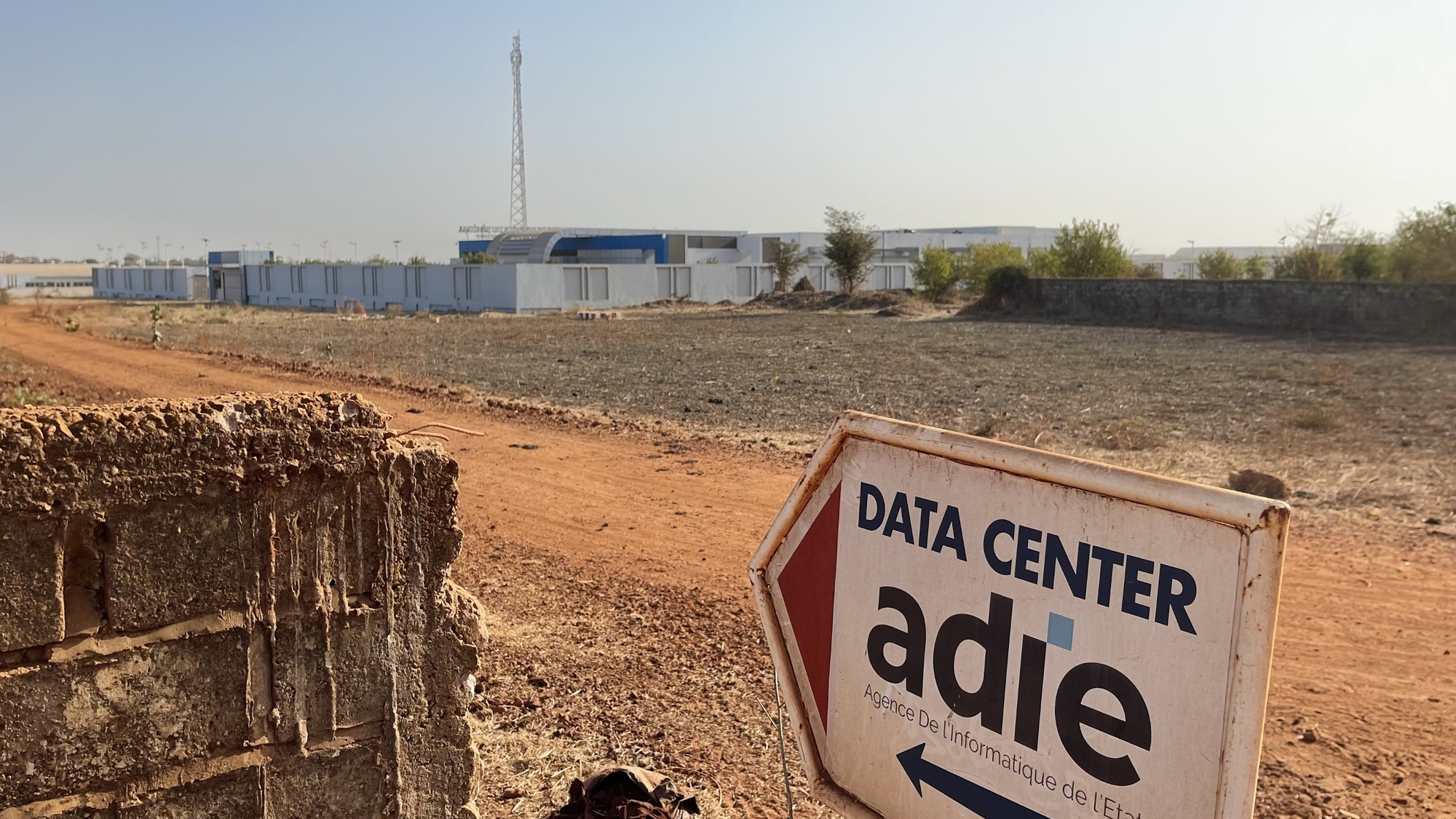

The Senegal government data center is a joint project with China, with servers provided by Huawei Technologies.
NIKKEI ASIA SCREENSHOT
China's Belt and Road Initiative is shifting from large infrastructure projects to less capital-intensive sectors such as information technology and biotechnology, according to a recent Nikkei Asia analysis of investment data.
The paper tapped China's new "greenfield" investment, from the Financial Times ' foreign direct investment monitor fDi Markets.
Digital
According to statistics, investment in information technology, communications and electronic components will total 17.6 billion USD by 2022, six times higher than in 2013, when the Belt and Road Initiative was launched.
That means more projects, like the Senegal government’s new data center, which is under military guard and a half-hour drive from the capital, Dakar. Due to be completed in 2021, the facility is a joint venture with China, with servers provided by Huawei Technologies.
Cheikh Bakhoum, director general of Senegal Numerique, the state agency that manages the facility, said the center has brought data back to Senegal that was previously stored on foreign servers run by Western companies. This reduces costs and restores digital sovereignty .
Senegal has also installed an undersea fiber optic cable and urban surveillance cameras funded by China. Data from the cameras is analyzed using specialized software.
China began exporting domestically developed digital infrastructure in the late 2000s, according to Dai Mochinaga, associate professor at Japan's Shibaura Institute of Technology.
“This trend accelerated around 2013, when Huawei expanded its overseas investments,” he said.
Biotechnology
Besides digital, biotechnology is another big growth area for Chinese investment, increasing 29-fold from 2013 to 2022 to $1.8 billion.
Covid-19 vaccine development is a prime example, with China exporting around 2 billion doses of vaccines worldwide by the end of 2022, reaching emerging countries.
Meanwhile, Europe's major vaccine manufacturers are largely focused on meeting local needs.
China's Abogen Biosciences has licensed its technology to develop a messenger RNA vaccine to Indonesian startup Etana Biotechnologies, which completed a vaccine manufacturing facility last year, with the goal of producing 100 million doses.
Licensing technology is a fast way to catch up with the world and China has responded quickly, said Andreas Donny Prakasa, head of corporate relations at Etana Biotechnologies.
Less expensive investment
China’s shift to areas such as IT and biotechnology has been accompanied by a decline in spending on major infrastructure projects. Experts say this is partly because investment in “soft” sectors such as IT is less expensive. Fossil fuel projects average $760 million and mining $160 million, while biotechnology requires just $60 million per project and IT services $20 million.
Source link






































































































Comment (0)