The cloned monkey is still alive and well.
The study, published in the journal Nature Communications on Tuesday, describes the newly cloned monkey, named Retro, a rhesus monkey. Falong Lu, one of the study's authors, said the monkey is healthy and thriving.
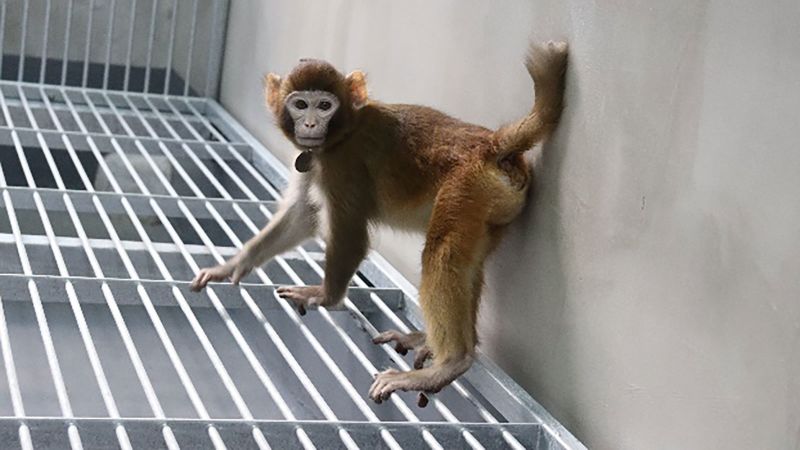

The cloned Rhesus monkey, named Retro, is alive and well. Photo: Nature Communications
"We have cloned the first healthy Rhesus monkey. This is such a big step that it seemed impossible, although the efficiency is very low compared to conventionally fertilized embryos," said Falong Lu, an expert at the State Key Laboratory of Molecular Developmental Biology and Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences .
Primates are one of the most difficult species to clone. Scientists have failed for years to replace cloned cells with cells from normal embryos. They hope to use the new technique to create identical Rhesus monkeys for medical research.
However, many researchers warn that the success rate of the new method is still very low, raising ethical questions surrounding cloning.
The first mammal to be cloned was Dolly the sheep, created in 1996 using a technique called somatic cell nuclear transfer, or SCNT.
Since that achievement, scientists have cloned many mammals, including pigs, cows, horses and dogs, a process that typically involves only a very small percentage of embryos being implanted into surrogate animals to produce viable offspring.
What is the new method of cloning?
In their study, the team used a modified version of the SCNT method on Cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) and further improved the technique to clone Rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta).
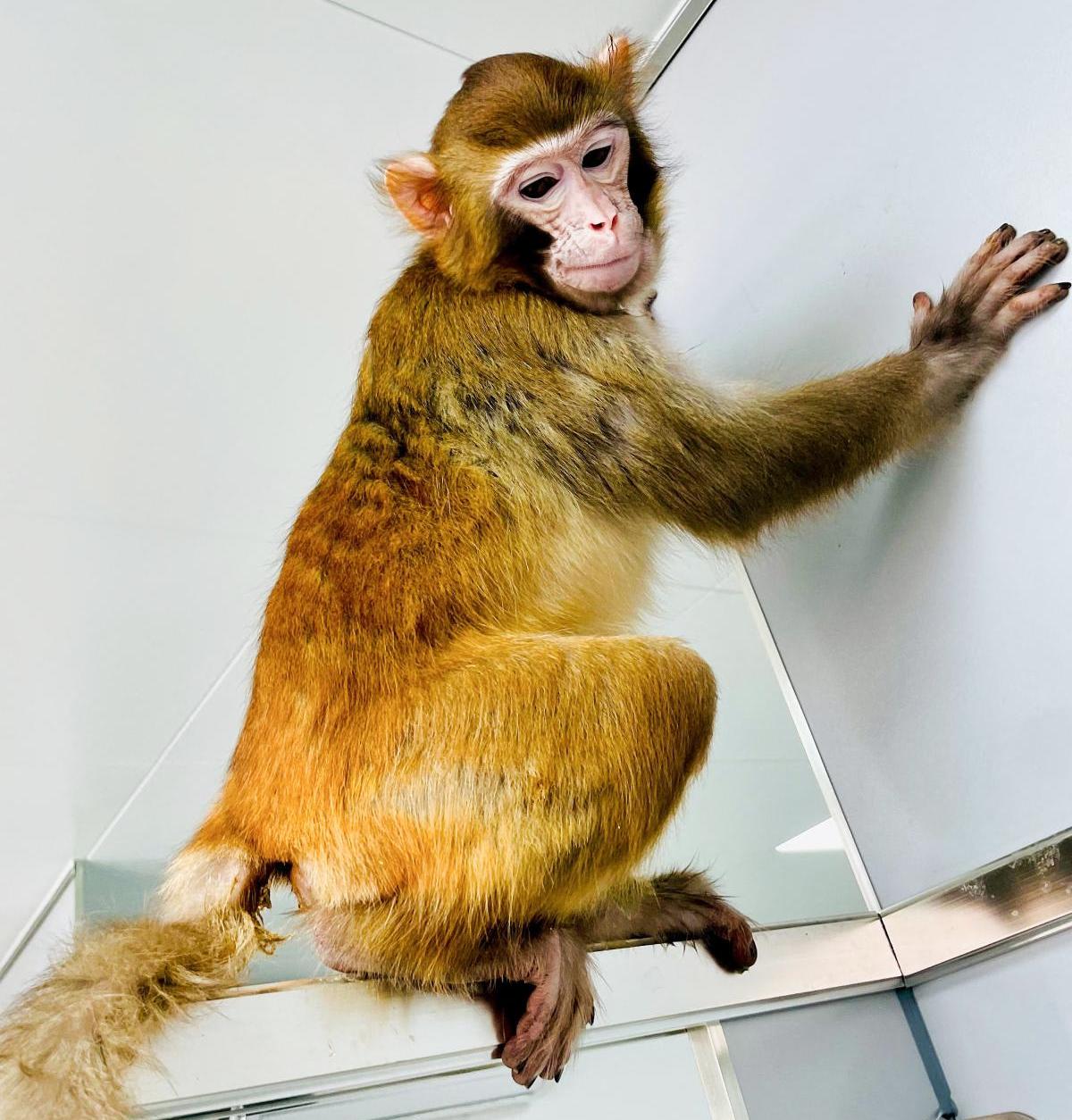

The cloned monkey Retro at 17 months old. Photo: Nature Communications
After hundreds of failures, they performed a process called inner cell mass transplantation, which involves introducing cloned inner cells into non-cloned embryos.
This allowed the clones to develop normally. The team then tested the new technique using 113 reconstructed embryos, 11 of which were implanted into seven surrogate animals. Only one survived.
"Our main focus in the future is studies to improve the success rate of SCNT in primates," said Falong Lu.
In fact, the first cloned monkey was not Retro, but a pair of identical long-tailed macaques (also known as crab-eating macaques) named Zhong Zhong and Hua Hua. The pair were created using SCNT in 2018 by researchers at the Institute of Neuroscience of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Shanghai.
Trung Trung and Hoa Hoa are now over six years old and are living happily and healthily with their fellow monkeys. Mr. Lu said that so far, researchers have not identified any potential limits to the lifespan of cloned monkeys.
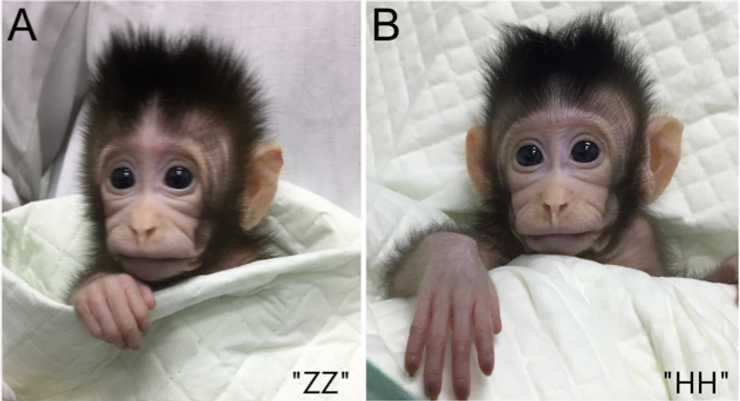
Identical cloned macaques Zhong Zhong (ZZ) and Hua Hua (HH). Photo: Liu et al Cell
Ethical debate
The use of monkeys in scientific research has been controversial on ethical grounds for animal welfare. Scientist Lluis Montoliu at Spain's National Biotechnology Center, who was not involved in the study, pointed out that only one of the original 113 embryos survived, meaning a success rate of less than 1%.
“First, it is possible to clone primates. And second, no less important, these experiments are very difficult to succeed with such low success rates,” said Mr. Montoliu.
He added that the low success rate of this experiment showed that human cloning was unnecessary and controversial, and that if attempted, it would be "extremely difficult and ethically unjustified".
Meanwhile, the UK's Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals said it had "serious ethical and welfare concerns surrounding the application of cloning technology to animals. Animal cloning requires procedures that can cause pain and discomfort to animals and has high failure and death rates."
The significance of monkey cloning
Amid mixed opinions, the research team said they still followed Chinese laws and guidelines on the use of non-human primates in scientific research.
Research on primates, which have many similarities to humans, will play a key role in leading to many medical advances, including the creation of a Covid-19 vaccine, according to a report released in May by a panel of the Chinese National Academy of Sciences , Engineering and Medicine.
The team said the successful cloning of monkeys could help speed up biomedical research, as scientists are currently limited when experimenting on mice. Mr. Esteban also believes that creating genetically identical monkeys could be useful in many ways.
"This study is proof that cloning can be performed in non-human primates and opens the door to new, more efficient methods. Cloned monkeys can be genetically modified in complex ways that wild monkeys cannot. This has many implications for disease modeling as well as conservation efforts," Esteban said.
Hoai Phuong (according to CNN, AFP)
Source



































































































Comment (0)