The Confrontation of Two Hybrid Philosophies
The C-segment sedan market in Vietnam is witnessing an interesting competition between two different approaches to hybrid technology. On one side is the Honda Civic e:HEV RS, representing the self-charging hybrid (HEV) philosophy that prioritizes a sporty driving experience. On the other side is the BYD Seal 5, the first plug-in hybrid (PHEV) in the segment, emphasizing pure electric operation and cost optimization. This confrontation is not only about parameters, but also about the difference in product development thinking.

Design: Japanese Sports and Ocean Inspiration
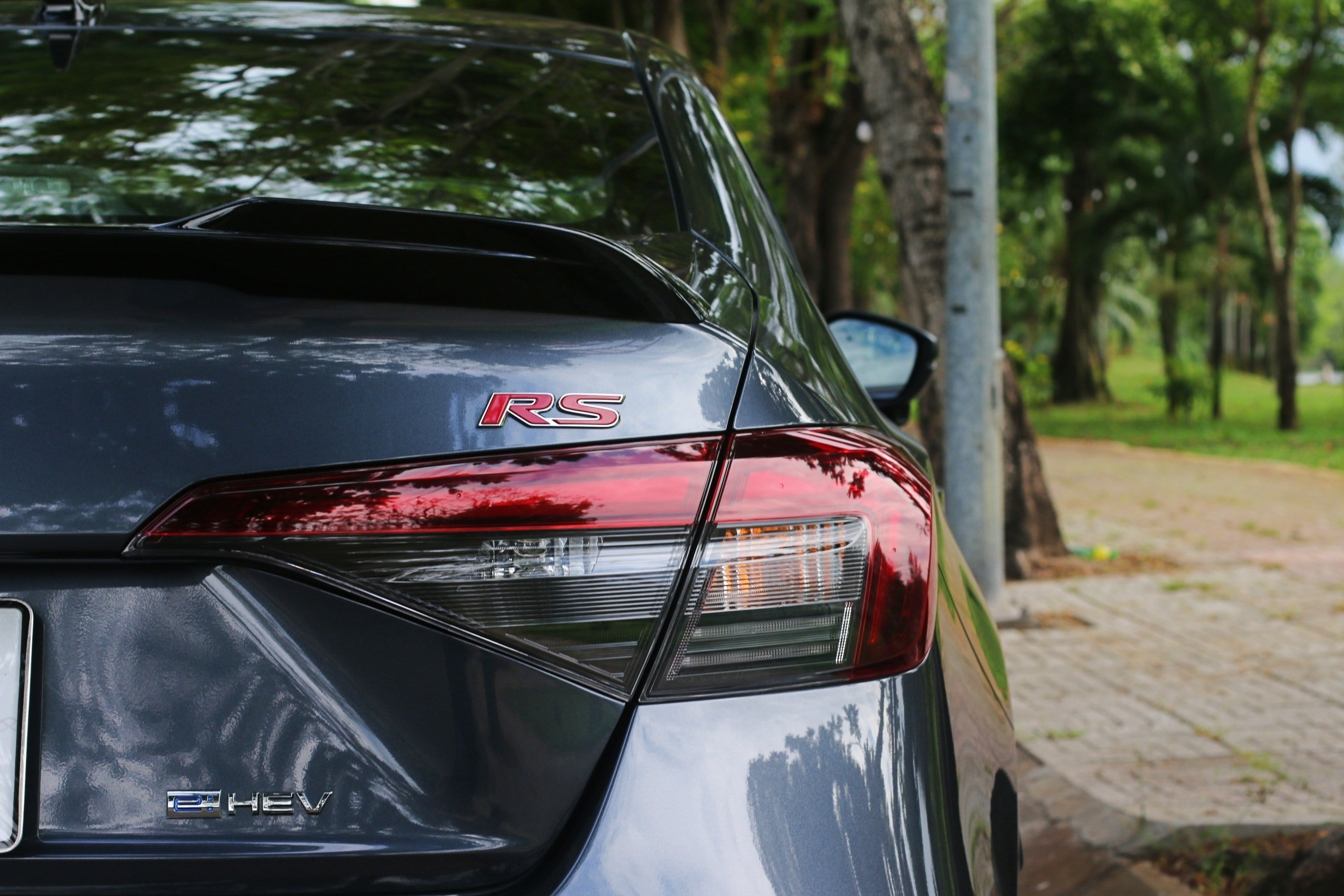
The Honda Civic e:HEV RS maintains the sporty DNA that has made the model famous. With dimensions of 4,681 x 1,802 x 1,415 mm and a wheelbase of 2,735 mm, the car has a long and dynamic body. Details such as the black-painted grille, red RS logo, and large air vents in the front bumper all emphasize aerodynamics and performance. In contrast, the BYD Seal 5 has a softer and more modern style, with overall dimensions of 4,780 x 1,837 x 1,495 mm. This model is slightly longer and wider, but the wheelbase is shorter at 2,718 mm. The rounded lines, chrome-trimmed grille, and slim LED lights give it an elegant, technological look.
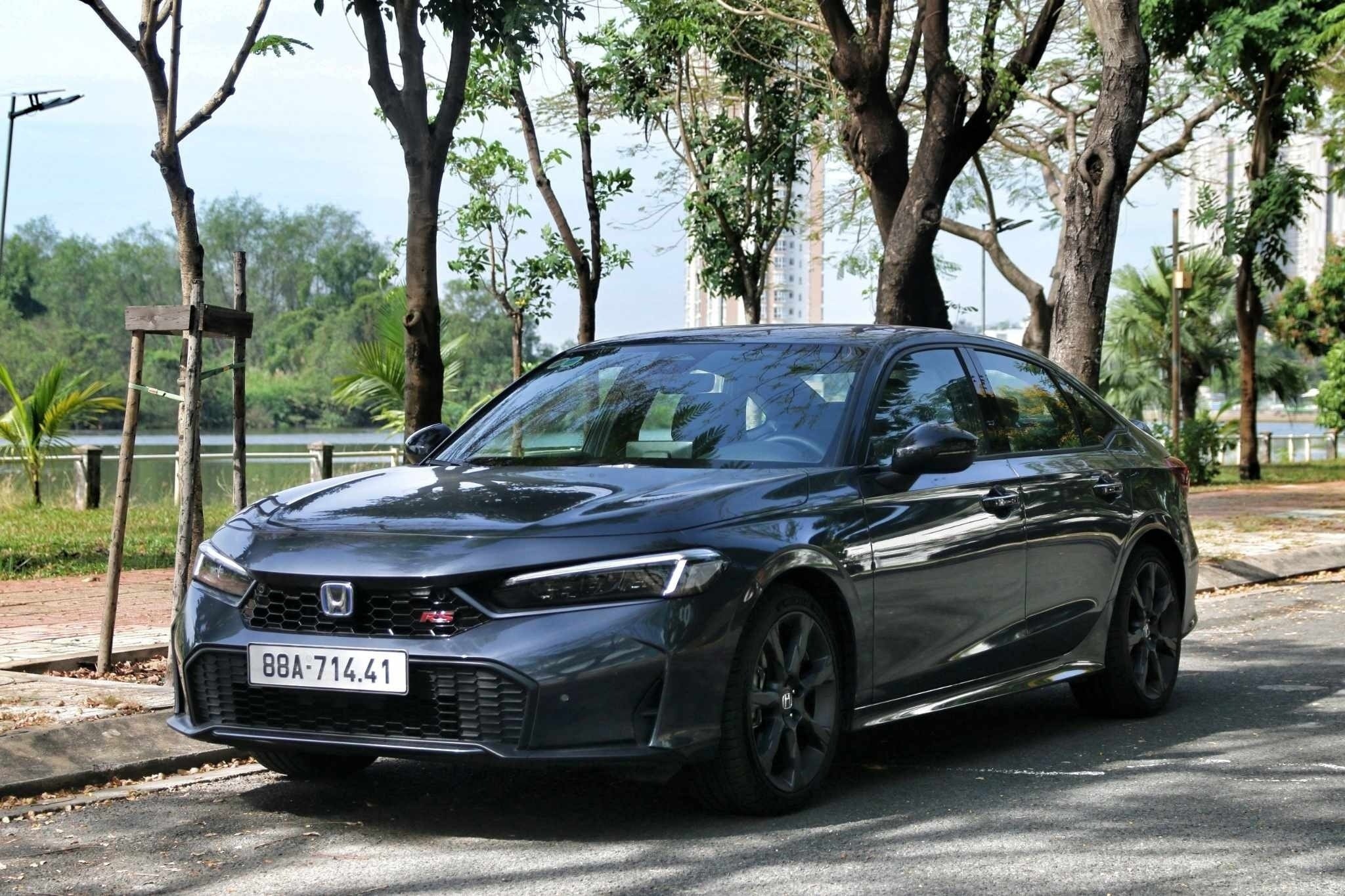
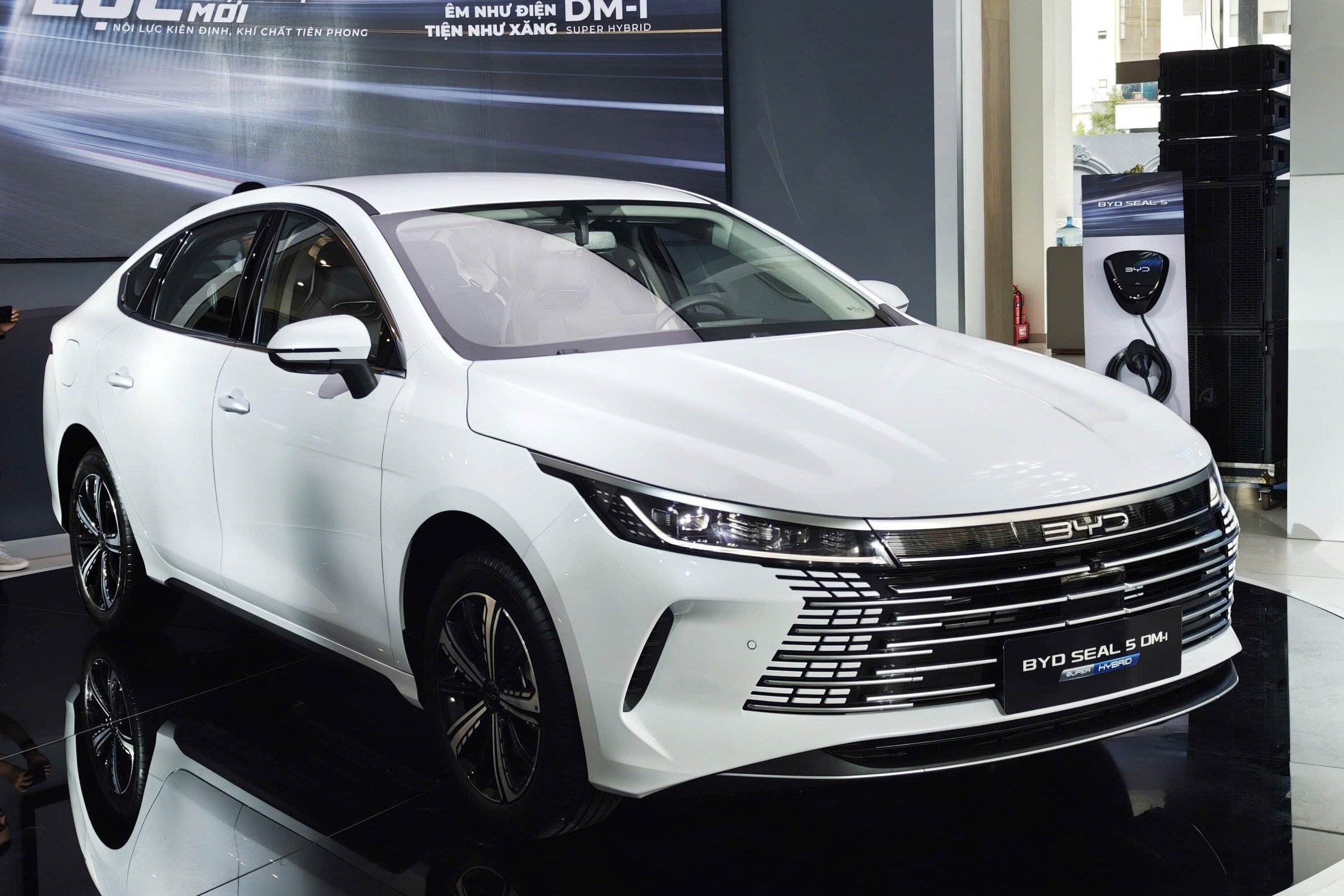


The differences are also evident in the suspension and wheels. The Civic RS is equipped with 18-inch wheels and a multi-link rear suspension, a configuration that is superior in terms of grip and stability when cornering. Meanwhile, the Seal 5 uses 17-inch wheels and a torsion beam rear suspension, a more popular choice in the segment to optimize space and cost.
Interior space: Between tradition and technology
Inside, the two models continue to show the contrast. The Civic e:HEV RS's cockpit is designed in a cockpit style, orienting every detail towards the driver. Red stitching on the seats and dashboard reinforces the sporty feel. In contrast, the BYD Seal 5 pursues a minimalist style, focusing on technology. Most of the physical buttons are removed and integrated into the large rotating center screen. An electronic handbrake replaces the traditional mechanical handbrake, creating an airy space for the center console.
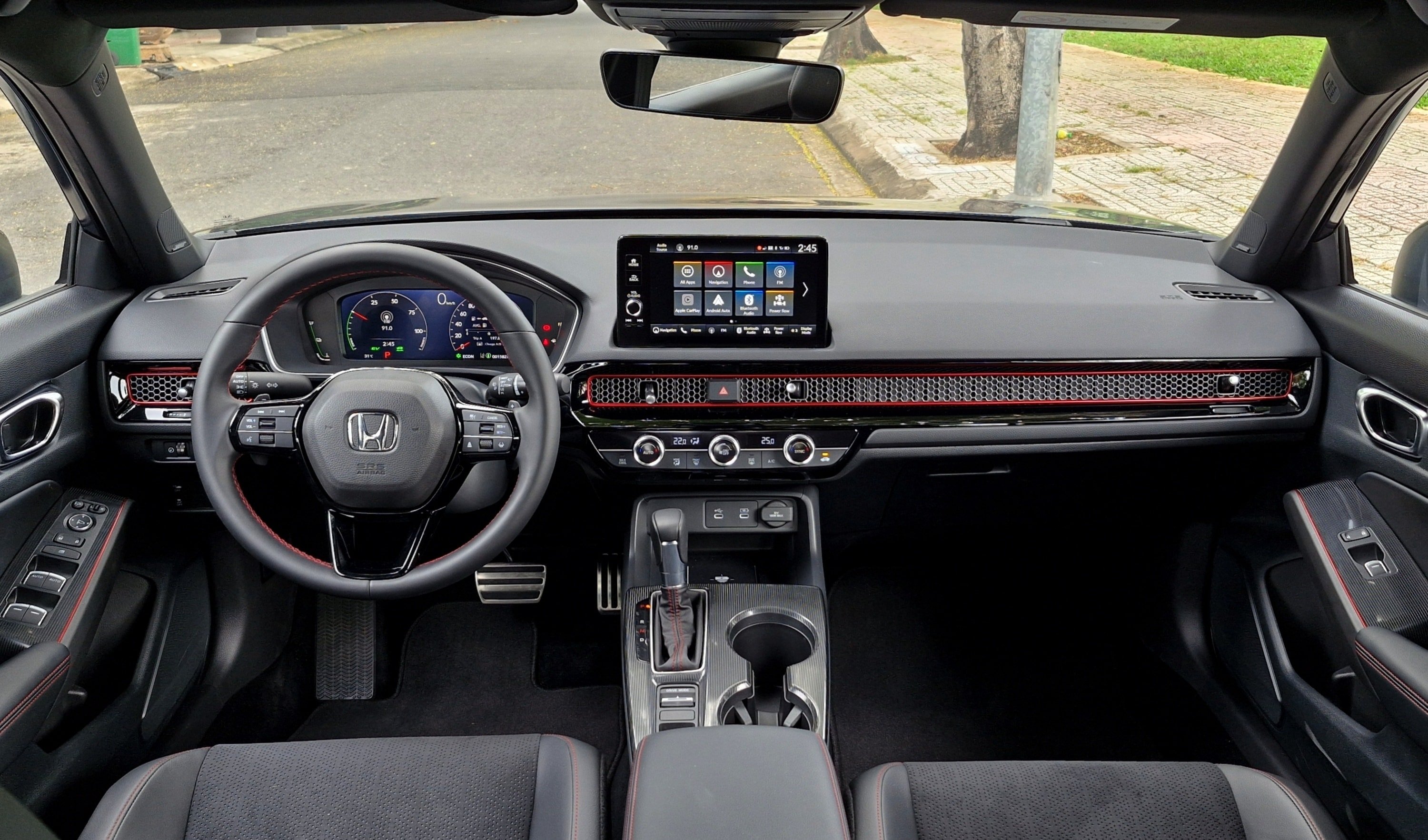

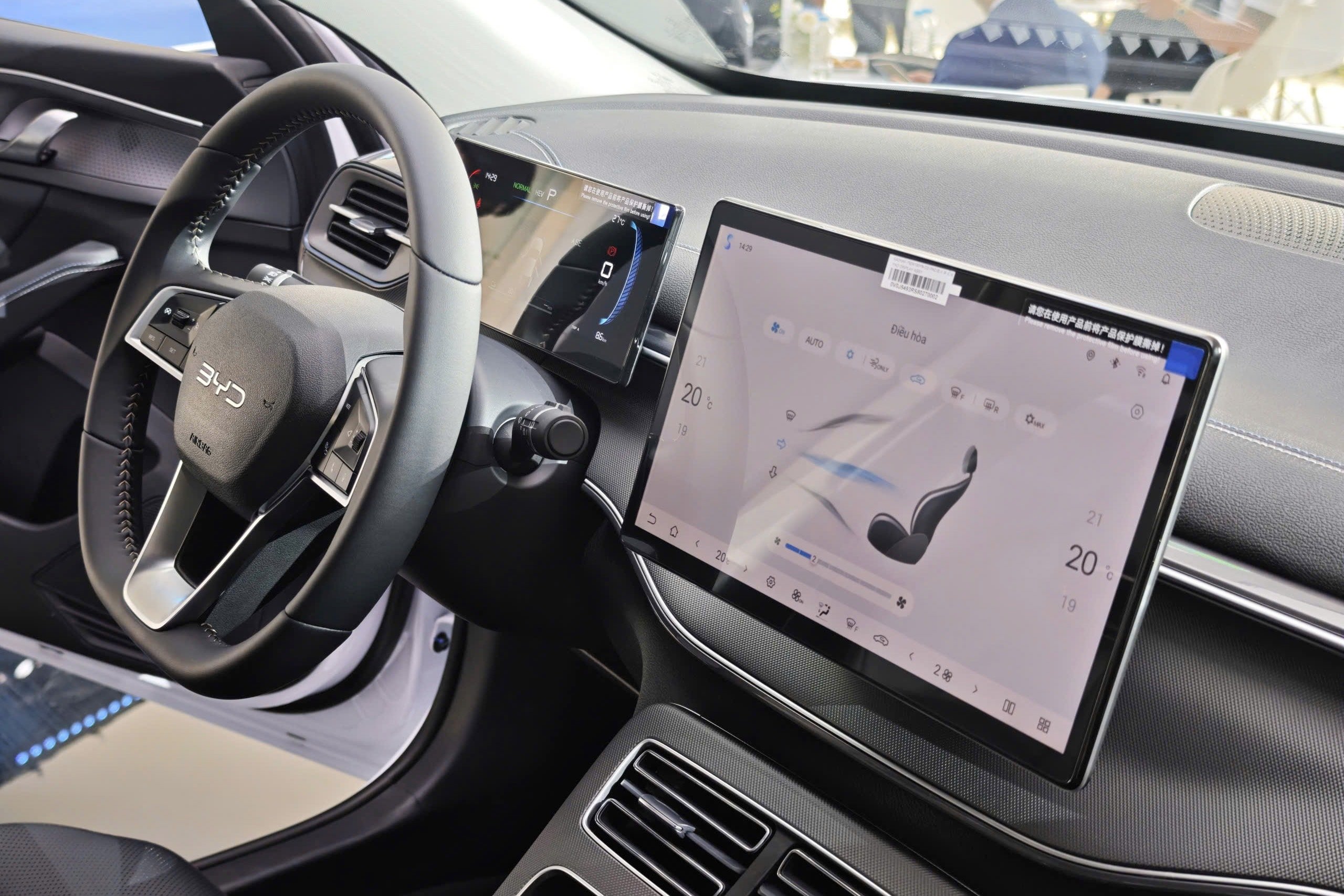
In terms of equipment, the Seal 5 is superior with an electric passenger seat and an integrated smart ecosystem. However, a downside of this PHEV model is the rear seat space. Because the battery pack is placed under the floor, the legroom is raised, which can cause fatigue for passengers on long journeys, despite the car's larger overall dimensions.
Two distinct electrochemical solutions
This is the most core difference between the two models. The Honda Civic e:HEV RS uses a self-charging hybrid system, combining a 2.0L gasoline engine and an electric motor, for a total output of nearly 200 horsepower and 315 Nm of torque. This system operates completely automatically, charging the battery itself through regenerative braking and does not require the user to plug in the charger. The driving experience still retains the characteristics of a gasoline car such as engine sound and sharp throttle response, but is supplemented by an electric motor for smooth acceleration and fuel economy. The published combined consumption is 4.56 liters / 100 km.

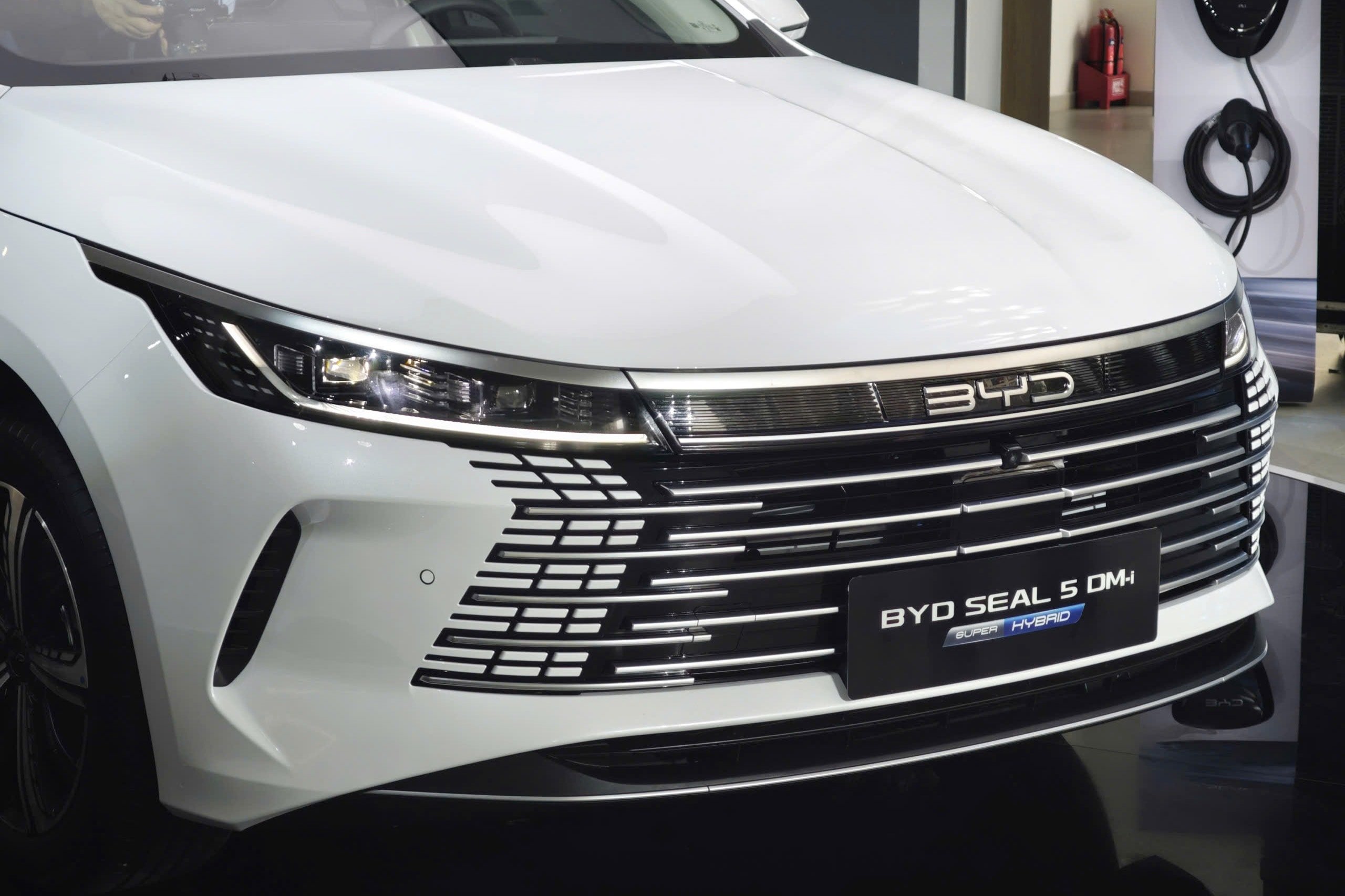
The BYD Seal 5 uses PHEV technology with the DM-i Super Hybrid platform. The vehicle combines a 1.5L turbocharged gasoline engine and an electric motor, producing a combined output of about 209 horsepower and 300 Nm of torque. The strength of the Seal 5 is its large battery pack that allows the vehicle to run purely on electricity for up to 120-180 km after each full charge. This means that users can travel daily in the city without using almost a drop of gasoline. The average fuel consumption is only 3.8 liters / 100 km, and the vehicle can travel more than 1,700 km with a full tank of gas and battery. In addition, the vehicle also has a V2L reverse charging feature, turning it into a mobile generator.

Selling price and market positioning
The difference in product philosophy is clearly reflected in the selling price. The Honda Civic e:HEV RS has a listed price of 999 million VND, targeting customers who are loyal to the Japanese brand, love the feeling of driving and want a simple "green" solution that does not change their usage habits. The value of the Civic lies in its durability, ability to retain value and a proven experience.
Meanwhile, the BYD Seal 5 is priced at 696 million VND, an extremely competitive figure. This price puts the Seal 5 in the position of a challenger, offering an advanced PHEV technology package, outstanding operating cost savings and rich equipment. This is an attractive choice for users who prioritize economic factors, technology and are ready to experience a new brand.
Conclusion: What are the options for Vietnamese users?
Both the Honda Civic e:HEV RS and the BYD Seal 5 are quality products, contributing to diversifying green car choices in Vietnam. The choice of which model depends entirely on the user's priorities. If you are looking for a sedan with a sporty driving feel, from a reputable brand and do not want to change your gasoline-fueled driving habits, the Civic e:HEV RS is a worthy answer. On the contrary, if you are a technology lover, want to maximize fuel economy, have the conditions to charge your car at home and are attracted by a competitive price, the BYD Seal 5 is an option that is hard to ignore.
Basic specifications comparison table
| Parameter | Honda Civic e:HEV RS | BYD Seal 5 |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission system | Self-charging hybrid (HEV) | Plug-in hybrid (PHEV) |
| Engine | 2.0L Gasoline + Electric Motor | 1.5L Turbo Gasoline + Electric Motor |
| Capacity | ~200 horsepower | ~209 horsepower |
| Torque | 315 Nm | 300 Nm |
| Rear suspension | Multipoint link | Torsion beam |
| Fuel consumption (combined) | 4.56 liters/100 km | 3.8 liters/100 km |
| Selling price (VND) | 999,000,000 | 696,000,000 |
Source: https://baonghean.vn/honda-civic-e-hev-rs-va-byd-seal-5-cuoc-doi-dau-hybrid-10308585.html


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with Speaker of the Hungarian National Assembly Kover Laszlo](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/20/1760970413415_dsc-8111-jpg.webp)


![[Photo] Da Nang residents "hunt for photos" of big waves at the mouth of the Han River](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/21/1761043632309_ndo_br_11-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh received Mr. Yamamoto Ichita, Governor of Gunma Province (Japan)](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/21/1761032833411_dsc-8867-jpg.webp)






































































































Comment (0)