Researchers calculate that there are nearly 44 million cubic kilometers of water in the Earth's crust, more than the water in ice caps and glaciers on land.
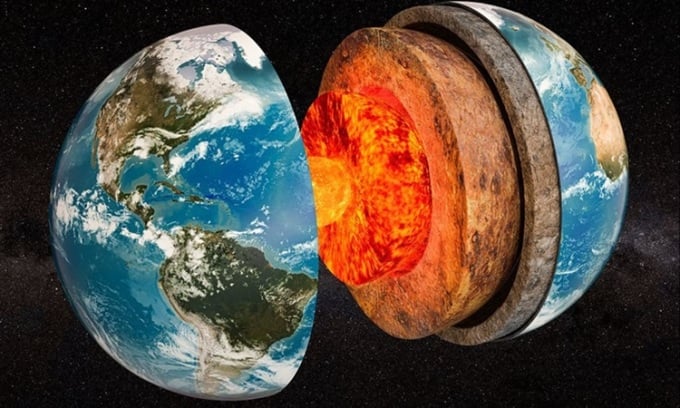

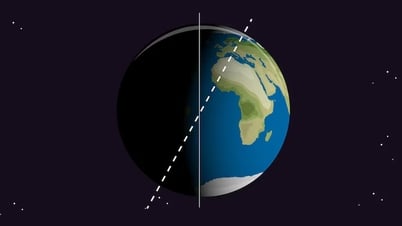
Simulation of the layers of the Earth. Photo: AlexLMX
A 2021 study in the journal Geophysical Research Letters found that more water is stored below the Earth's surface in soil or rock pores, called groundwater, than in ice caps and glaciers. "There are approximately 43.9 million cubic kilometers of water in the Earth's crust," said Grant Ferguson, a hydrogeologist at the University of Saskatchewan and lead author of the 2021 study. By comparison, Antarctica's ice sheet holds about 27 million cubic kilometers of water, Greenland's 3 million cubic kilometers, and glaciers outside Antarctica and Greenland hold 158,000 cubic kilometers, according to Live Science .
The Earth's oceans remain the world's largest source of water, containing 1.3 billion cubic kilometers, according to research. Outside of the oceans, groundwater is the world's largest water source. A 2015 study in the journal Nature Geoscience estimated that 22.6 million cubic kilometers of water are in the shallow subsoil, meaning water up to 2 kilometers below the surface. In contrast, the 2021 study looked at groundwater in the top 10 kilometers of the Earth's crust.
The discrepancy is due to previous estimates of groundwater below the top 2 km of the Earth’s crust focusing on low-porosity crystalline rocks such as granite. The 2021 study included sedimentary rocks, which are more porous than crystalline rocks. Overall, the 2021 study found a doubling of the amount of groundwater that exists between 2 and 10 km below the Earth’s surface, from about 8.5 million km3 to 20.3 million km3. The new estimate also places shallow groundwater at nearly 23.6 million km3.
According to Ferguson, the crust is typically 30 to 50 kilometers thick, much thicker than the 2021 study looked at. They focused on the top crust because it is relatively brittle, and therefore has a lot of fractured rock that could hold water. Below 10 kilometers, the crust becomes less porous and less able to hold water.
Groundwater aquifers, mostly freshwater, are located close to the surface and are used for drinking and irrigation. In contrast, groundwater at great depths is quite salty and cannot easily circulate or flow to the surface, so it is isolated from the rest of the planet’s water, according to Ferguson. However, the isolation of these aquifers means that in some places, salty water is stored for extremely long periods of time, which can provide valuable insights into Earth’s past.
In addition, ancient waters could support microbial ecosystems that are still active today. Such deep biomes could help shed light on how life evolved on Earth and how it thrived on other worlds .
An Khang (According to Live Science )
Source link


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives US Ambassador to Vietnam Marc Knapper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/c8fd0761aa184da7814aee57d87c49b3)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the ceremony to celebrate the 80th anniversary of the post and telecommunications sector and the 66th anniversary of the science and technology sector.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/8e86b39b8fe44121a2b14a031f4cef46)
![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the 8th Conference of full-time National Assembly deputies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/2c21459bc38d44ffaacd679ab9a0477c)

![[Photo] Many streets in Hanoi were flooded due to the effects of storm Bualoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/18b658aa0fa2495c927ade4bbe0096df)






























































































Comment (0)