The movement of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates was the main factor leading to the earthquake disaster on September 8, which killed thousands of people.
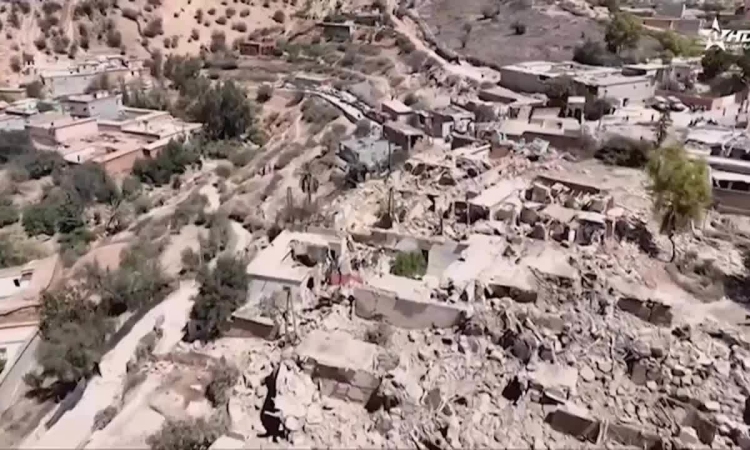
Soldiers and civilians search for survivors of an earthquake in the rubble in Taroudant province on September 9. Video : AFP
An earthquake with its epicenter in the High Atlas Mountains in Morocco at 11 p.m. on September 8 (5 a.m. on September 9, Hanoi time), shook many cities, destroyed a series of houses, and forced people to flee to the streets. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), the disaster measured 6.8 magnitude and was the strongest earthquake to hit this North African country in the past century.
The Moroccan Interior Ministry said on the night of September 9 that the disaster had killed at least 2,012 people, mostly in the epicenter province of Al-Haouz and Taroudant province. More than 2,000 people were injured, of whom 1,404 were in critical condition.
The USGS determined the quake's epicenter was at a depth of 18.5 kilometers, meaning it was relatively shallow. The epicenter was in the remote Ighil region, about 72 kilometers from Marrakech, a city of 840,000 people. The tremors were felt in the capital Rabat, 350 kilometers north in the High Atlas Mountains.
According to experts, such shallow earthquakes are more damaging because they carry more energy as they reach the surface. In deep earthquakes, seismic waves have to travel a long distance before reaching the surface, thus losing more energy to the surrounding environment. But in shallow earthquakes, seismic waves carry more energy to the surface and cause more damage.
Earthquakes are not common in North Africa, which means Morocco is not really prepared for such a disaster, according to the USGS. Most structures in the country, especially in the countryside and old cities, are not built to withstand strong tremors. "In places where devastating earthquakes are rare, buildings are not built strong enough. Many buildings collapse, resulting in high casualties," said Bill McGuire, emeritus professor at the University of London in the UK.
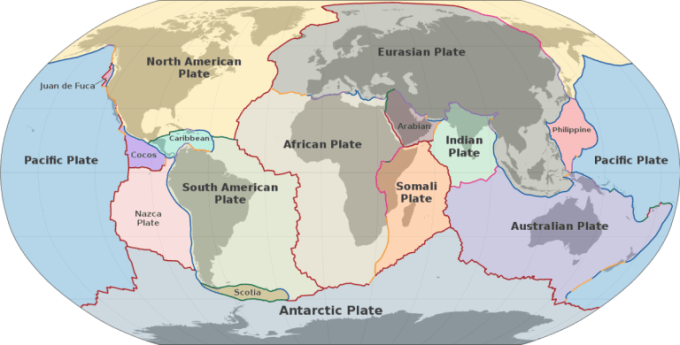
Map of the Earth's major tectonic plates. The Morocco earthquake occurred near the junction of the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. Photo: Wikimedia Commons
Although rare, earthquakes are not unheard of in the region. According to the USGS, devastating earthquakes have been recorded in Morocco, a country in the western Mediterranean. Such quakes are caused by the movement of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, which are converging at a rate of about 4.9 millimeters per year. As for the September 8 earthquake, the USGS said it was caused by a small-depth oblique reverse fault in Morocco's High Atlas Mountains.
A fault is a crack or fracture between two blocks of rock. Faults allow the rocks to move relative to each other, causing an earthquake if the movement is rapid. During an earthquake, the rock on one side of the fault suddenly slips relative to the rock on the other side.
Scientists use the angle of the fault relative to the surface (called the tilt) and the direction of slip along the fault to classify it. Faults that move along the direction of the tilt plane are called strike-slip faults, while faults that move horizontally are called strike-slip faults.
Dip-slip faults have characteristics of both oblique and strike-slip faults. The term “reverse” refers to a situation where the upper block of rock, above the fault plane, moves up and overrides the lower block. This type of fault is commonly found in compressional zones – where one tectonic plate is colliding with another.
In addition to the convergence of the African and Eurasian tectonic plates, other factors can contribute to earthquakes, including the type of rock. Rocks in the area where the September 8 earthquake occurred are known to be weak and brittle, making them more susceptible to earthquakes.
Thu Thao (According to India Express, Geology In, AFP )
Source link




![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives US Ambassador to Vietnam Marc Knapper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/c8fd0761aa184da7814aee57d87c49b3)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the 8th Conference of full-time National Assembly deputies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/2c21459bc38d44ffaacd679ab9a0477c)
![[Photo] Many streets in Hanoi were flooded due to the effects of storm Bualoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/18b658aa0fa2495c927ade4bbe0096df)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the ceremony to celebrate the 80th anniversary of the post and telecommunications sector and the 66th anniversary of the science and technology sector.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/8e86b39b8fe44121a2b14a031f4cef46)




























































































Comment (0)