What is the compulsory motorbike insurance compensation level when an accident occurs? What are the cases that exclude insurance liability? - Reader Thanh Luan
 |
| What is the compulsory motorbike insurance compensation level when an accident occurs? |
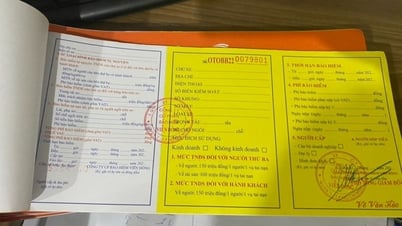
According to the provisions of law, the Certificate of compulsory civil liability insurance of motorcycle owners (commonly known as compulsory motorcycle insurance) is one of the mandatory documents for motorcycles.
Motorbike owners are responsible for purchasing compulsory motorbike insurance from insurance companies licensed to conduct insurance business according to the provisions of law.
Subjects of compulsory motorcycle insurance
Pursuant to Article 5 of Decree 67/2023/ND-CP, the subject of compulsory motorbike insurance is the civil liability of the vehicle owner to third parties and passengers as prescribed by law.
Compulsory motorcycle insurance compensation level
Pursuant to Article 6 of Decree 67/2023/ND-CP, the maximum compulsory motorbike insurance compensation level is as follows:
- The insurance liability limit for damage to health and life caused by the vehicle is 150 million VND per person in an accident.
- The insurance liability limit for property damage caused by two-wheeled motorbikes; three-wheeled motorbikes; motorbikes (including electric motorbikes) and vehicles with similar structures as prescribed by the Law on Road Traffic is 50 million VND per accident.
Compulsory motorcycle insurance coverage
Pursuant to Clause 1, Article 7 of Decree 67/2023/ND-CP, insurance companies are responsible for compensating for the following damages:
- Non-contractual damages to health, life and property of third parties caused by vehicle participation in traffic and activities.
- Damage to the health and life of passengers on the vehicle caused by the vehicle's participation in traffic or operations.
Insurance liability exclusions
Pursuant to Clause 2, Article 7 of Decree 67/2023/ND-CP, insurance companies are not responsible for insurance compensation in the following cases:
- Intentional acts causing damage by the vehicle owner, driver or injured person.
- The driver who caused the accident intentionally fled and did not fulfill the vehicle owner's civil responsibilities. In case the driver who caused the accident intentionally fled but has fulfilled the vehicle owner's civil responsibilities, it is not a case of insurance liability exclusion.
- The driver does not meet the age requirements as prescribed by the Law on Road Traffic; the driver does not have a driving license or uses an invalid driving license as prescribed by law on training, testing, and issuance of road driving licenses; the driving license is erased or uses an expired driving license at the time of the accident or uses an inappropriate driving license for a vehicle that requires a driving license.
In case a driver has his/her driving license temporarily revoked or his/her driving license revoked, he/she is considered to have no driving license.
- Damage causing indirect consequences includes: reduction in commercial value, damage associated with the use and exploitation of damaged assets.
- Damage to property caused by driving a vehicle with a blood or breath alcohol concentration exceeding the normal value as guided by the Ministry of Health ; using drugs and stimulants prohibited by law.
- Damage to property stolen or robbed in the accident.
- Damage to special assets including: gold, silver, precious stones, valuable papers such as money, antiques, rare paintings, corpses, and remains.
- Damage caused by war, terrorism, earthquake.
Source


![[Photo] Solemn opening of the 8th Congress of the Central Public Security Party Committee, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/f3b00fb779f44979809441a4dac5c7df)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the 8th Congress of the Central Public Security Party Committee](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/79fadf490f674dc483794f2d955f6045)


![[Photo] Bustling Mid-Autumn Festival at the Museum of Ethnology](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/da8d5927734d4ca58e3eced14bc435a3)



















































![[VIDEO] Summary of Petrovietnam's 50th Anniversary Ceremony](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/4/abe133bdb8114793a16d4fe3e5bd0f12)

![[VIDEO] GENERAL SECRETARY TO LAM AWARDS PETROVIETNAM 8 GOLDEN WORDS: "PIONEER - EXCELLENT - SUSTAINABLE - GLOBAL"](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/7/23/c2fdb48863e846cfa9fb8e6ea9cf44e7)































Comment (0)