New research shows that the increase in greenhouse gases threatens to reduce the number of satellites that can operate in Earth orbit.
According to research published in the journal Nature Sustainability on March 10, “satellite capacity” in low Earth orbit regions, or the maximum number of satellites operating in these areas, could decrease by 50-65% by 2100, due to the impact of greenhouse gases.
“Our behavior toward greenhouse gases on Earth over the past 100 years is affecting how we operate satellites over the next 100 years,” said Richard Linares, associate professor at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the US and lead author of the study, according to The Hill .
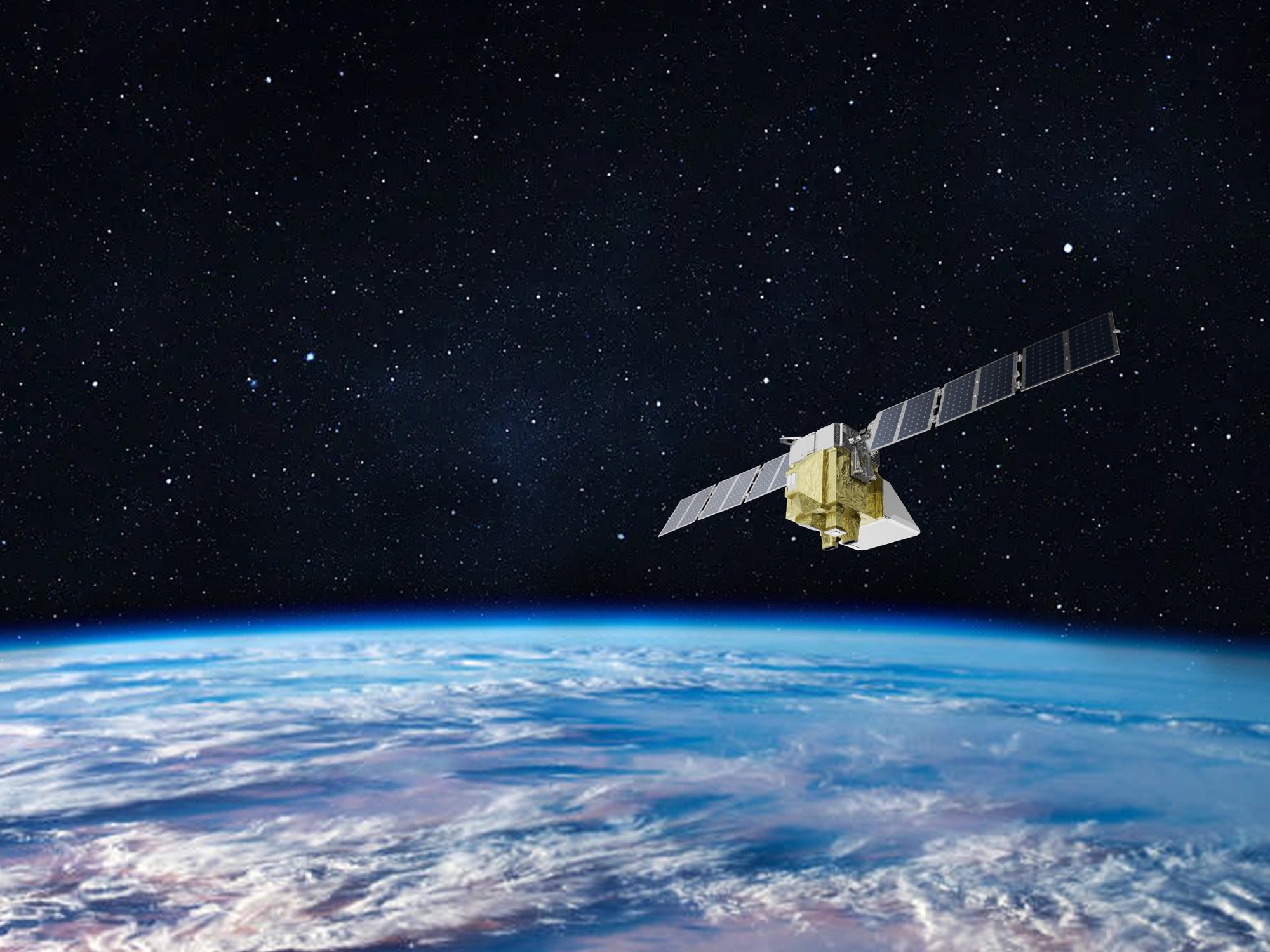

MethaneSat satellite has the function of identifying signs of leaks from oil and gas facilities.
Mr. Linares and his colleagues determined that carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and other greenhouse gases could cause the upper atmosphere to shrink. The researchers found that the contraction of the thermosphere - the layer of the atmosphere where the International Space Station operates - caused a sharp decrease in atmospheric density and caused a spillover effect.
This reduction in density reduces “atmospheric drag.” Atmospheric drag is what pulls old satellites and other debris, also known as “space junk,” down to altitudes where they burn up. With less drag, space junk can linger longer before burning up, polluting low Earth orbit and increasing the risk of collisions with active satellites.
The growing number of satellites, driven by demand for internet and other uses, also poses a risk of collisions and debris that could linger for decades, according to the research team. There are currently more than 10,000 satellites operating in low Earth orbit.
Because of space junk, insurance companies must be cautious.
Scientists analyzed the amount of space debris and the threat of satellite collisions to determine the future capacity of the low Earth orbit region. The study showed that if satellites were launched into orbit beyond their capacity, there would be a risk of uncontrolled instability, and a series of satellite collisions would further narrow the space for satellites to operate safely.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/yeu-to-bat-ngo-de-doa-den-ve-tinh-khong-gian-185250311100233572.htm






![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh launched a peak emulation campaign to achieve achievements in celebration of the 14th National Party Congress](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/5/8869ec5cdbc740f58fbf2ae73f065076)



























![[Photo] Bustling Mid-Autumn Festival at the Museum of Ethnology](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/da8d5927734d4ca58e3eced14bc435a3)























![[VIDEO] Summary of Petrovietnam's 50th Anniversary Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/abe133bdb8114793a16d4fe3e5bd0f12)

![[VIDEO] GENERAL SECRETARY TO LAM AWARDS PETROVIETNAM 8 GOLDEN WORDS: "PIONEER - EXCELLENT - SUSTAINABLE - GLOBAL"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/23/c2fdb48863e846cfa9fb8e6ea9cf44e7)
































Comment (0)