Specialist Doctor 2 Huynh Tan Vu, Day Treatment Unit, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that in some cases, food poisoning may be considered, when There are unusual symptoms related to eating or drinking certain foods; the food just eaten or drunk has a strange taste, is spoiled, or is past its expiration date...
"Depending on the cause of food poisoning and the type of toxin, symptoms of poisoning can occur immediately or many hours later, ranging from as little as 30 minutes to as long as 8 weeks. Common symptoms and manifestations of food poisoning include abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, mild fever, loss of appetite, fatigue and lack of energy, muscle pain, headache, chills...", Dr. Vu shared.
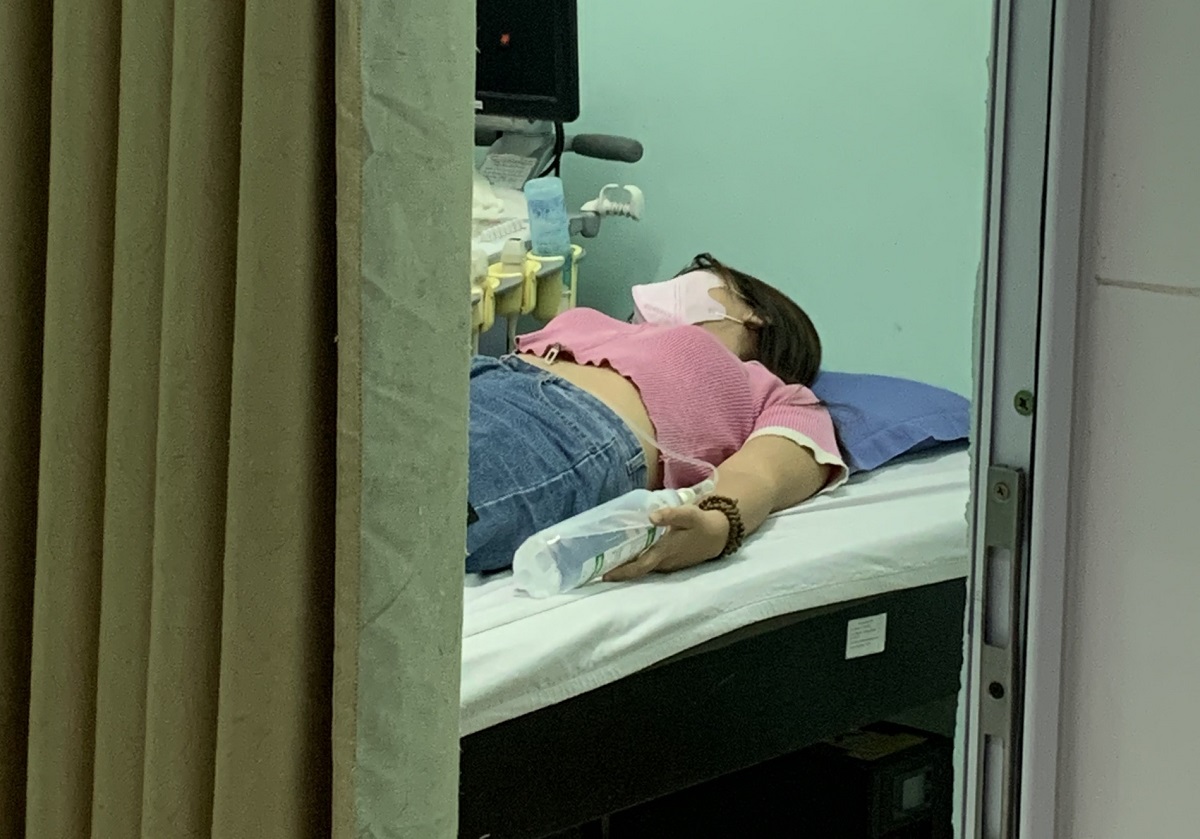
Food poisoning patients are given IV fluids immediately after being taken to a medical facility.
The disease is usually not serious, most patients can feel better after a few days. However, in cases of food poisoning with the following severe symptoms, you need to go to a medical facility for immediate treatment to avoid life-threatening: Diarrhea lasting more than 3 days, severe abdominal pain; frequent vomiting, vomiting blood or bloody stools, bloody urine; fever higher than 38.9 degrees Celsius; signs of severe dehydration (sunken eyes, thirst, dry mouth, little or no urination...); severe weakness, dizziness, lightheadedness, cold hands or feet, rapid or labored breathing, low blood pressure...
How to deal with food poisoning?
For conscious patients: Stop eating or drinking immediately. Use a clean hand to place on the base of the patient's tongue to stimulate the gag reflex. When inducing vomiting, the patient should lie on his side, with his head slightly elevated or sit with his head lower than his chest, so that vomit does not reflux into the lungs.
For unconscious, comatose, or convulsive poisoned patients: Do not induce vomiting because it can easily cause choking or suffocation. Place the patient on a safe side to keep the airway clear, do not inhale phlegm into the lungs. If the patient stops breathing or has a cardiac arrest, perform artificial respiration, call for assistance, and provide emergency care immediately. After first aid, take the patient immediately to a medical facility for appropriate treatment depending on the symptoms. Keep samples of suspected food when suspecting chemicals, natural toxins, or multiple people are affected, to help determine the cause of the poisoning and provide appropriate treatment.
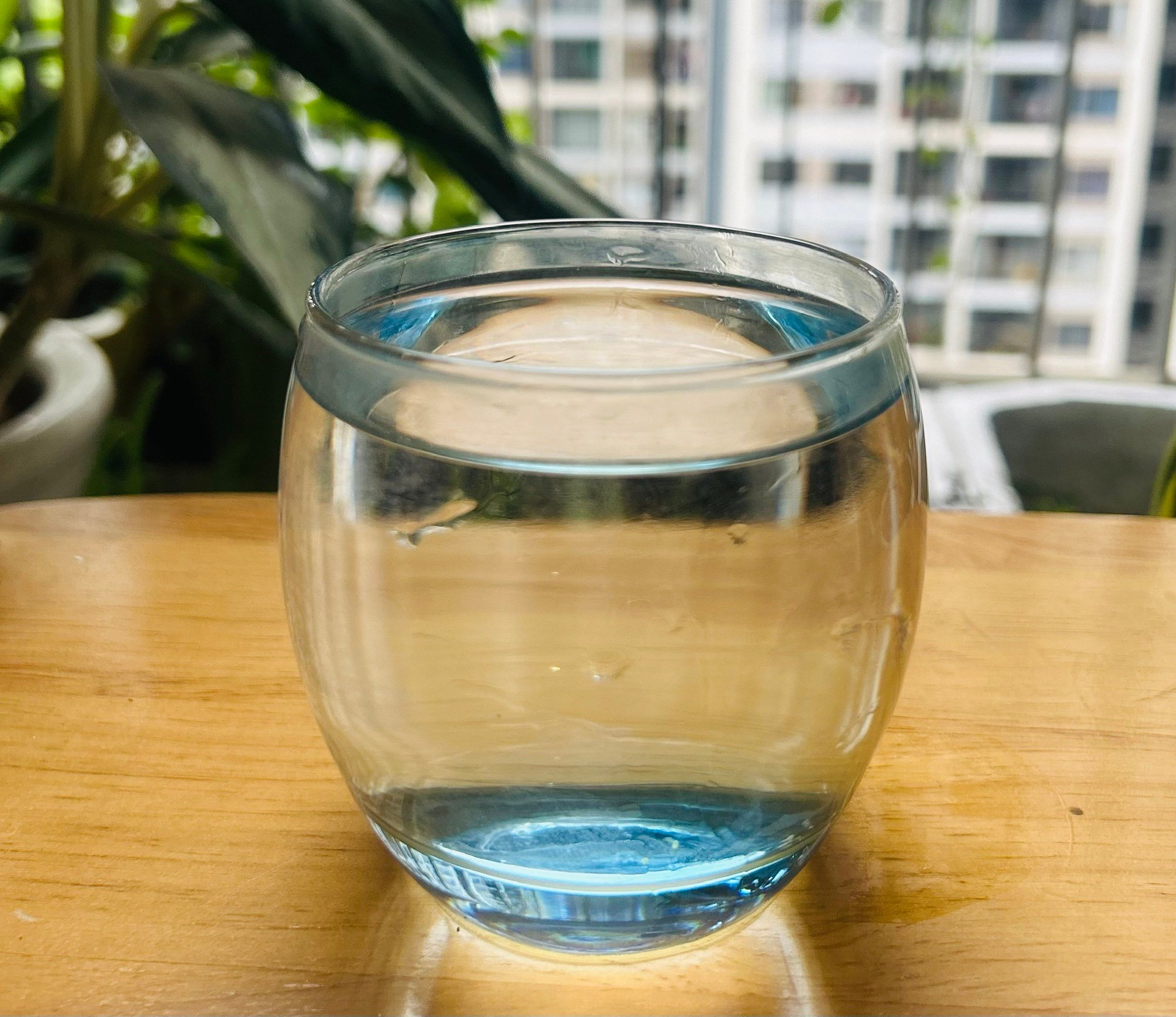

Rehydration for patients after first aid for poisoning
What to eat and drink after first aid?
After vomiting and diarrhea, the body is easily dehydrated, electrolyte loss makes the person tired, so the patient should drink water (drink gradually) and rest. Drink Oresol instead of water, when thirsty, feverish or diarrhea and follow the doctor's instructions.
Eat soft, easily digestible foods to reduce the burden on the stomach and intestines. Supplement foods containing probiotics for the digestive system such as yogurt, digestive enzymes, etc.
Limit sugary drinks, fatty foods, spicy and sour foods... because they can easily cause bloating and flatulence.
Prevent food poisoning
Ensuring food hygiene and safety is the key to preventing food poisoning:
- Choose food that is safe, of clear origin, and within its expiry date.
- Store food properly, whether it is unprocessed (frozen, salted...) or processed (covered, simmered, heated, chilled).
- Maintain hygiene during food preparation and eating. Wash your hands before preparing food and before eating. Clean cooking and eating utensils. Use separate utensils when cooking and preparing food.
- Prepare and process food hygienically and properly. Use clean water. Choose reputable restaurants and be careful when eating at restaurants outside.
- The motto to keep in mind is "eat cooked food, drink boiled water". eat and drink thoroughly cooked food
- When traveling , you should eat moderately to let your body adapt gradually, and should only drink bottled water.
- Additionally, there are several vaccines that can help prevent serious food poisoning. Rotavirus vaccine is given to infants as part of their childhood immunizations. There are also other vaccines that may be recommended before traveling abroad.
Source link




![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the 16th meeting of the National Steering Committee on combating illegal fishing.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/07/1759848378556_dsc-9253-jpg.webp)





























![[Photo] Super harvest moon shines brightly on Mid-Autumn Festival night around the world](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/07/1759816565798_1759814567021-jpg.webp)



































































Comment (0)