The patient was then transferred to the General Surgery Department for monitoring and treatment according to the optimal regimen, using broad-spectrum antibiotics initially. The results of the culture of pus from the abscess showed that the patient was infected with ESBL bacteria, a type of E. coli bacteria that is resistant to many antibiotics. The patient's antibiotics were changed according to the cultured bacteria standard.
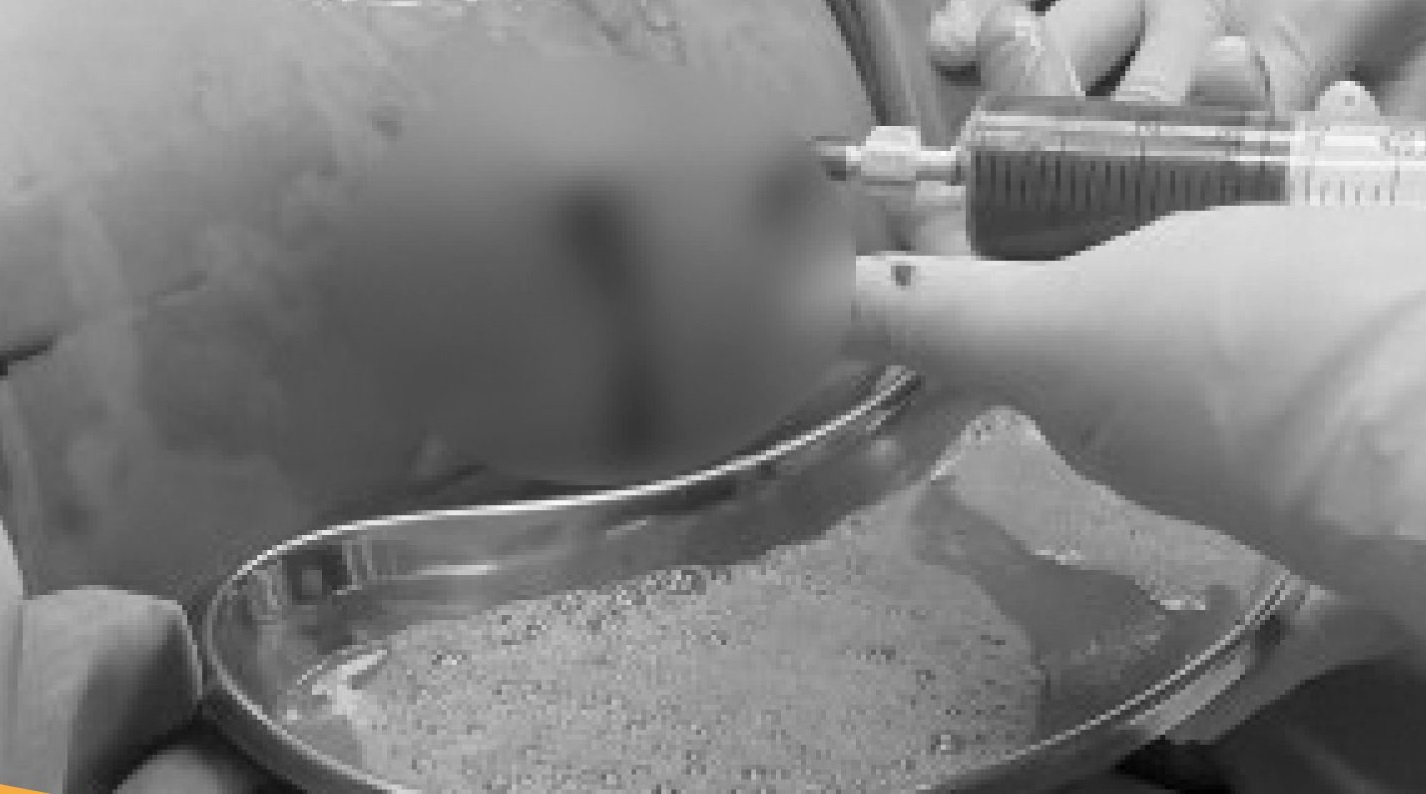

Pus suction to save liver abscess patient
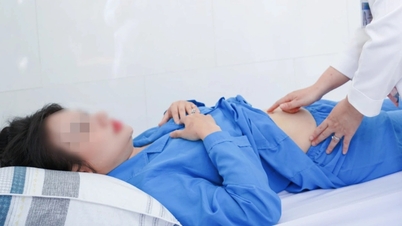
After 7 days, the patient's health progressed positively, clinical condition improved well and no more fever, no more pain, X-ray showed that the abscess had been completely drained and the patient was discharged from the hospital.
Dr. Nguyen Thanh Sang said that recently the department has treated many cases of liver abscesses from mild to critical, most of which are caused by bacteria, amoeba, etc. If liver abscesses are detected early and treated early, they will improve positively. However, the danger is that many patients with critical liver abscesses have large abscesses but the symptoms are only mild fever, right hypochondriac pain, etc., leading to late detection and treatment. Liver abscesses can rupture, causing sepsis, pericardial effusion, pleural effusion, etc., threatening the patient's life.
Source link



![[Photo] Keep your warehouse safe in all situations](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/3eb4eceafe68497989865e7faa4e4d0e)
![[Photo] President of the Cuban National Assembly visits President Ho Chi Minh's Mausoleum](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/39f1142310fc4dae9e3de4fcc9ac2ed0)


![[Photo] Hanoi morning of October 1: Prolonged flooding, people wade to work](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/189be28938e3493fa26b2938efa2059e)



































































![[Infographics] An Giang Agriculture 2020-2025: Stable growth, quality transformation](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/1/bf3a77ba3a0243a697e5253ed4cd6f9c)

















Comment (0)