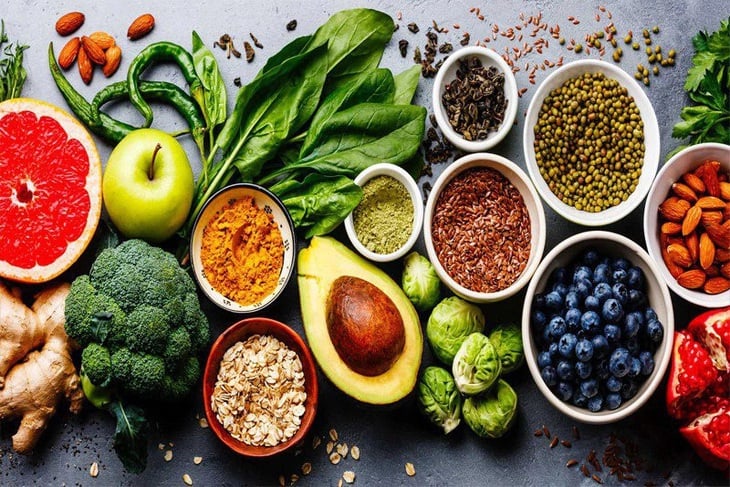

Vegetables, fruits, and seeds - daily sources of fiber - Illustration photo
Recommended Daily Intake of Fiber
The recommended intake of fiber for adults is 21-38g, according to the Institute of Medicine (IOM).
Age | Female | Male |
1-3 | 14g | 14g |
4-8 | 17g | 20g |
9-13 | 22g | 25g |
14-18 | 25g | 31g |
19-30 | 28g | 34g |
31-50 | 25g | 31g |
51 and up | 22g | 28g |
There is also a Daily Value (DV) for fiber, which represents the daily fiber intake based on a 2,000 calorie diet. The DV for fiber is 28g per day for adults and children over 4 years of age.
To easily visualize the amount of fiber in some foods, experts also calculated and said that 100g of guava contains 5g of fiber; 3 fresh apricots contain 1g of fiber and 5 dried apricots contain 2.9g of fiber;
100g of apple with skin contains 2.4g of fiber; half a grapefruit contains 6.1g of fiber; 1 orange contains 5g of fiber; 100g of strawberry contains 2g of fiber; 2 dried figs contain 3.7g of fiber; 1 cantaloupe contains 1.3g of fiber; 3 pieces of dried peach contain 3.2g of fiber; 100g of banana contains 2.6g of fiber...
Foods rich in fiber
Fiber is found in plant foods such as vegetables, fruits, and nuts. Here are some good sources of fiber in your diet:
- Vegetables: Sweet potatoes, peas, collard greens, amaranth
- Fruits: Avocado, raspberry, guava, pear
- Seeds: Chia seeds, sunflower seeds
Health benefits of fiber
There are two main types of fiber: soluble fiber and insoluble fiber. Soluble fiber dissolves in water, passes through the small intestine, and is broken down by bacteria in the colon (large intestine). Insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and remains intact as it moves through the intestines.
Benefits of soluble fiber:
- Strengthening the intestinal mucosa
- Improve immune function
- Absorbs water into the stool, making it soft and easy to pass.
- Reduce high blood pressure
Key benefits of insoluble fiber: Promotes comfortable and regular bowel movements by increasing stool bulk.
Benefits of a high fiber diet
- Reduce your risk of several common diseases, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and colon cancer
- Regulate appetite
- Promote weight loss and reduce the risk of obesity
What do you do if you need to increase your fiber intake?
- Eat plenty of whole foods of plant origin: this can include fruits, vegetables, beans, nuts...
- Taking fiber supplements: While fiber supplements may benefit some people, they are not appropriate or safe for everyone. Talk to your doctor before starting.
- Increase your overall water intake: Because fiber binds water in your digestive tract, you need to drink enough of the recommended amount of water.
- Increase fiber intake slowly: Increasing fiber intake slowly over time can help your digestive system adjust to the higher fiber intake and reduce the risk of digestive symptoms such as gas, bloating, and diarrhea. These symptoms can occur when switching to a higher fiber diet too quickly.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/ban-can-bao-nhieu-chat-xo-moi-ngay-20251005080457777.htm



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh launched a peak emulation campaign to achieve achievements in celebration of the 14th National Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/8869ec5cdbc740f58fbf2ae73f065076)

![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's online conference with localities](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/264793cfb4404c63a701d235ff43e1bd)


















































































Comment (0)