Studies show that the severity of heat disorders tends to increase with age. For example, at the same temperature, an 18-year-old may only get heat cramps, a 40-year-old may get heat exhaustion, but a person over 60 may get heat stroke.
Some people should be careful when it is too hot, such as: The elderly (over 65 years old) and young children; people with chronic diseases, especially those with heart disease or high blood pressure, people who are taking certain medications such as antidepressants, insomnia or blood circulation drugs, according to the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

Severe heat can cause heat-related illnesses.
Who should be cautious?
People with epilepsy, heart, kidney, or liver disease who need to limit their fluid intake or have difficulty retaining fluids should consult their doctor before increasing their fluid intake.
People on salt-restricted diets, such as those with kidney disease, heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes, should consult their doctor before increasing their salt intake or drinking sports drinks, according to the CDC.
How to prevent heat-related illness
Stay cool. In air-conditioned areas, adjust the temperature accordingly. Fans can provide cooling, but when temperatures reach above 90 degrees Fahrenheit (32 degrees Celsius), they will not prevent heat-related illness, according to the CDC.
Be careful when doing outdoor activities. Try to do outdoor activities during the coolest times, such as morning and evening.
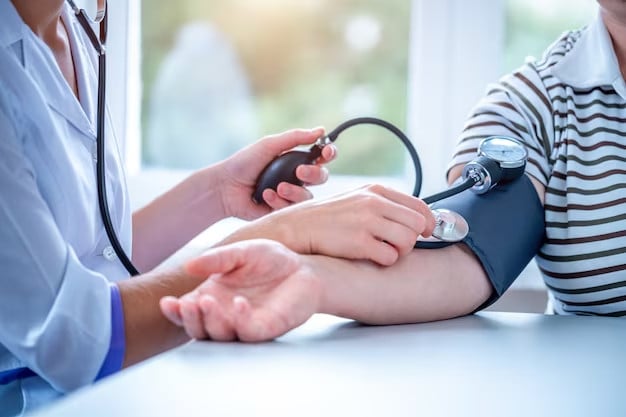
People with chronic diseases, especially those with heart disease or high blood pressure... are at risk when the weather is too hot.
Reduce activity. Reduce exercise in hot weather. If exertion in the heat causes your heart to race and you to gasp for air, stop all activity. Get to a cool or shady place and rest, especially if you feel dizzy, confused, weak, or faint.
Cover up when you go outside. Sunburn affects your body's ability to cool itself and can lead to dehydration. When you go outside, wear lightweight, light-colored clothing, a wide-brimmed hat, sunglasses, and sunscreen.
Limit heat-producing foods. Protein increases metabolic heat production and increases water loss.
Stay hydrated . Drink plenty of water; don't wait until you're thirsty. Avoid soft drinks and alcohol. Also avoid drinks that are too cold, as they can cause stomach cramps. Sports drinks can replace salts and minerals lost through sweat.
Source link





























































































Comment (0)