Scientists have officially achieved quantum teleportation technology, opening a new era for distributed quantum computing.
However, this technology does not involve teleporting objects or people like in science fiction movies, but the ability to share data between two quantum computers.
Scientists have long known about the ability to "teleport" information through the phenomenon of quantum entanglement.
Recently, a report in the journal Nature published a groundbreaking study by a group of scientists at Oxford University (UK), in which they successfully sent a quantum algorithm wirelessly from one quantum processor to another.
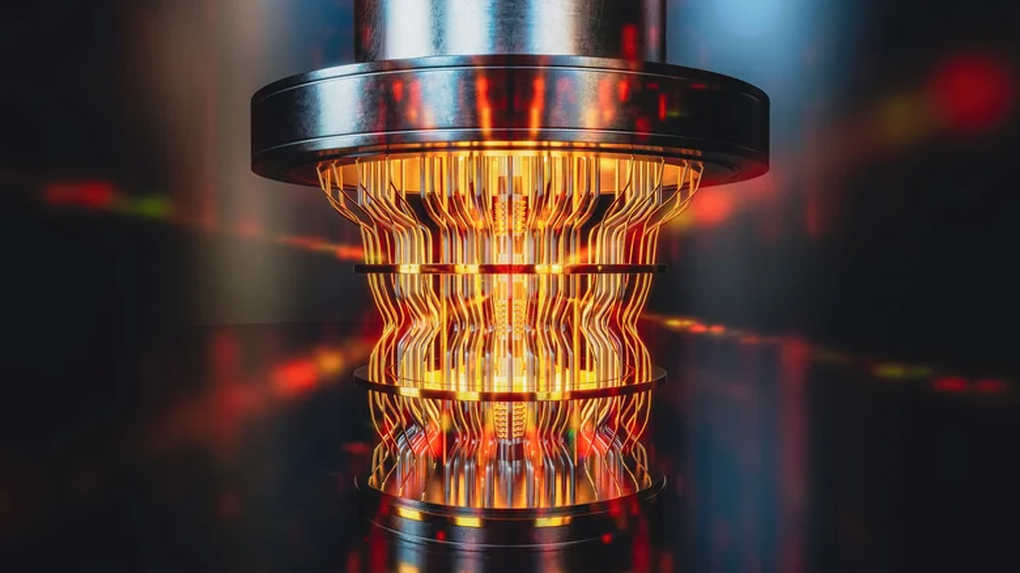

The main goal of the research is to allow two extremely powerful quantum computers to work together as a supercomputer. This would boost their power to solve complex problems that cannot be tackled by individual computers.
The basic principle behind this technology is the instantaneous transmission of information through the phenomenon of quantum entanglement. This occurs when two particles, such as photons or electrons, remain connected, or “entangled,” with each other even when they are very far apart. In quantum computers, those particles are qubits (the basic units that represent quantum information).
However, in the experiment, no matter actually moved. The light particles (data) remained in the same place while being separated by a distance of two meters. Therefore, teleportation here is not the same as the traditional concept of moving matter from one location to another.
Instead, quantum entanglement allows two computers to “see” each other’s data, share that information instantly over long distances, and merge resources.
This breakthrough would pave the way for distributed quantum computing, where multiple remote quantum processors could be combined into a single quantum computer.
Distributed Quantum Computing: The Power of Disruption
Distributed quantum computing is an important concept that promises to bring superior computing power. Quantum computers use qubits instead of binary bits (1s and 0s) like standard computers.
Qubits can exist in multiple states at once, allowing for the storage of an infinite amount of information and the processing of data in entirely new ways.

Google has already built a quantum supercomputer that can solve problems that would take a conventional computer decades. With distributed quantum computing, this power will be multiplied many times over.
In a distributed configuration, individual quantum processors, though far apart, can still communicate to solve a “super problem” by pooling their resources.
Distributed quantum computing can be envisioned as a form of cloud computing in the quantum world . This breakthrough could also spur the development of a quantum internet, the next generation of internet connectivity that would allow for the exchange of quantum data.
This promises to soon bring computers with incredible computing power, opening up many new possibilities in science and technology.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/khoa-hoc/khoa-hoc-da-dat-duoc-dich-chuyen-tuc-thoi-ve-chia-se-du-lieu-20251012235455606.htm















































































































Comment (0)