Genital warts is the general name for many diseases, including genital warts, but it is still possible to distinguish genital warts from benign genital warts.
Dr. Vo Thi Tuong Duy, Dermatology - Cosmetic Dermatology specialist, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that genital warts are nodules or bumps that grow in the genital area, related to many different diseases.
Risk factors for genital warts include: Accumulation of harmful bacteria due to poor hygiene of the genital area; unsafe sex, sexually transmitted diseases such as Herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HIV/AIDS..., wearing unhygienic underwear, wearing tight clothes, scratching the genital area frequently, accidentally bringing in dirt and bacteria from the outside, using feminine hygiene solutions with inappropriate pH levels.
For the most part, papillomas such as genital warts, molluscum contagiosum, Fordyce spots... are relatively benign, mainly affecting the patient's aesthetics and psychology. However, with viral papillomas such as genital warts, molluscum contagiosum... patients should see a doctor for early treatment. It is possible to distinguish the types of papillomas by observing the manifestations on the skin.
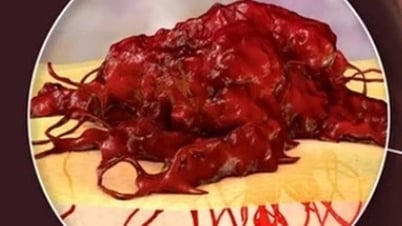
Benign genital warts are pinkish-white in color, not clustered together but are discrete, do not have a common stalk and do not contain pus. Genital warts grow very slowly, almost do not increase in size over time. In some cases, warts can grow on the tongue but this is very rare.
Initially, genital warts are papules that grow individually, then develop into clusters, resembling cauliflower or cockscombs, so they are called genital warts. Genital warts are light pink in color, protruding above the skin surface, increasing in size and number over time. In addition to growing on the genitals, genital warts also appear on the tongue, mouth, anus and are easily transmitted through sexual intercourse, from mother to child, and contact with open wounds.

Unsafe sex is the cause of genital warts. Photo: Freepik
Dr. Vo Thi Tuong Duy said that to diagnose genital warts, doctors examine with the naked eye, ask about the symptoms encountered, review living habits and sexual life. Blood tests help determine the cause of genital warts or associated diseases (if any). A part of the wart can be taken for biopsy, helping to determine whether the patient has benign or malignant genital warts, and what causes the disease.
Because the external manifestations are quite similar, benign genital warts are easily confused with warts caused by viruses. Therefore, when detecting abnormal warts on the genitals, patients should immediately go to the hospital for Dermatologists - Dermatologists to diagnose and develop a timely treatment regimen.
Phuong Nga
Source link



![[Photo] Solemn opening of the 12th Military Party Congress for the 2025-2030 term](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/2cd383b3130d41a1a4b5ace0d5eb989d)
![[Photo] The 1st Congress of Phu Tho Provincial Party Committee, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/1507da06216649bba8a1ce6251816820)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam, Secretary of the Central Military Commission attends the 12th Party Congress of the Army](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/9b63aaa37ddb472ead84e3870a8ae825)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives President of the Cuban National Assembly Esteban Lazo Hernandez](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/4d38932911c24f6ea1936252bd5427fa)
![[Photo] Panorama of the cable-stayed bridge, the final bottleneck of the Ben Luc-Long Thanh expressway](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/391fdf21025541d6b2f092e49a17243f)


























































































Comment (0)