Master - Doctor Ngo Thi Mai Phuong, Pediatrics - Immunization Clinic, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, said that meningococcal meningitis is an inflammation of the brain's protective membranes that extends from the brain to the spinal cord, caused by the meningococcal agent or Neisseria meningititis.
Meningococcus can cause many different clinical conditions such as meningitis, sepsis, septic shock; causing complex complications such as arthritis, vasculitis, iritis, pleurisy and pericarditis... Of which, meningitis is the most common manifestation (accounting for 40-65% of cases) of invasive meningococcal disease.
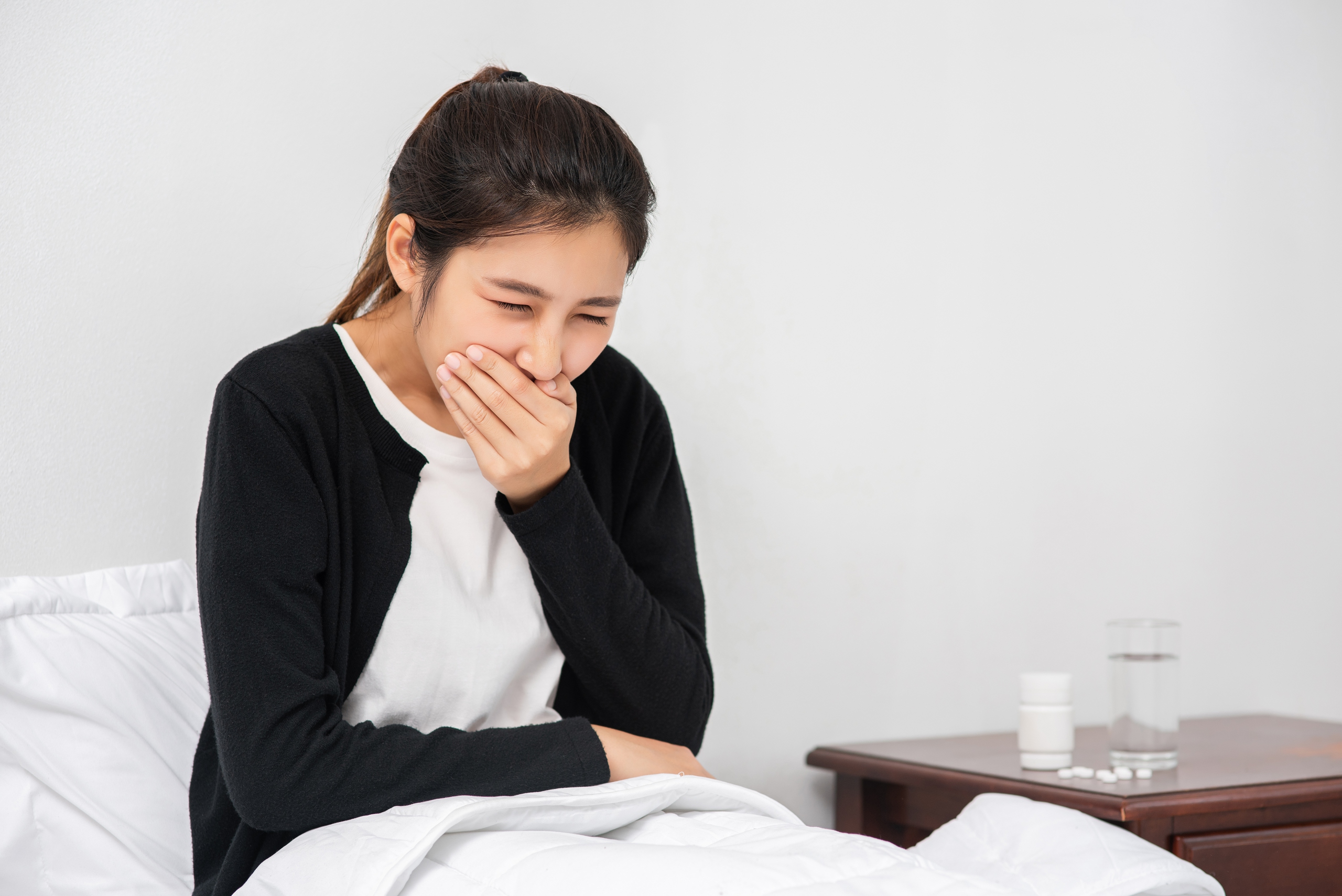

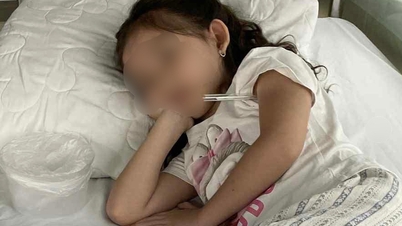
In adolescents and adults with meningococcal meningitis, symptoms often include sudden headache, fever, vomiting, muscle pain, photophobia...
Symptoms of the disease
In adolescents and adults, meningococcal meningitis often presents with sudden headache, fever, vomiting, myalgia, photophobia, irritability, decreased ability to concentrate, anxiety, drowsiness, turbid cerebrospinal fluid with or without rash. Patients may have focal neurological signs and seizures.
Some patients with meningococcal meningitis present with lethargy and abnormal reflexes.
Children under 5 years of age may present with symptoms such as fussiness or drowsiness, fever, vomiting, impaired consciousness or convulsions. Infants may present with inconsolable crying, poor feeding and a bulging fontanel.
Can be transmitted from person to person
According to Master - Doctor Ngo Thi Mai Phuong, meningococcal meningitis can be transmitted from person to person through respiratory droplets or throat secretions from the patient; close and prolonged contact such as kissing, sneezing, coughing, or living with an infected person will facilitate the rapid spread of the disease.
Disease prevention measures
The best way to prevent meningococcal meningitis is to get vaccinated. In addition, limit contact with people who are sick during the period of high transmission, practice good hand hygiene, encourage environmental sanitation, and early detection, diagnosis and timely treatment of the disease.
In cases of suspected contact with a patient with meningococcal disease, the doctor should be notified immediately to receive prophylactic antibiotics.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/viem-mang-nao-mo-cau-nguy-hiem-the-nao-co-lay-truyen-tu-nguoi-sang-nguoi-185240613115250592.htm


![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man chairs the 8th Conference of full-time National Assembly deputies](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/2c21459bc38d44ffaacd679ab9a0477c)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives US Ambassador to Vietnam Marc Knapper](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/c8fd0761aa184da7814aee57d87c49b3)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends the ceremony to celebrate the 80th anniversary of the post and telecommunications sector and the 66th anniversary of the science and technology sector.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/8e86b39b8fe44121a2b14a031f4cef46)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam chairs the meeting of the Central Steering Committee on preventing and combating corruption, waste and negativity](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/fb2a8712315d4213a16322588c57b975)
![[Photo] Many streets in Hanoi were flooded due to the effects of storm Bualoi](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/9/29/18b658aa0fa2495c927ade4bbe0096df)
































































































Comment (0)