For people with diabetes, bean sprouts play an important role in stabilizing blood sugar thanks to their low glycemic index, rich fiber content and many essential micronutrients that help slow down the absorption of glucose, according to the Times of India (India).
However, eating raw bean sprouts can potentially pose a risk of bacterial contamination. Therefore, users need to wash them thoroughly, cook them lightly and store them properly to both retain their nutrients and ensure long-term health safety.
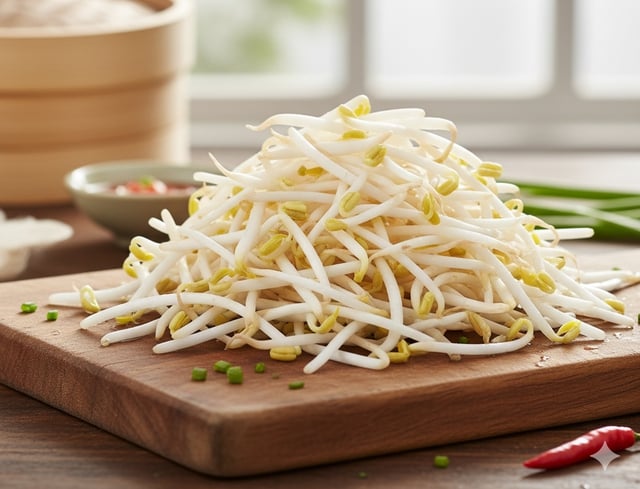

Bean sprouts play an important role in stabilizing blood sugar thanks to their low glycemic index.
Photo: AI
A valuable source of nutrition for diabetics
Bean sprouts contain important bioactive compounds such as sulforaphane, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. According to a 2013 study published in the journal Food Chemistry , these compounds have the ability to increase insulin sensitivity, reduce oxidative stress, and improve blood lipids. These are important factors that help people with type 2 diabetes manage their disease more effectively.
In addition, the high fiber content in bean sprouts helps regulate blood sugar by slowing down glucose absorption.
Low glycemic index
Most bean sprouts have a low glycemic index, which helps blood sugar rise gradually instead of spiking after eating.
Regularly eating foods with a low glycemic index helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, reduces sudden insulin spikes, and limits the risk of long-term complications.
Bean sprouts are rich in fiber.
Bean sprouts are high in fiber, which helps slow the absorption of glucose into the blood and improve insulin sensitivity.
In addition, fiber also plays an important role in supporting digestion, preventing constipation and controlling appetite.
Fiber-rich foods like bean sprouts have also been shown to improve HbA1c levels, an indicator of blood sugar control.
Antioxidant effects
Active ingredients like sulforaphane and flavonoids in bean sprouts have the ability to fight oxidative stress, a common condition in people with diabetes that can damage blood vessels and organs over time.
Antioxidants also help reduce inflammation, protect pancreatic beta cells, and may improve insulin sensitivity, thereby contributing to improved blood sugar control.
Heart and weight support
The combination of fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients in bean sprouts helps lower cholesterol, reduce triglycerides, improve blood vessel function, and help stabilize blood pressure. This is important because people with diabetes are at high risk of cardiovascular disease.
In addition, bean sprouts are low in calories but rich in protein, vitamins and fiber. This helps create a feeling of fullness for a long time, limits excess energy intake and supports effective weight control.
Benefits for the intestines and provides micronutrients
Bean sprouts also contain prebiotic fiber that helps nourish beneficial intestinal bacteria, creating a balance of microflora.
A healthy digestive system can improve glucose metabolism, reduce inflammation and boost immunity.
For people with diabetes, this means better disease control and a reduced risk of metabolic complications.
In addition, bean sprouts provide many essential micronutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin K, folate, magnesium and potassium, which help produce energy, maintain nerve function and protect the heart.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/gia-do-voi-nguoi-tieu-duong-thuc-pham-vang-hay-can-kieng-ky-185250930160850518.htm





![[Photo] Binh Trieu 1 Bridge has been completed, raised by 1.1m, and will open to traffic at the end of November.](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/2/a6549e2a3b5848a1ba76a1ded6141fae)








![[Video] Ministry of Health issues document to rectify medical examination and treatment work](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/402x226/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/10/2/54913f30a9934e18bcbb246c2c85f11d)



















































































Comment (0)