Mackerel is rich in omega-3.
Modern nutritional research shows that omega-3 fatty acids are one of the essential nutrients for the human body but cannot be synthesized by itself.
Therefore, supplementing omega-3 through food is essential to maintain cardiovascular health, control inflammation, support brain development and strengthen the immune system. Among foods rich in omega-3, mackerel is considered one of the optimal and easily accessible choices.
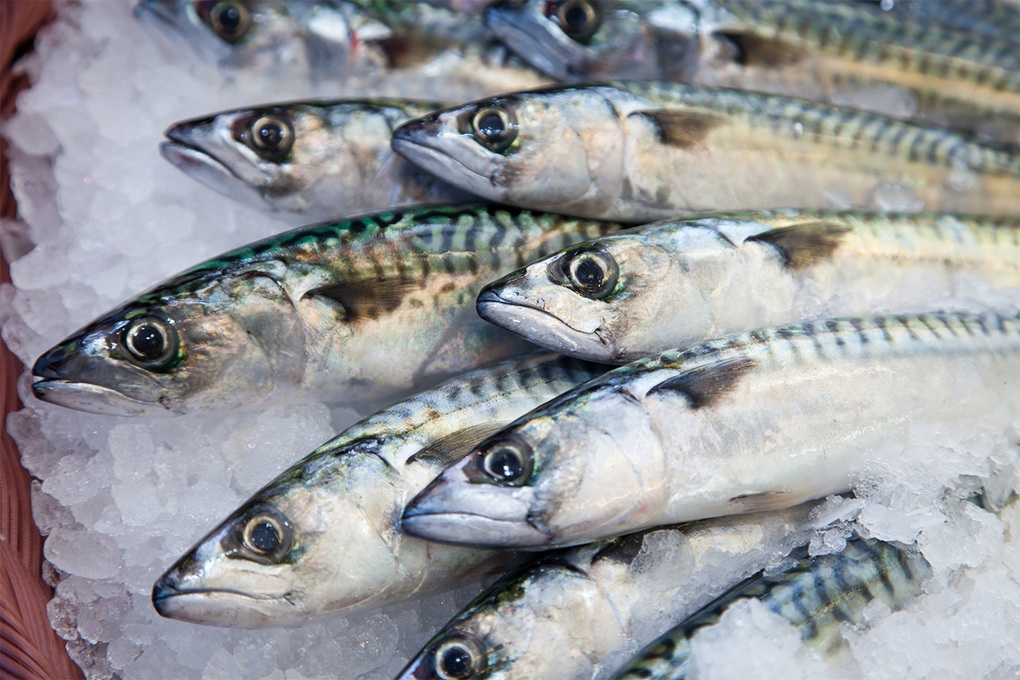

Among foods rich in omega-3, mackerel is considered one of the optimal and easily accessible choices (Photo: Getty).
According to a publication in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, the omega-3 content in mackerel reaches about 2,616mg/100g of fish meat, higher than that of conventional farmed salmon (about 2,260mg).
It is worth mentioning that the ratio of EPA and DHA in mackerel is considered ideal, helping to protect cardiovascular health, improve brain function and slow down neurodegeneration.
Eating mackerel 2 to 3 times a week can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, stabilize blood pressure, support blood sugar control and enhance nervous system activity.
For children, DHA in omega-3 plays an important role in intellectual development and memory. For adults and the elderly, omega-3 helps maintain alertness, reduces the risk of memory loss and diseases related to brain degeneration.
In addition to omega-3, mackerel also contains high levels of protein, is easy to digest, and is rich in B vitamins, especially vitamin B12.
This is a nutrient that helps support red blood cell production, boosts metabolism and improves nerve health. The iron content in mackerel is also higher than many freshwater fish, helping to prevent anemia, especially in women and children.
Importantly, omega-3 from natural foods like mackerel is more bioavailable than from supplement form. This is why many experts recommend prioritizing dietary intake over dietary supplements.
Popular fish with many ways to prepare
Mackerel can be easily processed into many familiar dishes such as braised mackerel with tomato, fried mackerel, mackerel in tomato sauce, steamed mackerel with ginger or grilled mackerel with turmeric.
Not only suitable for Vietnamese family taste, this type of fish is also convenient to prepare, does not take much time, is easy to preserve and can be combined with many other vegetables to increase nutritional value.
Another plus point is that mackerel has few small bones, soft and fragrant meat, easy to eat for both the elderly and children. Therefore, this is considered a dish suitable for many ages, especially good for those who need to recover their health or supplement omega 3, vitamin D, calcium naturally and safely.
Although mackerel has many benefits, if used improperly, users can still face health risks.
To take advantage of its nutritional value without causing harm, mackerel should be used in main meals, with rice and vegetables to balance protein and fiber.
People with stomach problems, gout or digestive disorders should limit eating on an empty stomach, this is when stomach acid increases, easily causing purine in fish to convert into uric acid, increasing the risk of arthritis, especially in people with a history of gout.
At the same time, users should prioritize cooking by steaming or braising instead of frying with a lot of oil to reduce the burden on the digestive system.
How to choose fresh mackerel:
- Fresh mackerel will have red gills, clear eyes, and closed mouth.
- When you press the fish with your hand, you will feel that the fish meat is firm and elastic. If the fish meat is mushy and crumbly, it is definitely old fish. When buying unfrozen fish, you will easily choose fresh fish rather than frozen fish.
- Fresh fish will not have an unpleasant odor, the skin will be intact, not scratched or scaly.
Source: https://dantri.com.vn/suc-khoe/loai-ca-re-beo-giau-omega-3-hon-ca-hoi-nhieu-nguoi-viet-an-moi-ngay-20250916092856374.htm


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting to deploy overcoming consequences of storm No. 10](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/3/544f420dcc844463898fcbef46247d16)
![[Photo] Students of Binh Minh Primary School enjoy the full moon festival, receiving the joys of childhood](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/3/8cf8abef22fe4471be400a818912cb85)
































































































Comment (0)