Satellite images reveal that the saltwater lake Urmia was flooded in September 2020, but by September this year, the lake had almost turned into a giant salt flat.
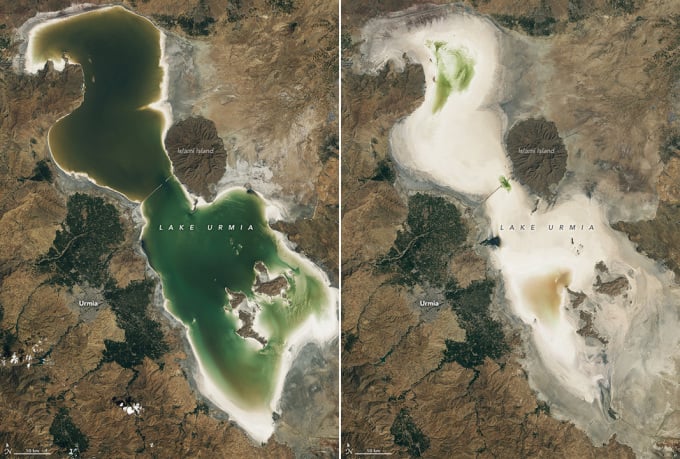

Lake Urmia in satellite images from September 2020 (left) and September 2023 (right). Photo: NASA
At around 5,200 square kilometers, Lake Urmia in northwestern Iran was once the largest lake in the Middle East and one of the largest hypersaline lakes on Earth at its peak. However, the lake has now almost turned into a vast salt flat, SciTechDaily reported on October 15. The change is evident in images taken by Landsat 8 in September 2020 and Landsat 9 in September 2023.
In 2020, most of the lake was submerged and salt was only present around the lake’s edges. This was due to above-average rainfall during the previous period, which caused freshwater to flood into the lake and expand the water body. But since then, dry conditions have caused water levels to drop.
The long-term trend of Urmia is one of gradual drying. In 1995, Lake Urmia was at its highest level, but over the next two decades it dropped more than 7 m and lost about 90% of its area. Repeated droughts, agricultural use and damming of rivers that feed the lake have all contributed to this decline.
The shrinking of Lake Urmia has had a number of impacts on ecosystems and human health. The lake, its islands and surrounding wetlands form a valuable natural habitat and are designated as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve, a Ramsar site and a national park. It is a breeding ground for waterfowl such as flamingos, white pelicans and white-headed ducks, and a stopover for migratory species. However, with the water levels low, the remaining water in the lake has become saltier, affecting shrimp populations and other food sources for larger animals.
The drying up of the lake also increases the risk of dust being picked up by the wind, which can lead to poor air quality. Recent studies have shown that the low water levels in Lake Urmia are affecting the respiratory systems of local residents.
The impacts of climate, water use and dams on Lake Urmia's water levels are controversial. The lake has seen some recovery during a 10-year restoration program that began in 2013. However, the true impact of the program is difficult to assess because of the heavy rainfall that also fell during that time. Some studies have concluded that climate factors are key to the recovery.
Thu Thao (According to SciTechDaily )
Source link

































































































Comment (0)