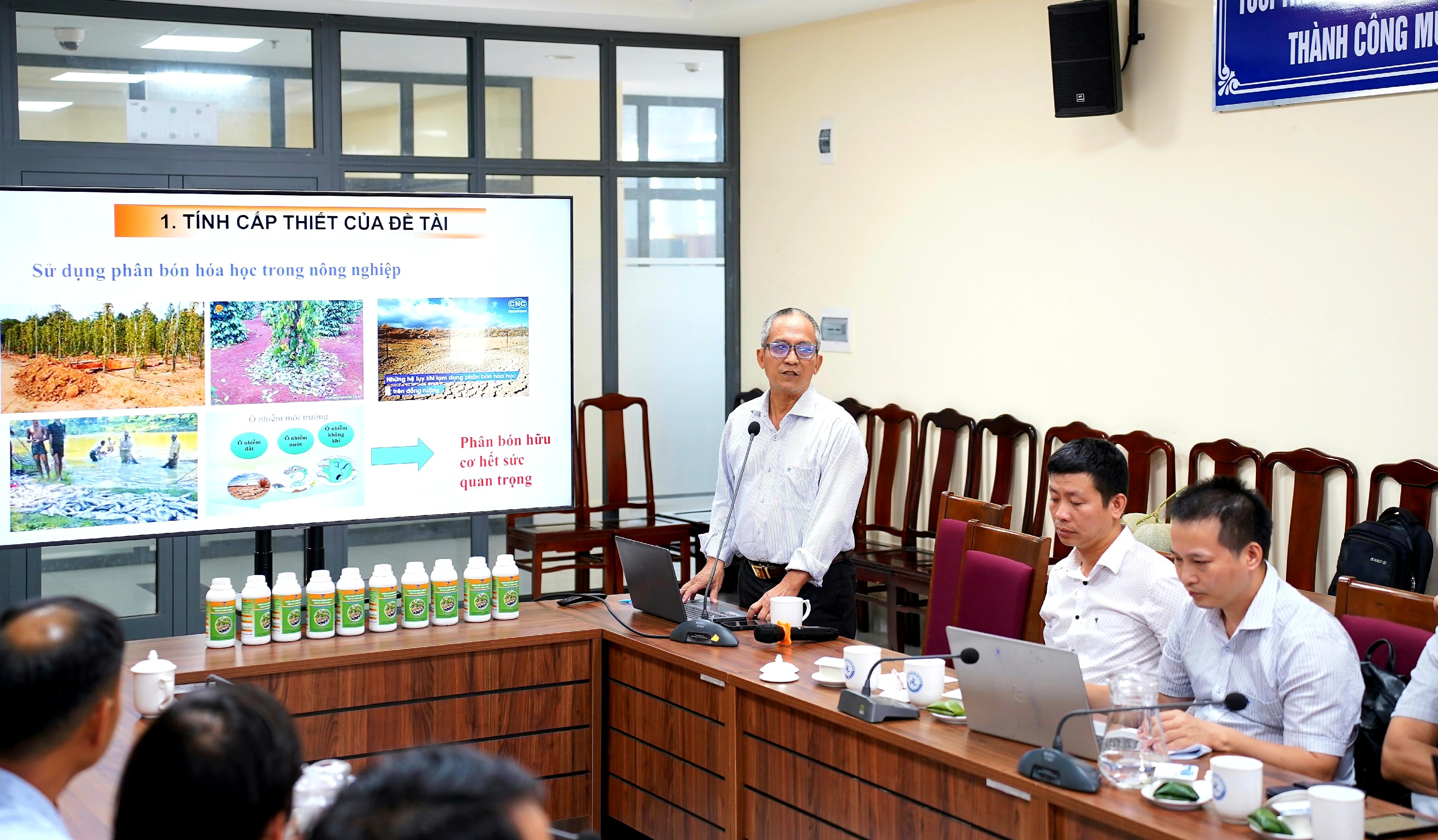
Prof. Dr. Dinh Quang Khieu, project manager, reports on the project implementation results. |
After 2 years of implementation (from August 2023 to July 2025), the project has completed the work contents compared to the requirements. The research team has assessed the current status of peat mines in Hue city, including 3 mines with a total area of more than 149 hectares, with an estimated resource reserve of more than 1.85 million tons. The chemical composition of peat in the mines is very rich and diverse, an essential source of nutrients for plants, with 2 main components with the highest proportion: humic acid (accounting for nearly 17.8%) and average humus content (accounting for 30.86%).
Researching on animal bones, the project team has determined that the main chemical components of bones are Ca and P, which account for a high proportion. Recycling waste into useful materials can replace the components that are currently being exploited as phosphorus fertilizers, providing a clean source of phosphorus fertilizers, capable of fixing heavy metals on the soil and usefully amending the soil.
The project also developed a process for preparing humic acid from peat, which is a good alternative to remediate eroded soil, reducing costs, leaving no polluting residues, and easily providing nutrients to soil and plants. The research successfully studied the process for preparing and producing organic nanophosphate fertilizer from peat and animal bones. A homogeneous and stable nano-hydroxylapatite fertilizer suspension consisting of chitosan-stabilized hydroxyapatite nanoparticles dissolved in water and humic substances extracted from peat was made. This fertilizer significantly increased the photochemical process, resulting in improved crop quality (melon model) in terms of vitamin C and sugar compared to the control sample of melon.
The Council highly appreciated the effectiveness of the topic as well as the required contents to perform the S&T tasks. |
As a result, the project team successfully applied the model of using organic nano phosphate fertilizer for melon and peanut plants according to VietGAP standards in Vinh Loc and Dan Dien communes. The result of melon yield increased by 22.2% compared to the control model, better quality, economic efficiency reached over 15%. The result of peanut yield increased by 22% compared to the control. The economic efficiency of using organic nano phosphate fertilizer for peanut cultivation was 20% higher than the control.
In addition to some comments suggesting revisions to complete the project results report from the reviewers, the project was highly appreciated by the council for its scientific significance and practical value. Many comments suggested that it is necessary to transfer the project's research results to businesses to complete the process of commercializing research products, and soon apply research results to practice, bringing practical benefits to the economy, the environment and society.
NOSTALGIA
Source: https://huengaynay.vn/kinh-te/khoa-hoc-cong-nghe/san-xuat-phan-lan-nano-tu-than-bun-xuong-dong-vat-va-ung-dung-san-xuat-nong-nghiep-tot-157849.html




![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives US Ambassador to Vietnam Marc Knapper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/c8fd0761aa184da7814aee57d87c49b3)
![[Photo] Many streets in Hanoi were flooded due to the effects of storm Bualoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/18b658aa0fa2495c927ade4bbe0096df)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the ceremony to celebrate the 80th anniversary of the post and telecommunications sector and the 66th anniversary of the science and technology sector.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/8e86b39b8fe44121a2b14a031f4cef46)


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the 8th Conference of full-time National Assembly deputies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/2c21459bc38d44ffaacd679ab9a0477c)































































































Comment (0)