8 years and 10 million images contributed by the Pokémon Go community
According to information published by Niantic - the developer of the game Pokémon Go, they are developing a Large Geospatial Model (LGM), applying image data and geographic coordinates from their mobile games, especially Pokémon Go and the Scaniverse application.
Unlike conventional AI models that use text, audio, or video data from the internet, LGM is built from more than 10 million real-world location images contributed by users over the past eight years. On average, about 1 million new scans are uploaded by users every week. Most of these scans are from the perspective of pedestrians, providing valuable data in areas inaccessible by cars or street cameras.
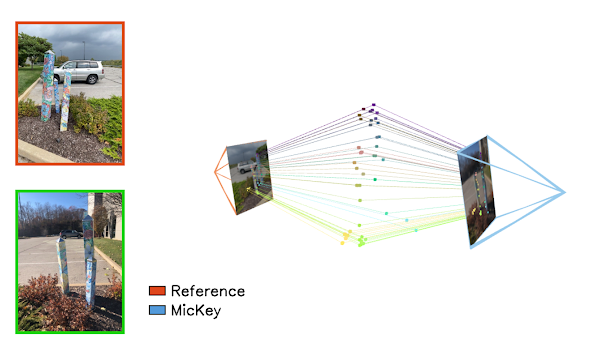
Illustration of how Niantic uses data from different perspectives to build accurate 3D models of space
LGM model development process
For five years, Niantic has been focused on building a Visual Positioning System (VPS). This system allows to determine location and direction from a single image, based on 3D maps created from user image data. From here, LGM was conceived as a step further, processing physical space through geo-coordinated images, similar to the way large language models (LLM) process text and natural language.
Niantic revealed that it trained more than 50 million neural networks, each representing a specific location or perspective. These neural networks compressed thousands of images into digital representations, with a total of 150,000 billion parameters. Combining the local networks, Niantic hopes LGM will be able to recognize any location in the world , even if the image was taken from angles never seen before.
Niantic describes the power of LGM with an example: “If you’re standing behind a church and the model only recognizes the front door, it won’t know where you are. But with LGM, we have data from thousands of churches around the world. While churches aren’t exactly the same, they share similar architectural features. LGM will use that knowledge to recognize you.”
LGM is an evolution of the current Lightship VPS positioning system, which allows players to place virtual items in real space with centimeter accuracy. The Pokémon Playgrounds feature in Pokémon Go demonstrated this capability, allowing Pokémon to be placed in real-world locations for others to find.
In addition to supporting augmented reality (AR) and mixed reality (MR) products, Niantic said LGM also opens up potential in many other areas such as robotics, automation, autonomous vehicles, logistics and space planning.
The question, however, is whether Pokémon Go players are fully aware that the data they generate is being used to develop AI. While this may be mentioned in the game's terms of service, details have only recently been made public. The incident could cause a backlash in the coming months, as players become increasingly concerned about their privacy and how their data is used.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/niantic-dung-du-lieu-pokemon-go-de-phat-trien-mo-hinh-ai-dinh-vi-185241120235020012.htm


![[Photo] Panorama of the cable-stayed bridge, the final bottleneck of the Ben Luc-Long Thanh expressway](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/391fdf21025541d6b2f092e49a17243f)
![[Photo] The 1st Congress of Phu Tho Provincial Party Committee, term 2025-2030](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/1507da06216649bba8a1ce6251816820)
![[Photo] Solemn opening of the 12th Military Party Congress for the 2025-2030 term](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/2cd383b3130d41a1a4b5ace0d5eb989d)

![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives President of the Cuban National Assembly Esteban Lazo Hernandez](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/4d38932911c24f6ea1936252bd5427fa)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam, Secretary of the Central Military Commission attends the 12th Party Congress of the Army](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/9b63aaa37ddb472ead84e3870a8ae825)












































































![[Infographic] Key tasks in the 2025-2030 term of Dong Nai province](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/30/59bd43f4437a483099313af036fef0db)


















Comment (0)