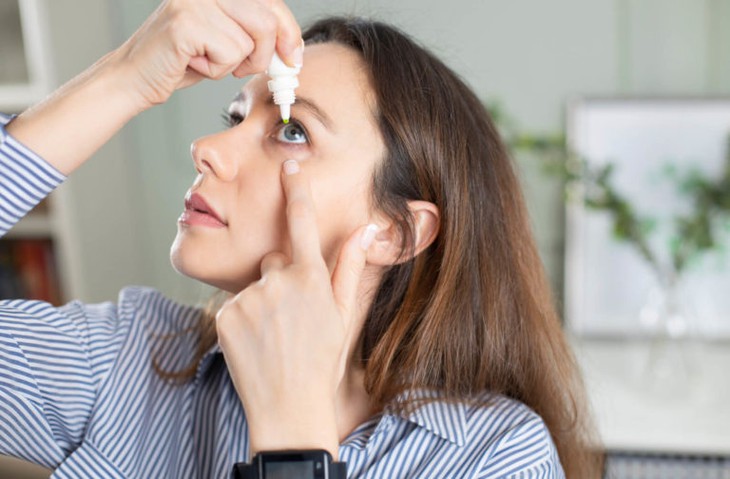

Hundreds of millions of people around the world are facing presbyopia, when the eyes have difficulty focusing on close-up vision, especially when reading books, newspapers or using the phone - Photo: queenswayoptometric
Presbyopia is a condition in which the ability to focus on objects close to the eyes gradually decreases, usually occurring in people aged 40 and over. Currently, the most common solution for people with presbyopia is wearing reading glasses or surgery, but many people find it inconvenient to wear glasses all the time and not everyone has the conditions or desire to have surgery.
A new study presented at the European Society of Cataract and Refractive Surgery (ESCRS) conference in Copenhagen has shown that using eye drops twice daily can significantly improve vision and the effect remains stable over two years.
The trial was conducted on 766 patients in Argentina, each receiving eye drops in the morning and then about 6 hours later. The patients were divided into three groups, with solutions containing the same amount of diclofenac (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug - NSAID) but different concentrations of pilocarpine: 1%, 2% and 3%.
The results showed that in the 1% group of 148 people, most of them could read at least two more lines on the eye chart. In the 2% group of 248 people, 69% could read three or more lines. Meanwhile, in the 3% group of 370 people, 84% achieved this level of improvement.
Just one hour after the first dose, patients had an average improvement of 3.45 Jaeger lines, the standard measure of near vision, said Dr. Giovanna Benozzi, director of the Center for Advanced Presbyopia Research in Buenos Aires.
According to the doctor, the results showed that all three concentrations provided significant and sustained improvement, while also helping to increase the ability to focus at a variety of distances. Notably, 99% of patients in the 1% group achieved optimal near vision, able to read at least two additional lines.
These eye drops combine pilocarpine, an active ingredient that constricts the pupil and adjusts the eye muscle to change the curvature of the lens, allowing the eye to focus at different distances, with diclofenac, an anti-inflammatory that helps maintain the treatment's effectiveness. Some common side effects include temporary blurred vision, discomfort when instilled, and mild headache.
Experts say this is a big step forward in the treatment of presbyopia, but larger, longer-term studies on different patient groups are still needed to confirm safety and effectiveness.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/thuoc-nho-mat-moi-thay-the-kinh-lao-hieu-qua-toi-2-nam-20250917082019221.htm



![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the 80th Anniversary of the Traditional Day of Vietnamese Lawyers](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/09/1760026998213_ndo_br_1-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs a meeting of the Government Standing Committee on overcoming the consequences of natural disasters after storm No. 11](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/09/1759997894015_dsc-0591-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam visits Kieng Sang Kindergarten and the classroom named after Uncle Ho](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/09/1760023999336_vna-potal-tong-bi-thu-to-lam-tham-truong-mau-giao-kieng-sang-va-lop-hoc-mang-ten-bac-ho-8328675-277-jpg.webp)





























































































Comment (0)