SGGP
After 10 years of research, a group of scientists at Northwestern University, USA, have developed a synthetic version of melanin that can have millions of uses, including helping to prevent blisters and speed up the healing process of tissue samples on newly injured human skin.
The team now plans to further develop the “super melanin” as both a treatment for skin wounds and a potential anti-aging and sun protection product.
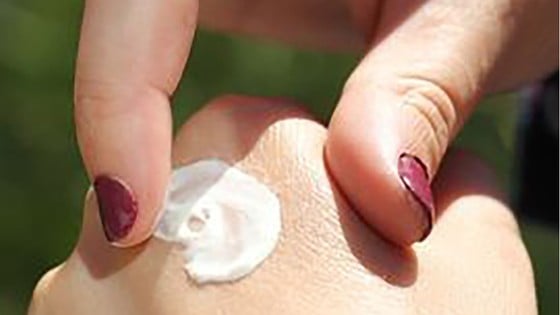 |
Testing super melanin on human skin |
In the study, scientists tested melanin on two mice exposed to chemicals and UV radiation and human skin tissue samples exposed to the chemicals.
In both cases, melanin reduces or even completely prevents damage to the upper and lower layers of skin, primarily by scavenging harmful free radicals generated on the skin after exposure, thereby reducing inflammation and speeding up the healing process.
Source


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's online conference with localities](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/264793cfb4404c63a701d235ff43e1bd)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh launched a peak emulation campaign to achieve achievements in celebration of the 14th National Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/8869ec5cdbc740f58fbf2ae73f065076)















































![[VIDEO] Summary of Petrovietnam's 50th Anniversary Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/abe133bdb8114793a16d4fe3e5bd0f12)

![[VIDEO] GENERAL SECRETARY TO LAM AWARDS PETROVIETNAM 8 GOLDEN WORDS: "PIONEER - EXCELLENT - SUSTAINABLE - GLOBAL"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/23/c2fdb48863e846cfa9fb8e6ea9cf44e7)

































Comment (0)