macroeconomic conditions of VND have improved.
For example, Vietnam’s current account surplus has almost returned to its previous peak of nearly 5% of GDP, thanks to a strong trade surplus, abundant remittances and rising tourism revenues.
Similarly, many other international organizations also have a cautious view when predicting a cut in operating interest rates. In the East Asia and Pacific Economic Update report, October 2023, experts from the World Bank (WB) assessed that the continued loosening of monetary policy is considered appropriate for the economic context of Vietnam. However, continued interest rate cuts will increase the interest rate differential with global markets, potentially putting pressure on the exchange rate.
At the Vietnam Socio-Economic Forum 2023, Mr. Jochen Schmittmann, Resident Representative of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) in Vietnam, also recommended that the State Bank of Vietnam should carefully consider lowering interest rates because there is almost no room left.
According to the IMF representative, monetary policy easing played a very important role in boosting the economy in the first half of this year, but there is not much room left for further easing.
Vietnam's interbank interest rate is close to 0%, much lower than that of developed economies. Therefore, IMF experts believe that if the operating interest rate continues to be lowered, it will have a significant impact on the exchange rate.
In a different view, UOB maintained its forecast for another policy rate cut in the fourth quarter, with a further 100 basis point cut in the refinancing rate. However, UOB said the decision may still need to be considered as the central bank will consider balancing both growth and inflation risks.
According to UOB experts, inflation has been higher in recent months and the risk is that consumer price pressures may increase in the near term due to recent increases in food and energy prices as major oil producers cut production, the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine and changes in climate/weather. UOB maintains its CPI inflation forecast for Vietnam at 3.9% for 2023.
“Therefore, our forecast of continued interest rate cuts by the SBV in the fourth quarter of 2023 is still dominated by uncertain factors,” the bank forecasted.
Source link




![[Photo] Keep your warehouse safe in all situations](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/3eb4eceafe68497989865e7faa4e4d0e)
![[Photo] Hanoi morning of October 1: Prolonged flooding, people wade to work](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/189be28938e3493fa26b2938efa2059e)

![[Photo] President of the Cuban National Assembly visits President Ho Chi Minh's Mausoleum](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/39f1142310fc4dae9e3de4fcc9ac2ed0)
























































































Comment (0)