Global cruise ship passenger numbers exceed pre-pandemic levels, EU increases Russian gas imports, US moves closer to interest rate cuts, IMF raises China's growth forecast, South Korea's auto exports hit new highs... are some of the world economic highlights of the past week.
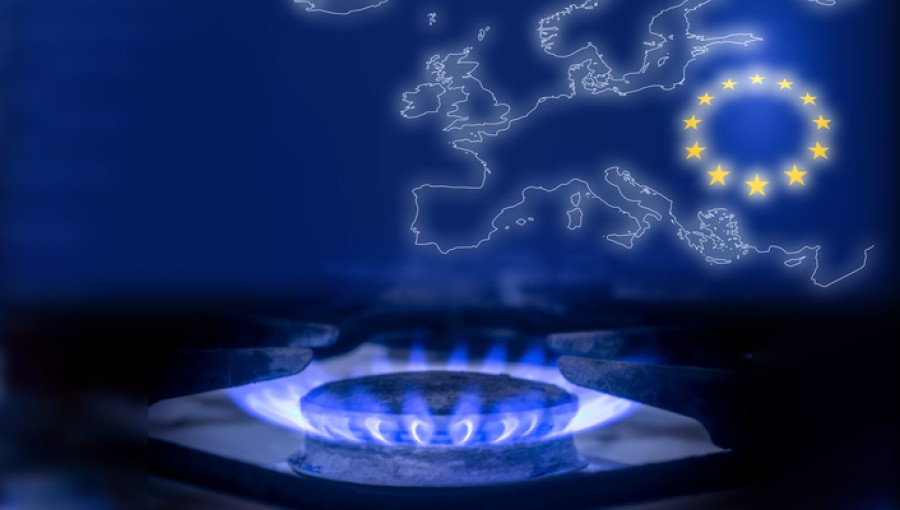 |
| The volume of Russian gas exported via pipeline to EU countries in the first 6 months of 2024 increased by 24%. (Source: bne IntelliNews) |
World economy
Global cruise ship passenger numbers exceed pre-pandemic levels
The global cruise industry estimates passenger numbers will increase by 10% in 2028 from 31.7 million in 2023, when they will exceed pre-Covid-19 levels, but some itineraries could be affected by protests as overcrowding continues.
According to the European director of the Cruise Lines International Association (CLIA), Marie-Caroline Laurent, lines have ordered 57 more ships to supplement the approximately 300 currently in operation to meet demand.
Meanwhile, carriers are converting ships to use electricity instead of highly polluting marine fuels when moored in ports and are ready to comply with European Union (EU) marine environmental regulations by 2030.
However, as demand continues to rise, cruise operators face growing controversy over the large numbers of tourists pouring into busy European port cities such as Spain's Barcelona, the continent's largest cruise port.
According to CLIA representatives, cruise ship visitors account for only 4% of total visitors to Barcelona.
Barcelona Mayor Jaume Collboni said the city government would seek a new agreement with the port to reduce the number of visitors per day.
Ms Laurent said the violent protests could impact future schedules.
Cruise lines may boost itineraries in Asia, Northern Europe and the Caribbean in coming years as well as steer passengers to other Mediterranean ports.
The World Travel and Tourism Council estimates that Spain's tourism revenue will reach nearly 100 billion euros ($109 billion) this year, up 11% from 2019 levels, before the pandemic.
Meanwhile, cruise lines forecast a 5% increase in arrivals to Spain in 2024, while authorities expect a 13% increase in summer visitors.
America
* Recently, the Chairman of the US Federal Reserve (Fed) signaled that the central bank is getting closer to cutting interest rates , after 3 consecutive months of recording falling price pressure.
In a speech at the Economic Club of Washington, Jerome Powell said officials want to see evidence that inflation is returning to the 2% target on a sustained basis, adding that officials will not wait for inflation to return to that level before cutting borrowing costs.
While Mr. Powell did not specify the timing of the rate cut, he said the economy was now in a “better balance.”
* Morgan Stanley Bank announced on July 16 that its second-quarter 2024 profit exceeded expectations thanks to a surge in investment banking and trading revenue, overcoming dismal results in asset management.
The bank joined other Wall Street banks, including Bank of America and JPMorgan, in reporting a rise in investment banking revenue as growing market confidence in the US economy prompted firms to raise more money and do deals.
Morgan Stanley shares rose nearly 2%, reversing earlier losses. The bank is on track to hit its target of 30% pretax profit margin in its wealth business, a key efficiency target.
China
* A new 60% tariff on all Chinese exports to the US would cut the world's second-largest economy's annual growth rate by more than half, according to new research by UBS Group. The forecast highlights the risks for Beijing if former President Donald Trump returns to the White House.
As early as 2024, Mr. Trump was reportedly considering a flat 60% tariff on Chinese imports, which, if implemented, would cut China’s gross domestic product (GDP) by as much as 2.5 percentage points the following year.
China is looking to achieve growth of around 5% in 2024, after the economy grew 5.2% in 2023.
* In the updated report on the world economic outlook released by the International Monetary Fund (IMF) on July 16, this financial institution raised China's growth forecast in 2024 to 5%, up 0.4 percentage points from the previous forecast.
According to the update, global economic activity and world trade strengthened earlier this year. Asia's export growth, especially the region's strong growth in technology, has provided the impetus for trade growth.
Europe
* A survey by the European Central Bank (ECB) showed that credit demand of households in the eurozone increased for the first time in two years as they became more optimistic about the economic situation and interest rates fell.
Sixteen percent of lenders polled in the ECB's Bank Lending Survey (BLS) reported an increase in loan demand from households in the three months to June 2024. This was the first increase since 2022, and respondents expect the trend to continue this quarter.
* On July 17, the European Court of Auditors (ECA) said that the EU's targets in producing and importing green hydrogen fuel are "unrealistic and difficult to achieve", despite billions of euros in funding.
The European Commission (EC) has set a target of producing up to 10 million tonnes of renewable hydrogen by 2030 and importing another 10 million tonnes. In the report, the ECA said the EU's environmental targets have been politicized and said there is a high chance the bloc will miss them.
* The Czech News Agency (CTK) on July 16 quoted the July report of the Gas Exporting Countries Organization (GECF) as saying that compared to the same period in 2023, the volume of Russian natural gas exported via pipeline to EU countries in the first 6 months of 2024 increased by 24% .
According to the report, a total of 80 billion cubic meters of natural gas were transported into the EU via pipeline systems in the first half of 2024, more than half of which was imported from Norway. The next main exporters were Algeria, Russia and Azerbaijan, respectively.
* According to the German central bank – Bundesbank, fighting high inflation is a test of patience. The Bundesbank report published on July 16 said: “Since the beginning of 2024, efforts to fight inflation have achieved only minor successes. In particular, rising service prices remain a persistent chronic problem.”
Inflation is falling only slowly. In the eurozone, inflation was 2.5% in June, compared with just over 5% a year ago and over 10% two years ago. However, inflation is unlikely to return to the ECB’s 2% target before the fall of 2025, if not later.
* Caddie, the famous French supermarket trolley manufacturer, will officially go bankrupt after failing to find a viable acquisition solution. Caddie currently has 110 employees working.
Caddie’s bankruptcy marks the end of an icon in the French retail industry. Founded in 1962, Caddie became a leading supplier of shopping trolleys to France’s largest supermarket chains, including Carrefour, Auchan and Leclerc. However, the company has struggled financially in recent years due to increased competition from low-cost manufacturers and changing consumer shopping habits.
Japan and South Korea
* Japanese media on July 17 accused search engines using artificial intelligence (AI) from US technology giants such as Google and Microsoft of potentially violating copyright .
Accordingly, the Japan Newspaper Publishers and Editors Association called on companies operating these services to seek permission from news organizations because AI search results often resemble articles that were sourced without permission.
The association analyzed that AI search engines sometimes return incorrect answers because they reuse or modify articles inappropriately, and stressed that companies need to ensure the accuracy and reliability of their services before launching.
* On July 17, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) released its July 2024 Asian Economic Outlook report, raising the Korean economic growth outlook for 2024 to 2.5%, 0.3% higher than the 2.2% ADB forecast last April.
The reason the ADB raised its economic growth outlook for Korea is because the export sector is maintaining steady growth momentum, focusing mainly on semiconductor chips, the South Korean Finance Ministry said.
Thus, the economic growth outlook for Korea given by ADB this time is equal to the outlook of the IMF and the Bank of Korea (BOK), but lower than the 2.6% level given by the government of this country, the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) and the Korea Development Institute (KDI).
* South Korea's auto exports rose to a new high in the first half of 2024 amid growing global demand for hybrid vehicles, official data showed on July 16.
Total auto exports reached US$37 billion in the January-June period, up 3.8% year-on-year. The number of exported cars reached 1,467,196 units, up 3.2% year-on-year.
South Korea's monthly auto exports have maintained a strong performance, staying above $6 billion since November 2024, except for February 2024 due to a long holiday, the ministry said in a statement.
ASEAN and emerging economies
* On July 16, the Thai Cabinet approved a preferential loan program for commercial banks worth 100 billion Baht (2.8 billion USD), to help small and medium-sized enterprises have easier access to loans.
Accordingly, the state-owned Government Savings Bank (GSB) will provide liquidity to commercial banks through loans with an interest rate of 0.01% so that they can lend to small businesses at an interest rate of no more than 3.5% for three years, in the context that retail lending rates among Thai banks are currently at more than 7%.
* Indonesia is reviewing the Policy to limit fuel, gasoline and oil subsidies.
Besides stimulating production and consumption, there are opinions that fuel subsidies will increase purchasing power, leading to increased consumption of gasoline and oil and will have negative impacts on the environment.
Former Indonesian Trade Minister Mari Elka Pangestu said the government’s fuel subsidy reform policy should not be considered in isolation but in a broader context, with appropriate targets and distribution methods. The roadmap towards zero subsidies should also be implemented in stages to avoid major impacts on society.
* On July 12, a report from the Singapore Ministry of Trade and Industry (MTI) said that GDP in the second quarter of 2024 increased by 2.9% over the same period last year, while the growth rate in the first quarter of 2024 was adjusted higher to 3%.
The growth rate in the first quarter of 2024 is the fastest since Singapore's 4.2% growth in the third quarter of 2022 .
On a quarter-on-quarter and seasonally adjusted basis, Singapore's economy grew 0.4%, the highest since the second quarter of 2023 and faster than the revised 0.3% growth in the first quarter of 2024. Growth was supported by a recovery in manufacturing to 0.5% year-on-year after a 1.7% contraction in the first quarter of 2024.
Source: https://baoquocte.vn/kinh-te-the-gioi-noi-bat-12-187-eu-van-chua-the-cai-nghien-khi-dot-nga-duc-kien-nhan-chong-choi-thu-thach-my-can-balance-tot-hon-279126.html







![[Photo] Binh Trieu 1 Bridge has been completed, raised by 1.1m, and will open to traffic at the end of November.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/2/a6549e2a3b5848a1ba76a1ded6141fae)




























































































Comment (0)