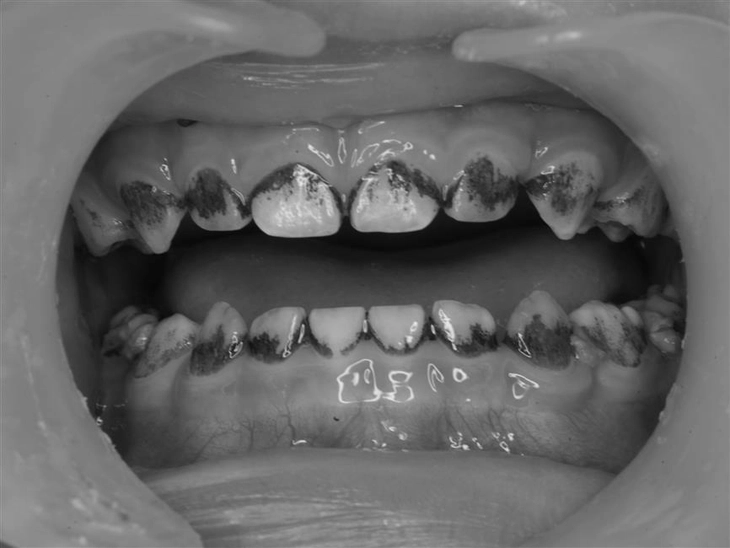
Illustration of black plaque on teeth
This phenomenon is called black stain or black plaque on teeth, a fairly common condition in children around the world as well as in Vietnam.
Interestingly, contrary to parental concerns, studies show that children with black plaque on their teeth are less likely to have cavities. This is an interesting paradox that has been elucidated by many scientific works over the past 60 years.
Origin of black plaque on baby teeth
Normally in adults, if we discover black plaque on permanent teeth, we often immediately think of the cause as drinking a lot of tea, coffee, or smoking. Babies do not have these habits. What is this black plaque on baby teeth?
This is an extrinsic staining, meaning that the coloring substances are attached from the outside, not due to the pathology of the tooth tissue itself. These patches often appear as black dots or bands, running parallel to the gum line, especially visible on the inside of the lower molars or the outside of the upper front teeth.
Black plaque adheres very firmly, is difficult to clean with normal brushing and often recurs even after the dentist has cleaned. Although it does not cause pain or weaken the teeth, this phenomenon significantly affects aesthetics, making many children afraid to smile and parents confused.
Causes and mechanism of black plaque formation on baby teeth
The mechanism of black plaque formation has been studied quite thoroughly. It is determined that they are mainly made up of insoluble iron salt compounds, called ferric sulfide. This process occurs when certain types of bacteria in dental plaque secrete hydrogen sulfide gas (H₂S), which combines with iron in saliva or gingival fluid to form black particles that adhere firmly to tooth enamel.
Common bacteria found in black-spot plaque include Actinomyces, Rothia, Neisseria, Porphyromonas, and Prevotella.
Additionally, the saliva of children with black stains is often richer in calcium, phosphate, copper, zinc and has a higher pH, along with better buffering capacity, so their teeth are less susceptible to acid dissolution and are more resistant to cavities. Diet also plays a role.
Factors that favor the formation of black plaque on teeth
- Tooth enamel surface and saliva: Rough tooth enamel surfaces can make teeth more susceptible to black plaque. Likewise, acidic saliva or dry mouth associated with mouth breathing increases the presence of bacteria that cause black plaque.
- Diet: Some foods rich in iron, soy sauce, beets or vegetables with high pigment can increase the risk of dark spots forming.
- Iron supplements: Iron-rich supplements, often prescribed for children with iron deficiency anemia, can lead to black or dark blue plaque on teeth.
- Long-term swimming: Exposure to chlorine and other compounds in pool water can contribute to tooth discoloration, depending on the quality and type of your child's enamel.
- Oral hygiene practices: Improper brushing and flossing can lead to plaque buildup, which is susceptible to mineralization and pigmentation by chromogenic bacteria, resulting in this type of black plaque.
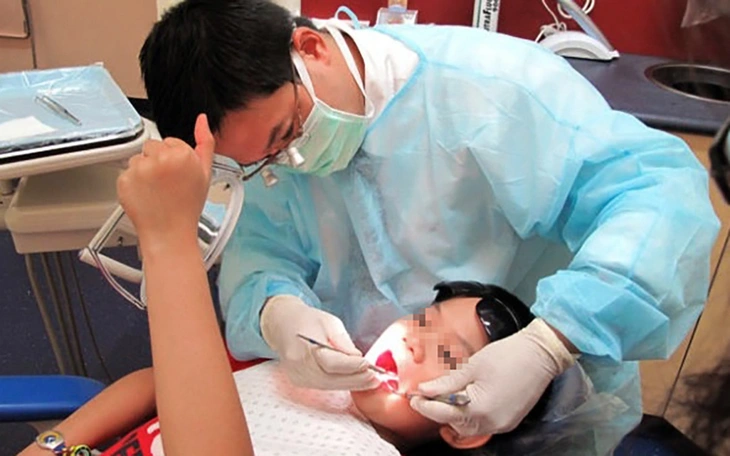
To treat children's teeth safely, dentists need to have experience and understand the psychology of children - Photo: TTD
How to recognize and remove black plaque?
Early detection of black plaque is not difficult, because parents can easily see it when observing the tooth surfaces.
These black stains are stubborn stains, unlike soft plaque left behind by food after eating, black plaque is not easily removed by brushing with a regular toothbrush. Areas with black plaque may feel rough compared to the rest of the tooth surface.
When preventative measures are not enough, a variety of treatments can effectively control staining:
The common treatment today is for the dentist to clean the plaque with ultrasonic or saline systems. The saline systems will clean better and faster, making the child feel more comfortable.
Some studies have tested lasers, photodynamics, biological antibacterial preparations or probiotics as supportive treatments to limit recurrence, but no method has been truly effective.
Since plaque is largely influenced by bacteria in the mouth, manipulating the oral environment can help prevent or reduce the intensity of plaque. Some children may have a change in their oral environment as they grow older or can modify their oral environment through the use of antibacterial mouthwashes (for children over 5 years old).
If using mouthwash for children, choose mouthwashes that do not contain alcohol.
What precautions can parents and caregivers use for their children?
Preventing black plaque involves good oral hygiene and dietary habits. Here are some effective preventive measures:
● Brush and floss regularly: Make sure your child brushes their teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque. Don't forget to clean their tongue, too.
● Balanced diet: Limit consumption of foods and drinks rich in colorants. Encourage a diet rich in fiber such as fruits and vegetables, and supplement minerals from dairy products to help keep teeth healthy.
● Regular dental check-ups: Children under 5 years old should have regular check-ups every 3 months and every 6 months when they are older to effectively remove plaque and monitor oral health, detect early and promptly treat dental problems.
● Managing iron supplementation: If iron supplementation is needed, consider a liquid form that can be taken through a straw to minimize contact with teeth or brushing afterward.
Many studies have shown that children with black plaque often have fewer cavities due to differences in microflora and saliva composition. However, for aesthetic and psychological reasons, parents should still take their children to a pediatric dentist for cleaning and home care advice.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/tre-co-mang-bam-den-tren-rang-sua-co-gay-mat-rang-20250927094156758.htm



![[Photo] Delegation attending the Government Party Congress visited President Ho Chi Minh's Mausoleum](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/12/1760240068221_dsc-3526-jpg.webp)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the 725th anniversary of the death of National Hero Tran Hung Dao](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/12/1760285740475_ndo_br_bnd-8978-jpg.webp)
![[Photo] The 1st Government Party Congress held a preparatory session.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/12/1760257471531_dsc-4089-jpg.webp)































































































Comment (0)