A 10-30 minute nap at noon will improve blood pressure and memory, but the risk of obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes increases if you sleep for more than this amount of time.
Scientists are still debating whether napping is a healthy way to jump-start the brain's systems at the lowest energy point of the day, or whether it threatens to disrupt circadian rhythms.
A new study in Spain, conducted by Harvard Business School, shows that people who nap for more than 30 minutes may increase their risk of obesity, high blood pressure and diabetes. This is because this group tends to overeat at lunch and not get a full eight hours of sleep at night. In contrast, people who nap for less than 30 minutes have improved blood pressure and memory.
Why do we nod off at noon?
Some people need to take a nap in the afternoon due to medical factors, but many find it enjoyable to take a 10-minute nap in the middle of the day.
"We all have very different biological mechanisms. Some people's bodies prefer to nap in the afternoon, even if they are perfectly healthy and not sleep-deprived. If a nap doesn't affect your work schedule, don't delay," says Sophie Bostock, founder of Sleep Scientist, a UK-based sleep consultancy.
Due to the way our circadian rhythms work, our energy levels naturally dip between 1pm and 3pm. This is when we are most likely to fall asleep. You are also more likely to feel sleepy in the afternoon if you are sick or sleep deprived, or if you simply overeat at lunch.
Benefits of napping
If done correctly, a good afternoon nap can play an important role in improving your quality of life. "Napping helps consolidate memories, promotes the conversion of short-term memories into long-term memories, and can improve your mood for the rest of the day," says Michael Breus, founder of Sleep Doctor.
Over the years, Breus has also found that napping can boost learning performance in the late afternoon. Students who take a quick nap after lunch perform better the rest of the day.
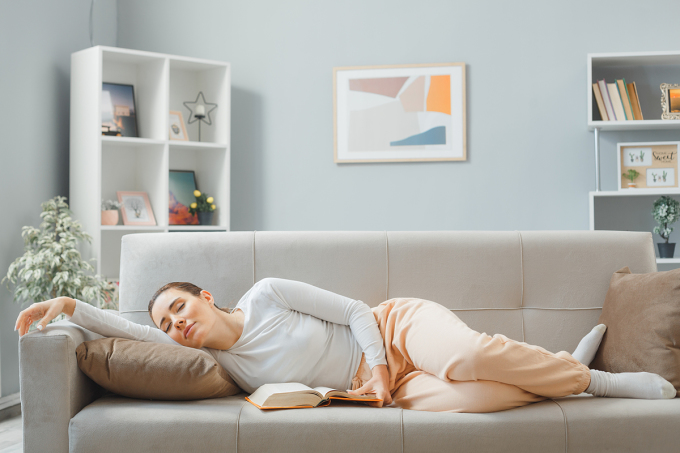

For healthy adults, the best nap should only last 10-30 minutes. Photo: Freepik
Long naps can be harmful to your health.
Bostock says long naps disrupt our circadian rhythms by keeping us from getting the most restorative sleep at night. Naps are better suited to people who sleep well at night.
“Taking too much nap time can reduce your need for sleep at night, which can be a problem for people who have trouble sleeping regularly,” says Breus.
How long should a nap last?
For healthy adults, the best naps last 10-30 minutes. If you nap longer, you'll move from stages one and two of sleep (which promote energy and focus) to stage three, which is great for restoring energy at night but not for daytime alertness.
“But if you have young children or are working shifts, taking advantage of daytime naps is a good strategy,” says Bostock.
Most of us wake up from a deep sleep in the afternoon feeling groggy. “The grogginess comes from sleep inertia. That deep sleep cycle starts 25 minutes after falling asleep, and it takes up to an hour for you to be fully awake if you’re woken during that cycle,” says Bostock, who recommends setting an alarm to avoid falling into the deep sleep cycle.
Hong Van (According to Telegraph )
Source link



![[Photo] Hanoi morning of October 1: Prolonged flooding, people wade to work](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/189be28938e3493fa26b2938efa2059e)































![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives President of the Cuban National Assembly Esteban Lazo Hernandez](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/4d38932911c24f6ea1936252bd5427fa)
![[Photo] The 1st Congress of Phu Tho Provincial Party Committee, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/1507da06216649bba8a1ce6251816820)
![[Photo] Panorama of the cable-stayed bridge, the final bottleneck of the Ben Luc-Long Thanh expressway](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/391fdf21025541d6b2f092e49a17243f)


























































Comment (0)