77-year-old male patient, bloating, indigestion, endoscopy doctor discovered a small tumor under the stomach lining, removed early to eradicate cancer.
The patient's gastroscopy and magnetic resonance imaging (CT) results showed a submucosal tumor in the antral body, posteriorly displaced, 1.5×2 cm in diameter.
Tumors with a size of 2cm are indicated for endoscopic surgery to remove the tumor, especially if there is a risk of malignancy, to prevent complications such as acute gastrointestinal bleeding causing black stools and vomiting blood. Chronic bleeding can easily lead to anemia.
 |
| Gastrointestinal cancer is one of the most common cancers in Vietnam. |
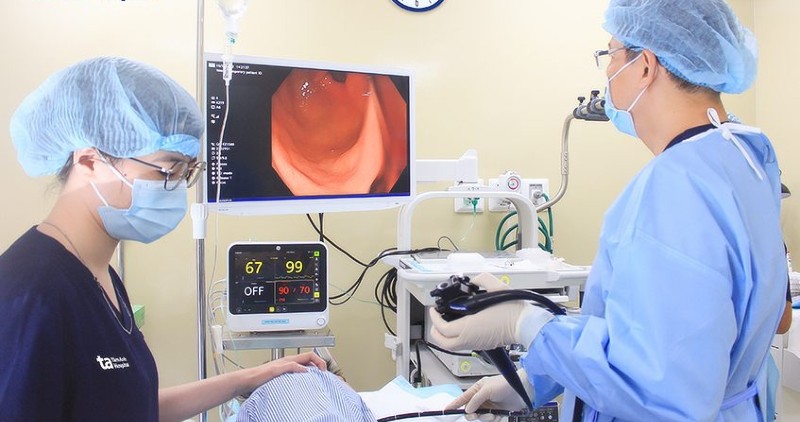
The patient had a history of gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis and duodenitis, hypertension, and type 2 diabetes. After consultation, the doctor indicated surgery using endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESSD).
Small submucosal tumors less than 2 cm are usually monitored, but this technique can remove the tumor early to eliminate the risk of malignancy.
ESSD mucosal dissection is applied to gastric submucosal tumors such as myomas, gastrointestinal stromal tumors that are not too large and have not invaded the gastric serosa and neighboring organs. This method is minimally invasive, preserves the digestive tract, the patient recovers well and has little pain.
The doctor performed an endoscopy, separating each layer of the stomach wall, removing the entire tumor up to the outermost layer of the stomach wall to completely treat the cancer while still preserving the stomach. The pathological results were gastrointestinal stromal tumor.
According to doctors, gastrointestinal stromal tumors are rare mesenchymal tumors, accounting for 0.1-3% of all malignant tumors in the gastrointestinal tract, difficult to diagnose and often discovered incidentally during endoscopy.
Dr. Do Minh Hung, Director of the Center for Endoscopy and Endoscopic Surgery of the Digestive System, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that gastrointestinal stromal tumors are often associated with mutations in the KIT gene. This gene stimulates cells to produce a protein called KIT CD117, accelerating the rate of growth and uncontrolled division.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumors can occur at any age, but are most common in middle-aged and elderly people. In addition to regular health check-ups and endoscopy, patients with suspicious symptoms such as vomiting blood, black stools, fatigue, dizziness, etc. should see a doctor early for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Gastrointestinal cancer is one of the most common cancers in Vietnam. Cancer screening and early detection and diagnosis, along with early treatment regimens, will help many patients have the opportunity to prolong their lives and have a high chance of recovery.
The most common gastrointestinal cancers today are colon cancer, stomach cancer and esophageal cancer. In many developed countries, including Japan, screening and early detection of cancer increases the patient's chance of survival.
In the early stages, patients only need endoscopic submucosal dissection, the treatment is highly effective, and the patient recovers quickly. On the contrary, patients who are diagnosed late often have to undergo major surgery (endoscopic or open surgery), the treatment is more complicated.
Screening for early detection of gastrointestinal cancer through endoscopy is the most effective and almost certain method today. Screening for early detection of gastrointestinal cancer should be performed in normal people over 50 years old. This is the group of people at risk of developing lesions in the gastrointestinal tract.
In addition, people who smoke a lot and drink a lot of alcohol should be screened because of the high risk of esophageal cancer.
People with a family history of stomach cancer or colon cancer should also have annual check-ups to detect precancerous lesions.
In addition, the group of subjects detected with gastritis and severe atrophic gastritis also needs to be classified and screened annually to have data to see how often they should be screened again by esophagogastroduodenoscopy or colonoscopy.
Young, healthy people without any special symptoms do not need to rush to be screened for gastrointestinal cancer.
People are advised to pay attention to abnormal symptoms in the digestive tract including: The upper digestive tract includes the oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, pancreas, liver, bile duct, and small intestine.
Disorders and symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, bloating, indigestion, gastric reflux, abdominal pain, prolonged nausea and vomiting of blood accompanied by fatigue, weight loss...
The lower digestive tract includes the colon, rectum, and anus. Disorders and symptoms such as constipation or prolonged diarrhea, bloody stools, etc. should be examined by a doctor for timely advice and treatment.
For patients with early stage stomach and esophageal cancer, doctors have removed the lining of the stomach and esophagus using endoscopic methods, without having to remove the stomach or esophagus.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/phat-hien-u-ac-tinh-tu-dau-hieu-kho-tieu-d219942.html




![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the 8th Conference of full-time National Assembly deputies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/2c21459bc38d44ffaacd679ab9a0477c)


![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam chairs the meeting of the Central Steering Committee on preventing and combating corruption, waste and negativity](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/fb2a8712315d4213a16322588c57b975)





















































































Comment (0)