Master - Doctor Le Ngo Minh Nhu, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City - Campus 3, said that starch (carbohydrate) after digestion will be converted into glucose, contributing to increased blood sugar. However, starch is not the only cause, but is an essential source of energy, accounting for about 50% of the total recommended dietary energy, even for diabetic patients.
The benefit of controlling starch (according to the appropriate amount of starch used) is to help control blood sugar more effectively, limit blood glucose fluctuations, and provide essential energy for the body... However, completely cutting out starch will cause hypoglycemia, increased blood ketone levels, fat metabolism disorders, and lack of fiber...
Therefore, complete elimination of starch for the treatment of diabetes is not recommended in current clinical practice. Instead, modern treatment guidelines encourage control of the amount and quality of starch intake, prioritizing appropriate choices.
Choose slow-absorbing starch (low GI - low glycemic index), such as brown rice, oats, sweet potatoes, whole grain bread, patients can control blood sugar better after eating. Choose a suitable diet for each individual. Combine starch with protein, fat, fiber to slow glucose absorption. Control total energy intake...
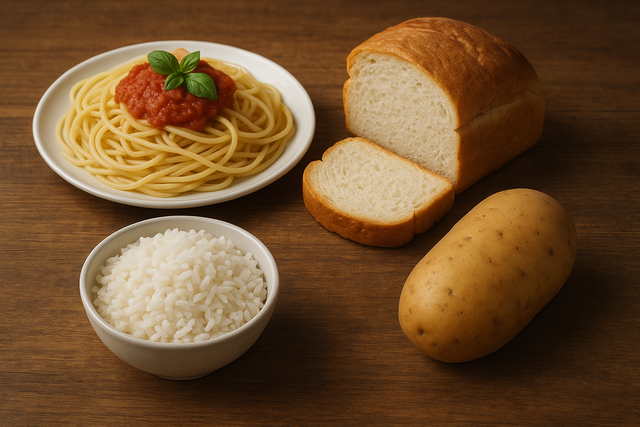

If you completely cut out starch, it will cause hypoglycemia, increased blood ketone, fat metabolism disorders, and lack of fiber.
PHOTO: AI
Appropriate nutrition for people with diabetes
The Ministry of Health predicts that by 2045, the number of people with diabetes in Vietnam will increase to 6.3 million, a significant increase from the current 5 million. With the dangerous complications that the disease can cause, diabetes is becoming an urgent health problem, attracting the attention of the whole society.
Dr. Le Thao Nguyen, Nam Sai Gon International General Hospital, said that to minimize complications caused by diabetes, in addition to complying with drug treatment, a reasonable diet plays an extremely important role in controlling blood sugar and improving the quality of life for patients.
Good food for diabetics
Fresh vegetables and fruits rich in fiber : Eat more than 500g of green vegetables and less than 300g of fruit per day to add fiber, which helps slow down the absorption of sugar.
Starch : Choose minimally processed, refined foods such as brown rice, whole grains, rye, millet, and quinoa to limit post-meal blood sugar spikes.
Healthy protein: Fish, lean meat, egg whites and beans are sources of high-quality protein and should be regularly included in the daily menu.
Fatty fish and nuts: Foods like salmon, peanuts, almonds and sesame seeds contain omega 3, which helps protect the heart and maintain health.
Choosing foods according to the glycemic index
The glycemic index (GI) reflects how quickly or slowly a food increases blood sugar after being eaten. Diabetics should prioritize foods with low GI (GI < 55), moderately consume foods with medium GI (56-69), and limit foods with high GI (GI > 70).
"Although foods with a low glycemic index (GI) help control blood sugar, eating too much can increase blood sugar as much as high GI foods. Therefore, people with diabetes need to pay attention to glycemic load (GL), a factor that more accurately assesses the impact of food portions on blood sugar," Dr. Thao Nguyen recommends.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/cat-tinh-bot-co-giup-tri-duoc-benh-tieu-duong-185250815105134677.htm
































































































Comment (0)