 |
| Mr. Paulo Medas, Head of the Vietnam Macroeconomic Consultation and Monitoring Delegation of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) |
The financial sector is playing a key role in promoting the development of Vietnam’s economy. How do you assess the importance of this sector in building fiscal policy and macroeconomic management in Vietnam?
Vietnam’s economic performance over the past two decades has been impressive. Average economic growth has been around 6.5% per year, higher than many countries in the world ; GDP per capita has increased from around 500 USD in 2000 to around 4,700 USD in 2024; poverty rates have fallen sharply.
The financial sector plays an important role in supporting Vietnam’s economic development and public finances. Steady credit growth has contributed to the development of the private sector, including supporting capital investment. Financial inclusion has also improved, with the proportion of adults with bank accounts increasing from around 20% in 2011 to around 70% in 2024. Banks, along with Vietnam Social Security, are also the main source of funding for the Government ’s budget.
When considering the link between fiscal policy and the financial sector, there are several aspects that need to be kept in mind. The financial system can be an important source of finance for the government, but care must be taken to avoid negative impacts on the private sector. For example, if the government borrows on a large scale, private businesses may face higher borrowing costs. In some countries with very high public debt, the government borrowing heavily from banks can increase the risks for those banks. This is one of the reasons why governments need to act cautiously, as Vietnam has done in recent years with prudent fiscal policy and low public debt.
The government has an important role to play in developing banks and promoting efficient, well-regulated capital markets to support economic growth. Healthy banks are more sustainable sources of funding and are more resilient to shocks. This is why the IMF has called for more capital for banks. Outstanding credit of banks in Vietnam is also currently high, at over 130% of GDP, much higher than in other developing economies. A major advantage of modern capital markets is that they help businesses easily access a variety of financial sources, avoiding over-reliance on the banking system.
Vietnam is restructuring its administrative apparatus and reforming the financial sector. In your opinion, which areas should be prioritized for reform and why?
There are many areas of reform that can help make the public sector more efficient. The aim is to improve planning, budgeting and policy implementation processes to achieve the stated objectives, namely promoting sustainable growth, providing quality public services (e.g., health and education) and developing a good social security system.
The Vietnamese government has initiated a major institutional reform to streamline the organizational structure. This is a very welcome step. Efforts to digitize the government and improve governance and transparency are also necessary. These efforts will benefit the entire economy, helping to reduce costs for businesses, improve the business environment and promote investment, while also helping to improve the quality of public services for citizens.
There is growing consensus around the world that governments need to strengthen their medium-term planning capabilities. Effective medium-term fiscal planning, combined with a modern budgeting process, is an effective tool to improve fiscal management. Annual budgeting with a medium-term vision helps increase the credibility of fiscal policy, limit excessive spending, and promote transparency and better risk management. This is increasingly important in the context that Vietnam will face great spending pressure to achieve development goals, address population aging, natural disaster risks and climate change.
A good fiscal strategy should include: a credible medium-term fiscal plan, with realistic macroeconomic forecasts (including revenue and expenditure), comprehensive risk assessment, and high-quality fiscal reporting and data.
Another important area is to improve the social security system and strengthen institutional capacity to respond to shocks. The revised Law on Social Insurance is a major step forward in expanding coverage and improving the level of security, but further efforts are needed to ensure that support measures are targeted, timely and effective. At the same time, the long-term sustainability of the pension system needs to be strengthened as the population begins to age.
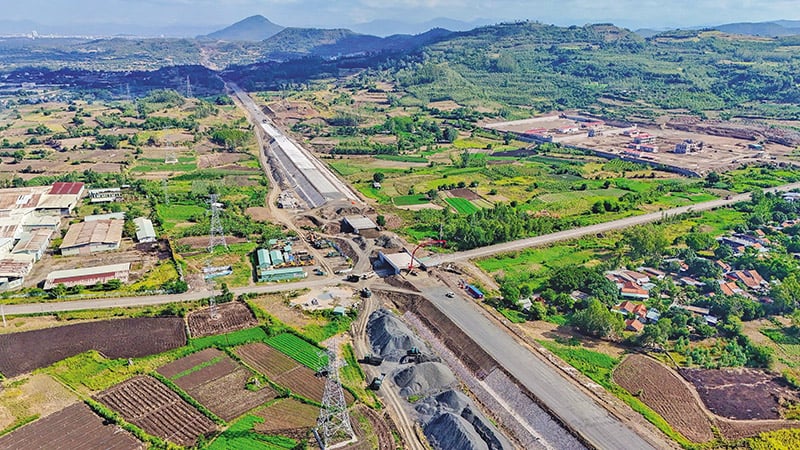 |
| Promoting public investment projects will contribute to boosting growth. In photo: Construction of the North-South Expressway, Eastern section, Chi Thanh - Van Phong section |
Regarding the budget issue, in the context of huge public investment needs to serve the people and businesses, how can Vietnam restructure budget revenue and expenditure? What recommendations does the IMF have, sir?
Vietnam has relatively low levels of public debt, which gives it more flexibility than many other countries struggling with high debt in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic. Global public debt is currently above 90% of GDP, while Vietnam's public debt is just over 30% of GDP.
However, spending pressures will increase over time due to planned expansion of public investment, the need to improve public services (e.g., improving public services in the health sector) and the impact of population aging (e.g., pension costs). Although Vietnam has room to borrow more, caution is needed to ensure public finances are sustainable.
 Investment in large-scale projects should not depend solely on increasing public debt. Funding strategies should be designed in a balanced manner, combining additional borrowing and increased mobilization of internal revenue sources. At the same time, a stable, transparent and reliable legal framework should be created to attract private sector participation.
Investment in large-scale projects should not depend solely on increasing public debt. Funding strategies should be designed in a balanced manner, combining additional borrowing and increased mobilization of internal revenue sources. At the same time, a stable, transparent and reliable legal framework should be created to attract private sector participation. 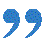
Vietnam could consider increasing its budget revenue, as its budget revenue is lower than that of other emerging and developed economies. Reforms could include: tax reduction, tax exemption, rationalization of tax incentives, expansion of the value-added tax base, etc. In addition, tax administration should also be improved to increase tax collection efficiency.
In addition, it is necessary to prioritize efficient and high-quality spending; prioritize investment; comprehensively review public spending to identify inefficiencies. A thorough cost-benefit analysis of public investment projects will help select and prioritize projects with the highest socio-economic benefits. Subsidy and support programs that are not properly targeted should be phased out.
Vietnam’s economy is undergoing a major policy shift towards supporting businesses and people. Could you share some international experiences in ensuring financial security while pursuing high economic growth?
Vietnam has announced plans to implement large-scale infrastructure projects as part of its reform program to boost economic growth. The design and implementation of these projects will be crucial to delivering the desired economic benefits while ensuring public debt sustainability and financial stability. Implementing large-scale infrastructure projects alongside comprehensive reforms to improve productivity will increase the likelihood of success.
International experience shows that expanding public investment can contribute to promoting growth, but the implementation process always comes with many challenges. Since these are very large-scale projects, they need to be implemented carefully, avoiding putting excessive pressure on the economy (for example, increasing inflation). This requires detailed planning and strengthening public investment management capacity, including selecting projects based on clear, transparent criteria and conducting rigorous cost-benefit analysis.
Investment in large-scale projects should not depend solely on increasing public debt. The capital mobilization strategy needs to be designed in a balanced manner, combining additional borrowing and increasing the mobilization of internal revenue sources. At the same time, it is necessary to create a stable, transparent and reliable legal framework to attract the participation of the private sector, for example, in the fields of renewable energy, transportation, etc. Investment forms under the public-private partnership (PPP) method can play an important role as directed by the Government, but need to be implemented cautiously. This includes building a modern PPP legal framework, organizing competitive bidding, reasonable risk sharing between the public and private sectors, ensuring transparency throughout the process.
Efforts to develop capital and bond markets will also be key in the context of huge financial needs, while avoiding excessive pressure on the banking system. Reforms to the government bond market are essential to promote the formation of market-based interest rates and diversify investor portfolios. Institutional capacity in public debt management also needs to be strengthened. These efforts will contribute to attracting more investors while ensuring funding for both the public and private sectors.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/linh-vuc-tai-chinh-dong-vai-tro-quan-trong-trong-phat-tien-kinh-te-d373211.html




![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Chairman of the State Duma of the Russian Federation Vyacheslav Volodin](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/3814a68959e848f586178624b6bd66e5)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh meets with Chairman of the State Duma of the Russian Federation Vyacheslav Volodin](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/08ca17cb0c46432dbdb94f9eaf73b47a)






















































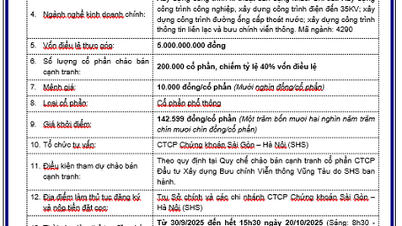
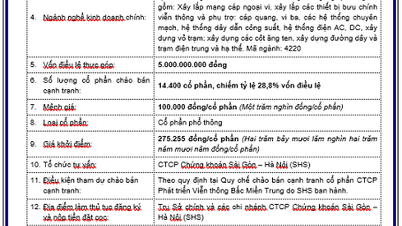

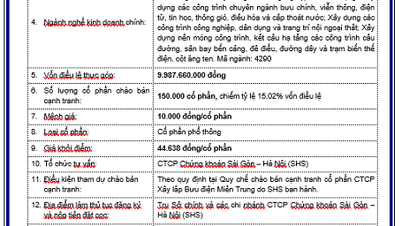


































Comment (0)